An advanced 4D bioprinting approach uses shape-morphing, biopolymer hydrogels to form the basis for blood vessels and other tubular structures in artificial tissues and organs.
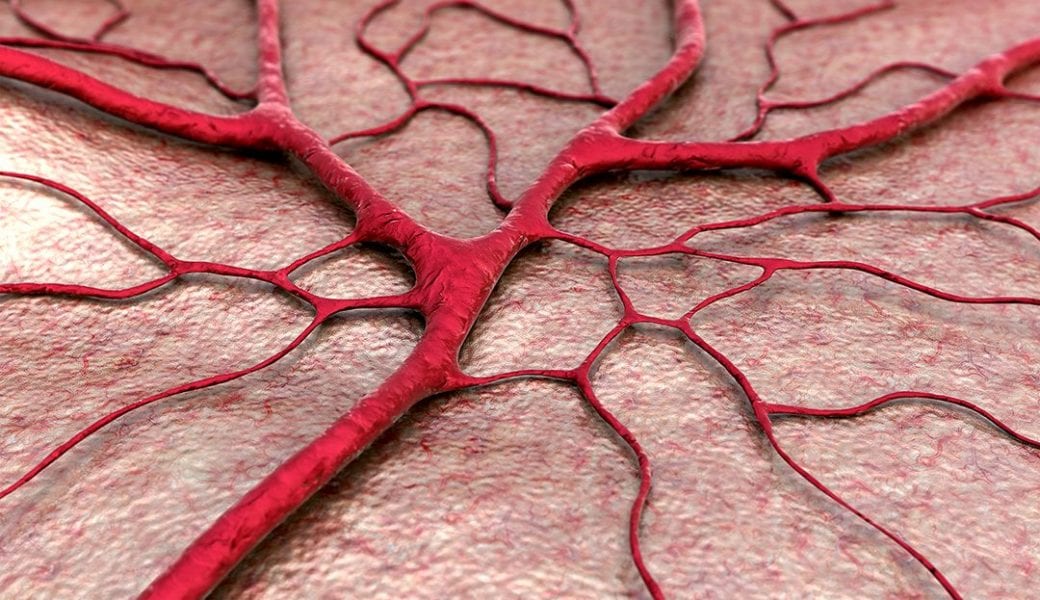


An advanced 4D bioprinting approach uses shape-morphing, biopolymer hydrogels to form the basis for blood vessels and other tubular structures in artificial tissues and organs.
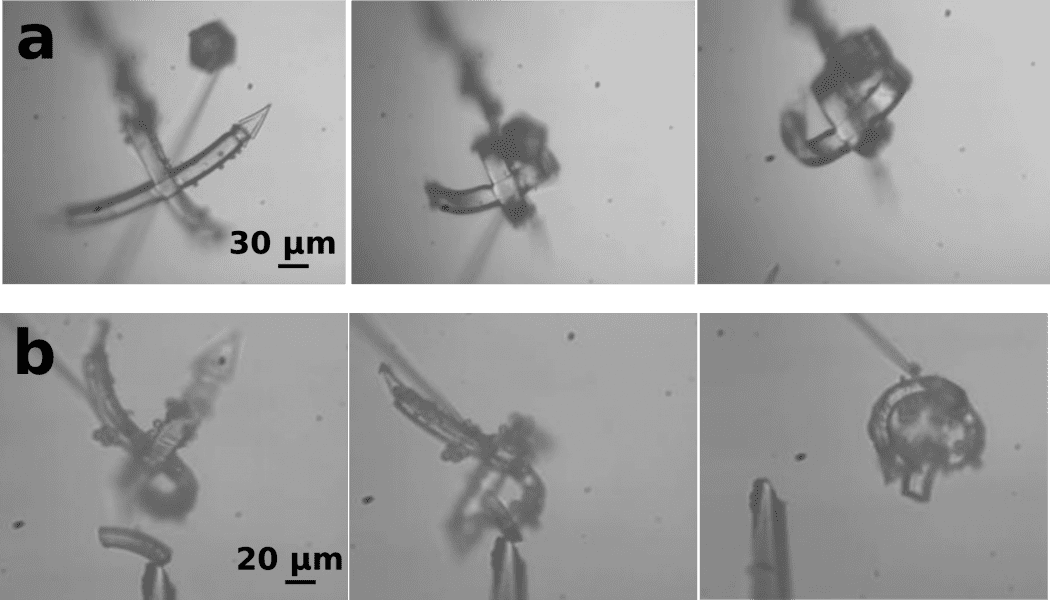

A microscopic light-fueled microhand designed to capture microscopic objects.
