The latest issue of Advanced Optical Materials is now available. You can sign up to access all Advanced Optical Materials articles right here!
These articles were highlighted on the covers of the Advanced Optical Materials July issue:
 Random Lasing
Random Lasing
On the front cover by F. G. Omenetto, R. Sapienza, and co-workers, biocompatible silk random lasing is featured, which is achieved in natural silk nanostructured as a disordered porous matrix via a self-assembly techniques. Lasing action is sensitive to pH variations in the aqueous environment opening up opportunities for biophotonic applications and biosensing.
White-Light Emitting Diodes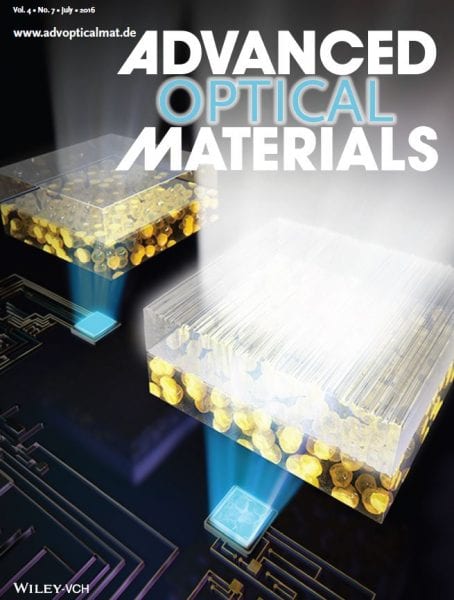
A printed layer of yellow phosphors on a surface-roughened glass substrate for white light-emitting diodes is presented on the inside cover. The layer of well-dispersed phosphors in a glass matrix is broadly applicable for a large scale planar lighting system. When combined with a nanoscale surface-roughening technique of the substrate, enhanced luminescence efficiency is achieved as a result of effective light extraction. Y. S. Cho and co-workers describe this simple processing methodology with experimental evidences.
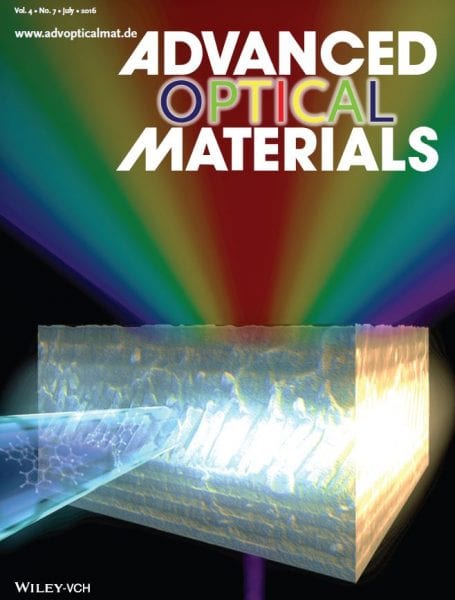 White Light Emission
White Light Emission
On the back cover, a wide-range in situ tunable 1D Bragg microcavity including a hybrid layer as white light emitter defect is shown by J. R. Sanchez-Valencia, A. Borras, and co-workers. White emission is obtained by Förster resonance energy transfer between blue (1,3,5-triphenyl-2-pyrazoline) and orange (rubrene) dyes homogeneously infiltrated within the host nanocolumnar SiO2 film, which is formed by glancing angle deposition. Sequential physical vapor deposition at low temperatures provides the organic dyes localization within the porous nanostructure of the defect layer.