The convergence of four broad but easily identifiable networked conditions, or “Four Horsemen”, are hurtling civilization towards potential self-destruction triggered by the current pandemic.
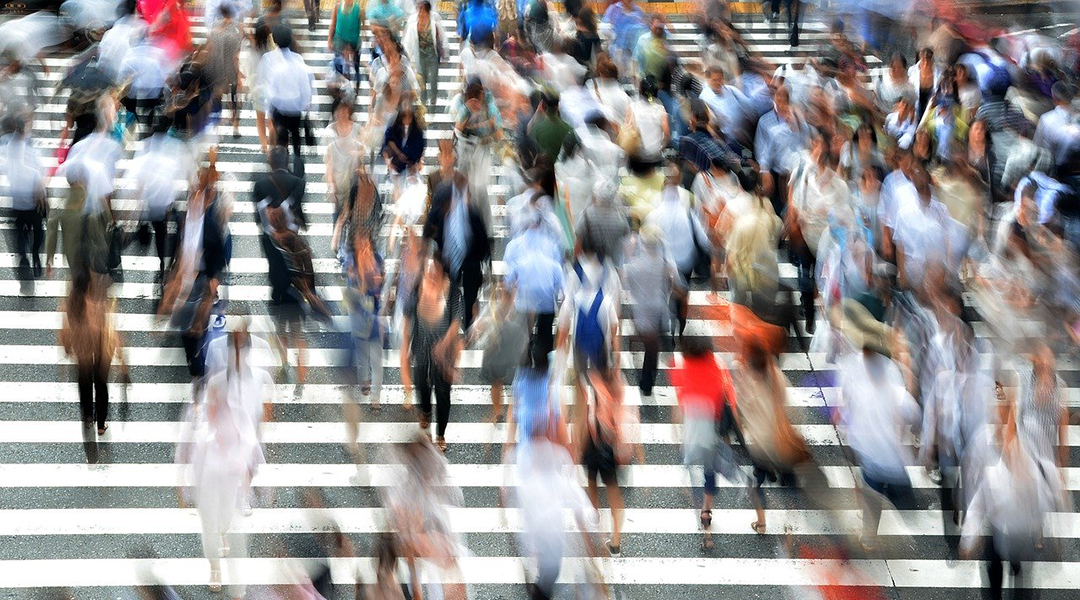



The convergence of four broad but easily identifiable networked conditions, or “Four Horsemen”, are hurtling civilization towards potential self-destruction triggered by the current pandemic.
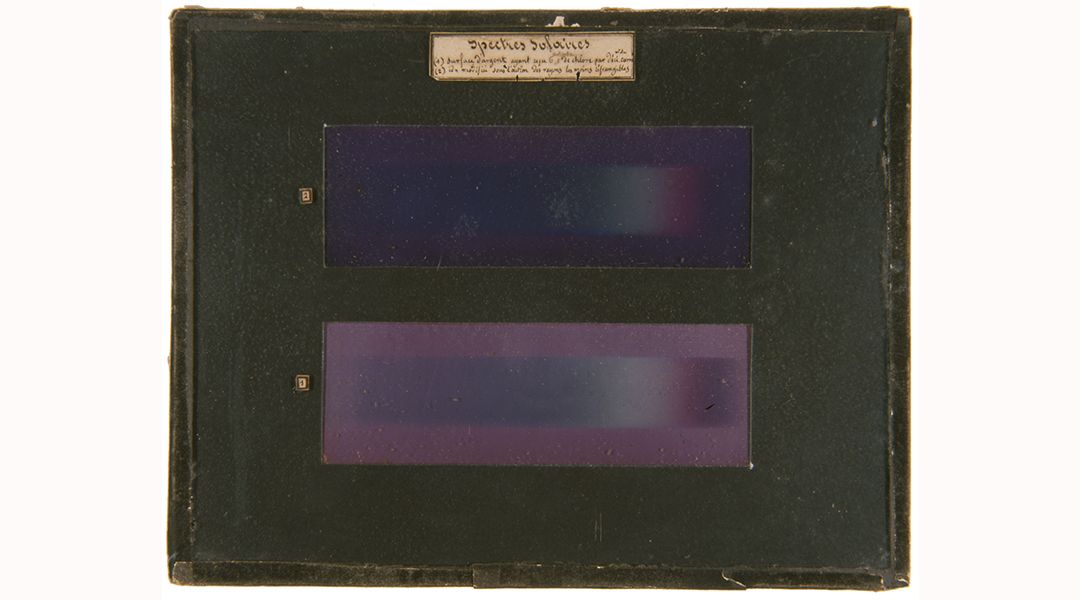

Mystery solved! Scientists finally understand the origin of the colors observed in the first color photographs taken by physicist Edmond Becquerel in 1848.
