New potential antibiotic molecules were found to destroy biofilms and acted against gram-positive bacteria.
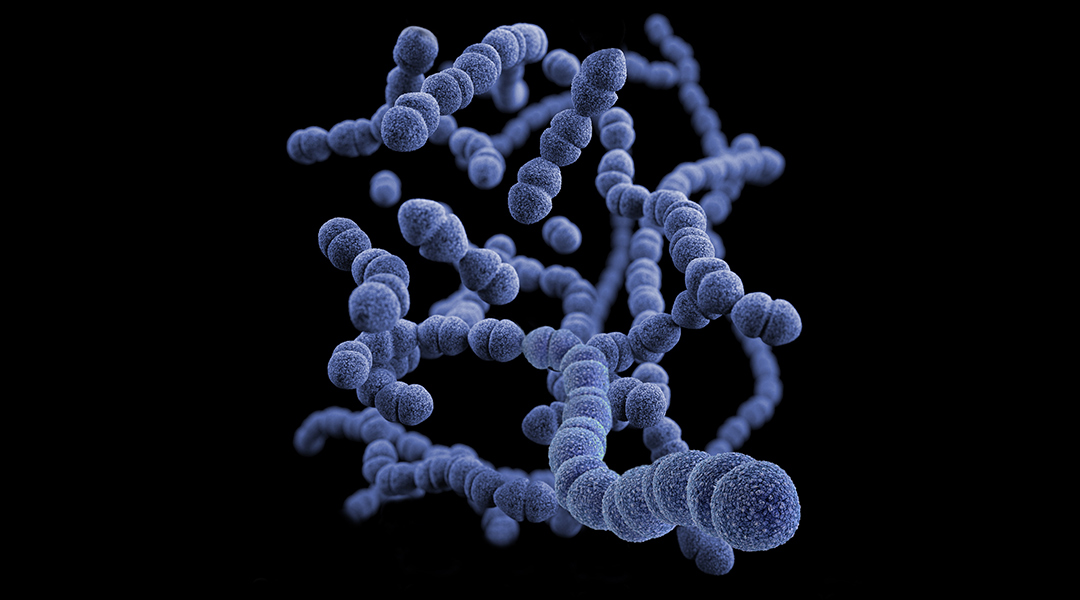


New potential antibiotic molecules were found to destroy biofilms and acted against gram-positive bacteria.
Artificial spider silk could be a smart and responsive alternative to traditional wound dressings, helping patients and medical staff to monitor recovery in real time.

Researchers are investigating ways to increase the efficiency and stability of solar cells, which could improve their commercial use as an alternative energy source.
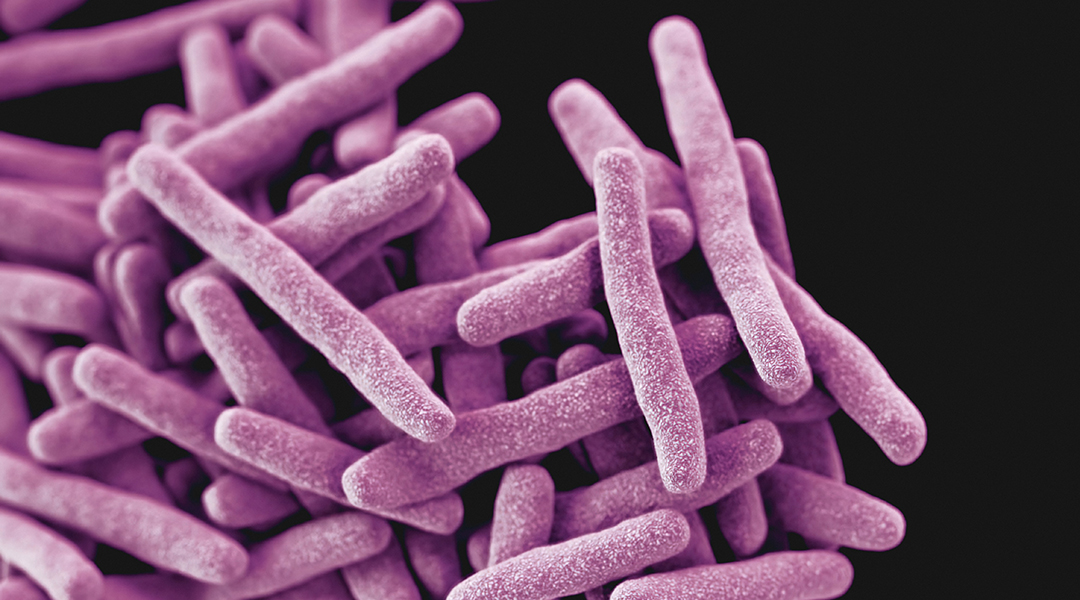
Researchers are devising a quicker and cheaper way to diagnose tuberculosis — and it’s based on how your skin smells.