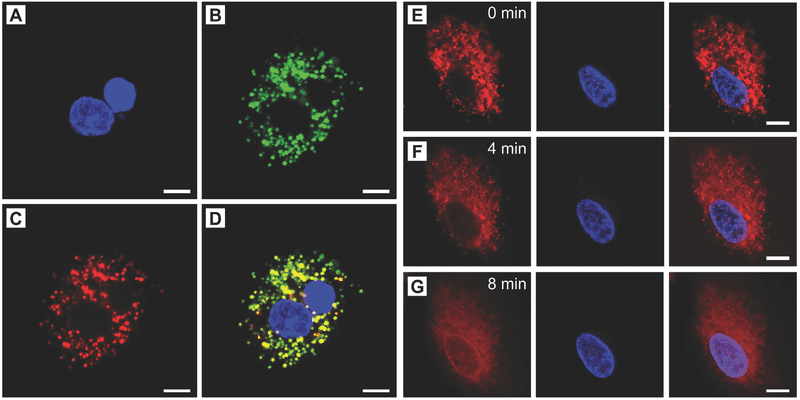
Natural fatty acid eutetic mixtures offer an inexpensive, chemically stable and biocompatible gating material alternative for NIR-triggered drug release nanoparticles for cancer therapy.
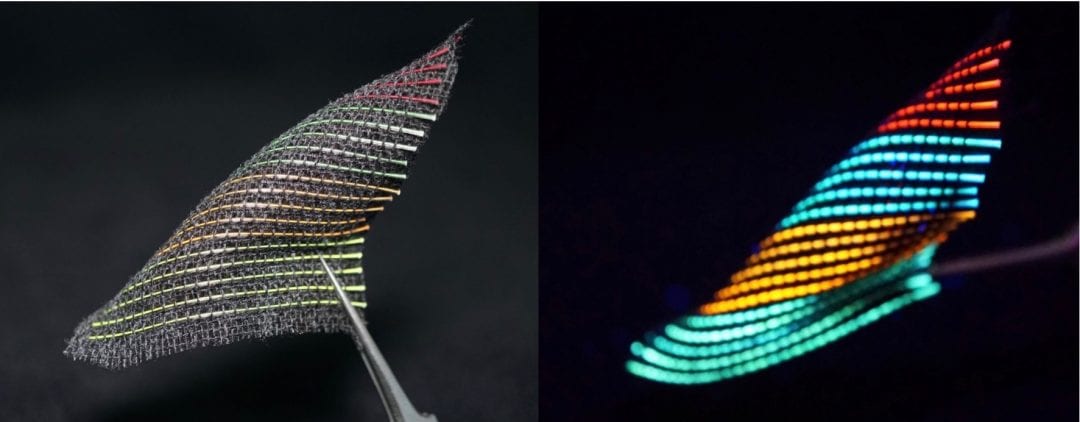
A novel family of colorful fluorescent supercapacitor fibers allows for continuous energy storage in flexible systems used in the dark.
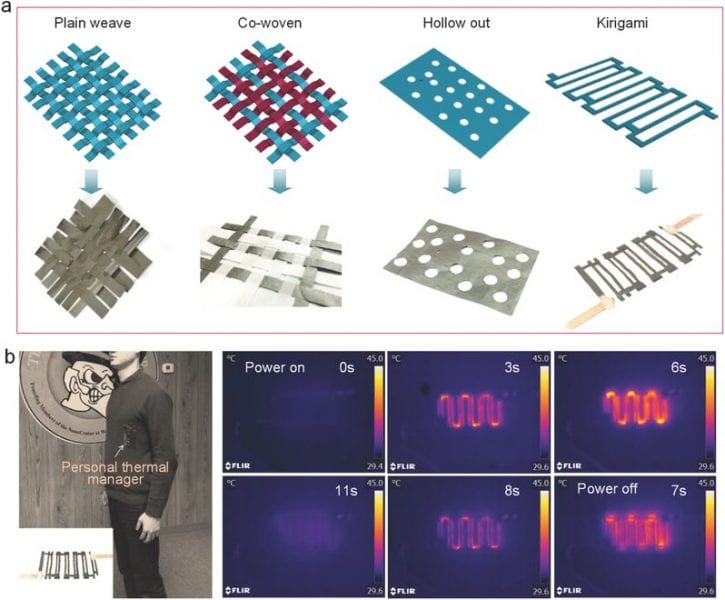
Graphene papers provide chemical and mechanical stability, high thermal conductivity and low electrical resistance in the development of personal thermal management systems.