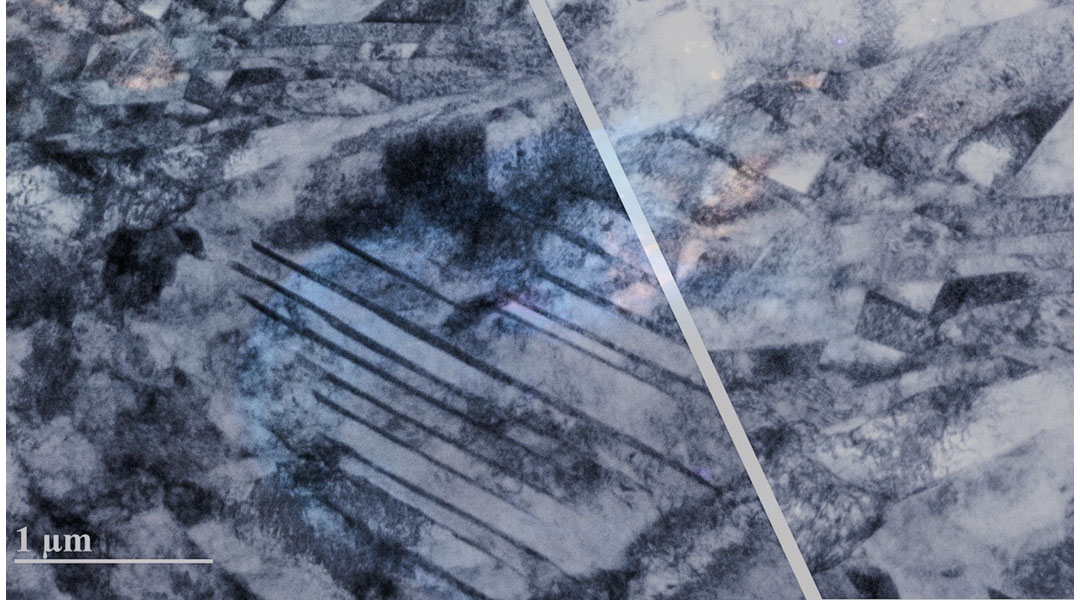

Researchers report a fast and efficient titanium alloy processing technique that requires up to 50% less heat.
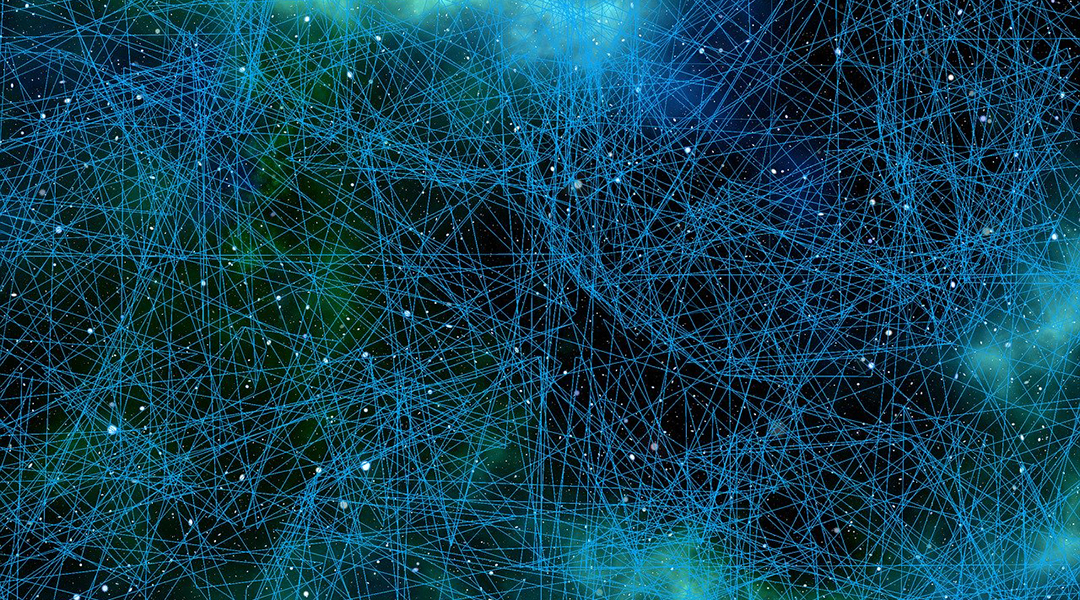

Controlling the probability of a series of seemingly random events is the key to mimicking the human brain to optimize neuromorphic learning.