A new algorithm helps researchers search out new molecules for applications in medicine, keeping their synthesis quick and cost-effective.
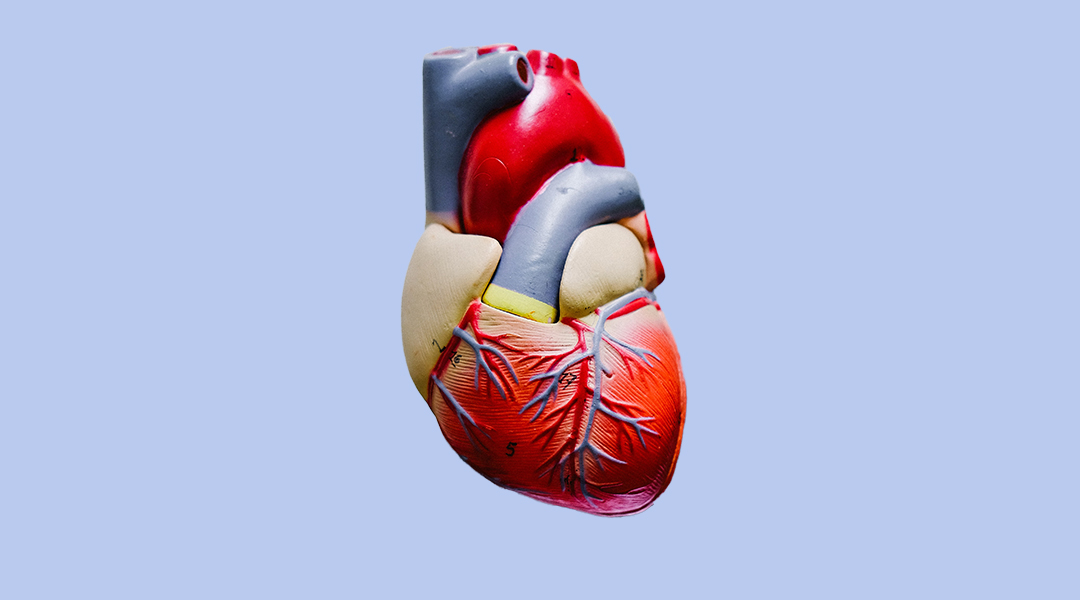
Researchers have created an improved material for arterial stents, which could alleviate the symptoms of coronary artery disease and reduce the risk of heart attack in patients.
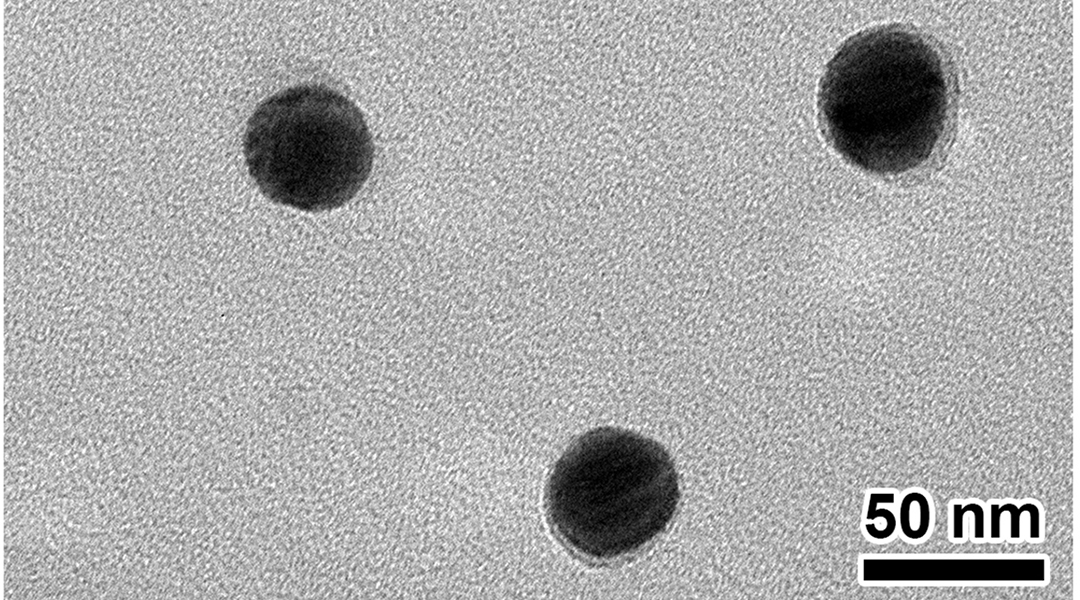
Scientists are looking to improve the outlook for patients with bladder cancer by advancing a laser-based photothermal therapy.