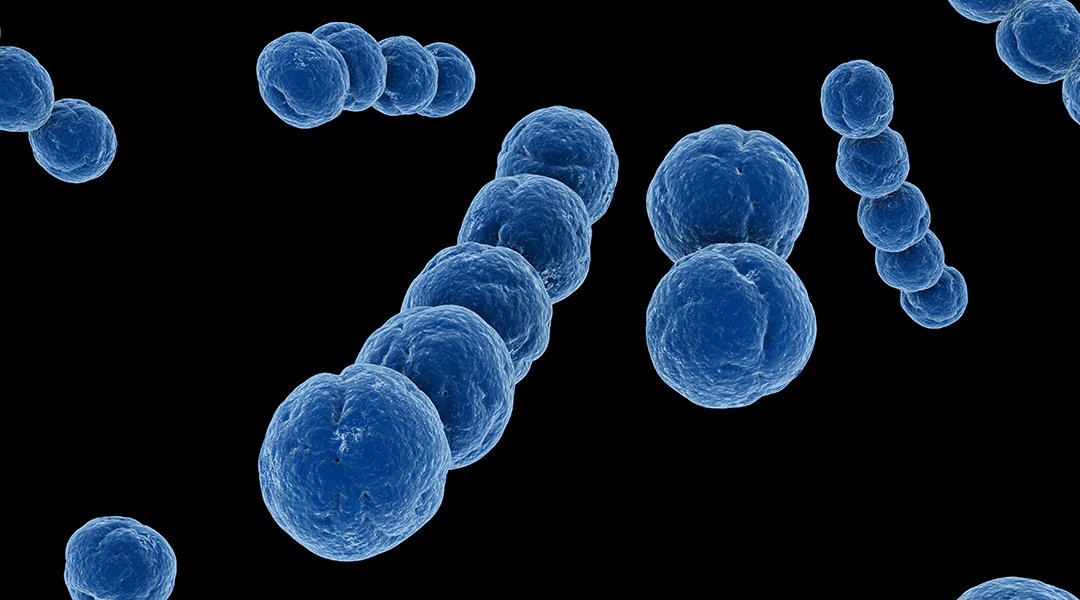
A recent study discovers that CRISPR can be used for a number of different purposes by diverse biological entities, not just humans and bacteria.
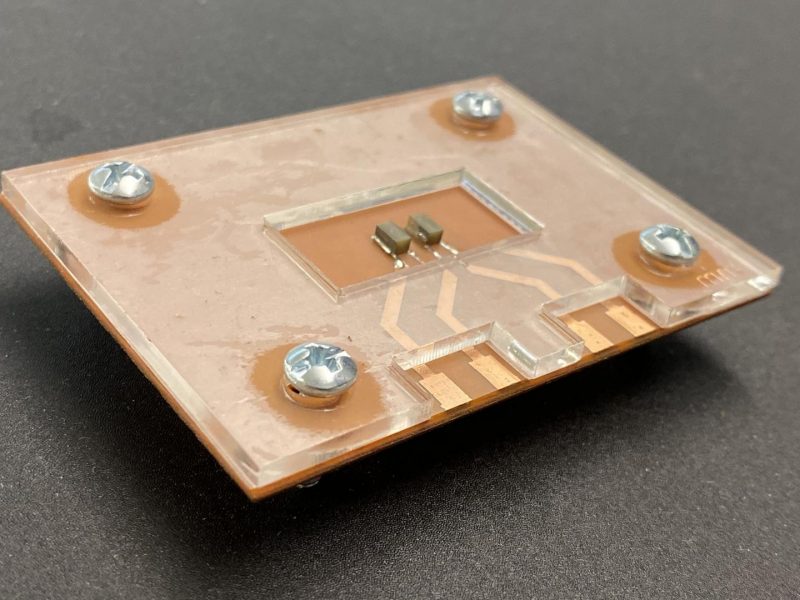
A device uses sound waves to detect the stiffness of an extracellular matrix, a structural network that contains cells, which researchers find can indicate the spread of disease.
Researchers at Osaka University are helping to power portable sensors that do not use batteries by generating electricity from heat that is otherwise wasted.
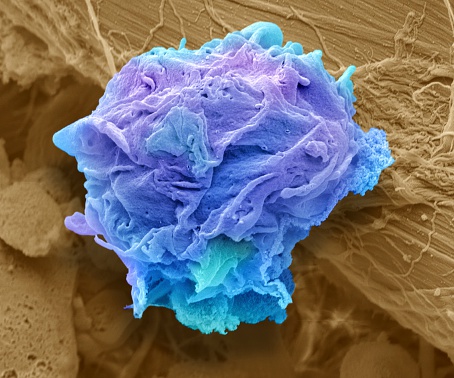
One drug, three modes of action: Clinicians combat the drug resistances of some cancer types by using a combination of different drugs.
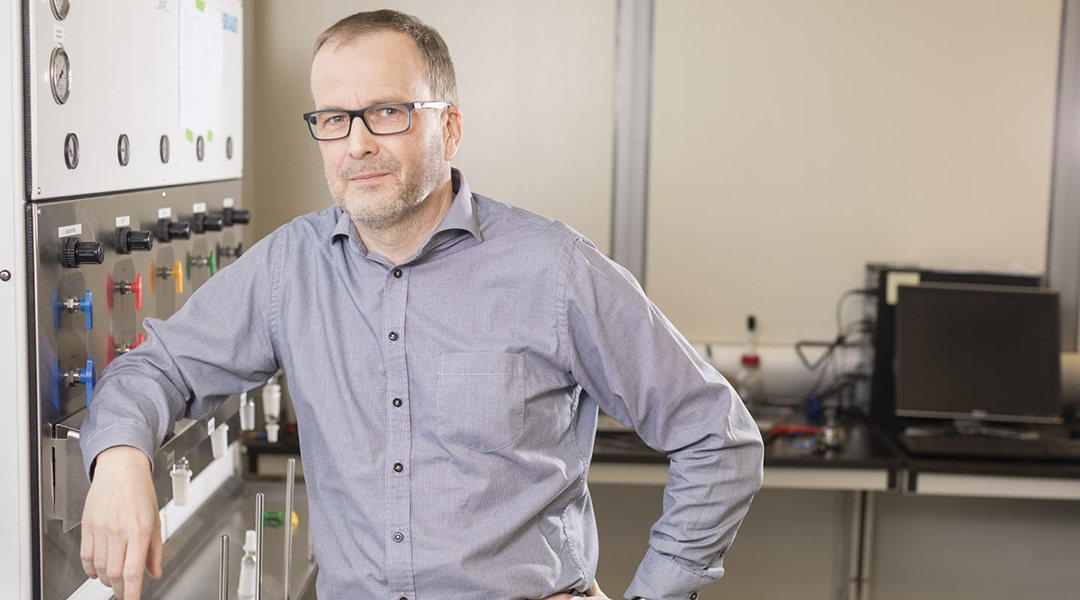

York University researchers have discovered a way to make lithium-powered batteries more environmentally friendly while retaining performance, stability and storage capacity.
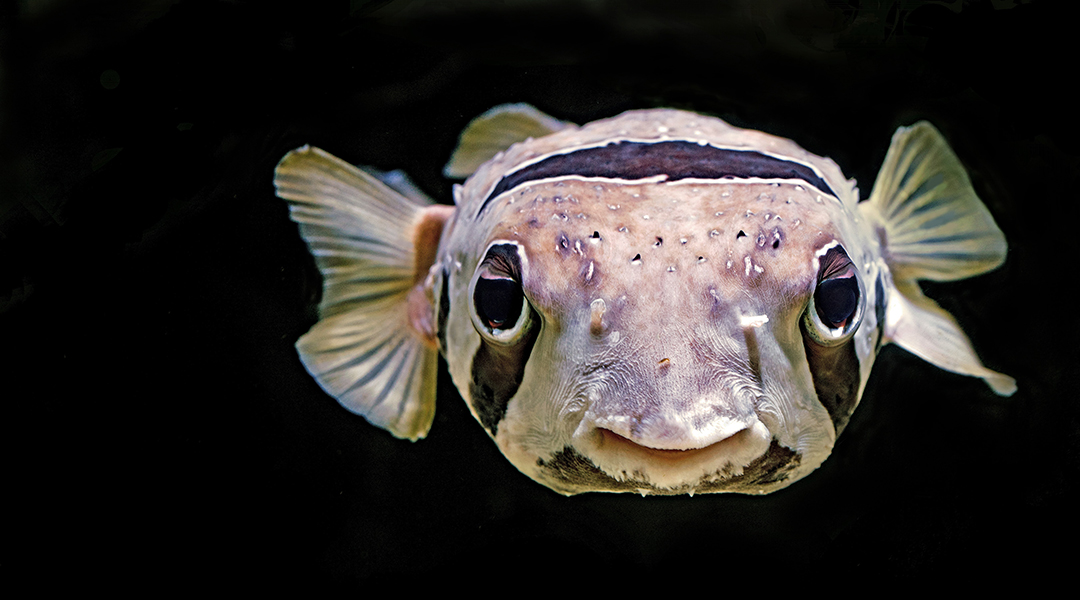

Scientists create a new route for the total synthesis of tetrodotoxin, a molecule in puffer fish that has promising medicinal benefits, such as pain relief.