Scientists use 3D printing to combine fundamental biology research methods with high-throughput screening of cell culture surface topographies.

Scientists in Japan have devised an efficient way to create the backbone to a whole family of natural products, thus unlocking potential new medicines.
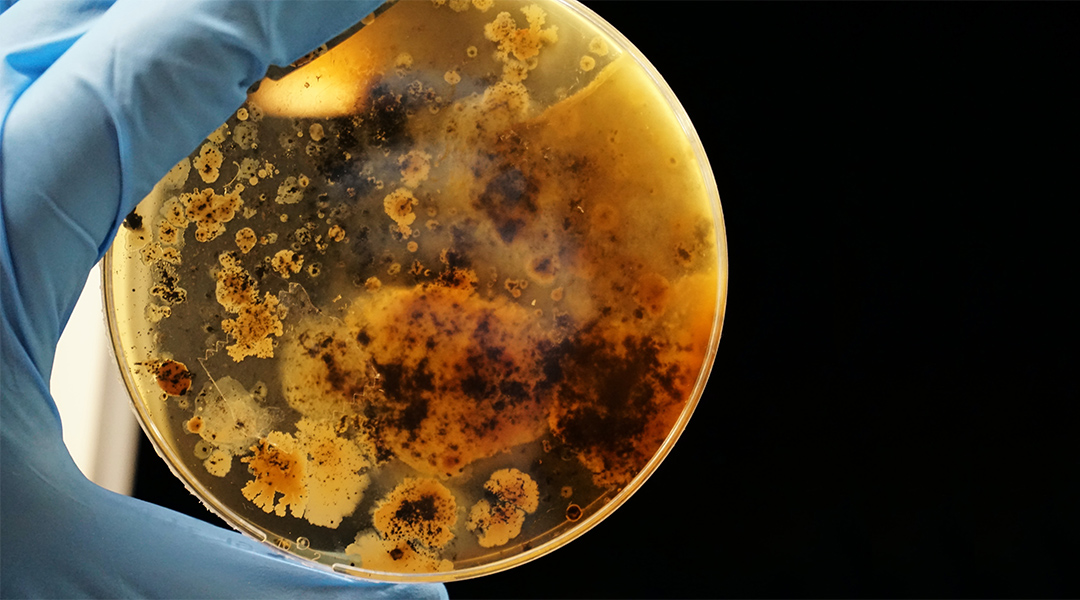
A team of scientists have created a cost-effective way to destroy bacterial biofilms, paving the way for advancements in everything from healthcare to utilities.