Click chemistry spins bacterial-produced spider silk into a biomedical marvel, promising innovations in fiber optics, wound healing, and tissue regeneration.
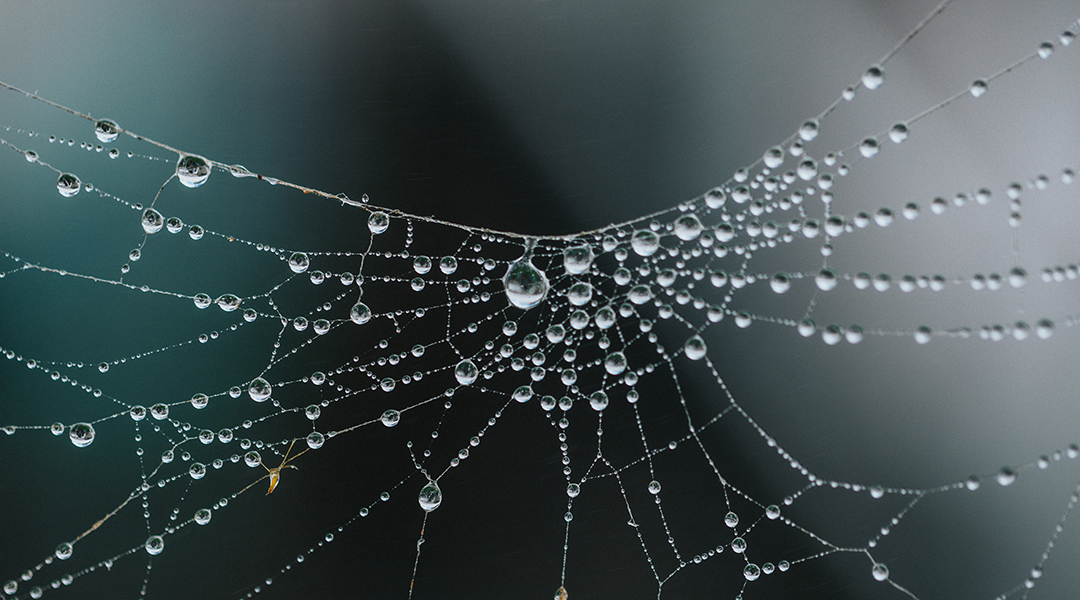



Click chemistry spins bacterial-produced spider silk into a biomedical marvel, promising innovations in fiber optics, wound healing, and tissue regeneration.

Scientists unlock nature’s green secrets to accelerate drug discovery, delivering eco-friendly pharmaceuticals with exciting potential.
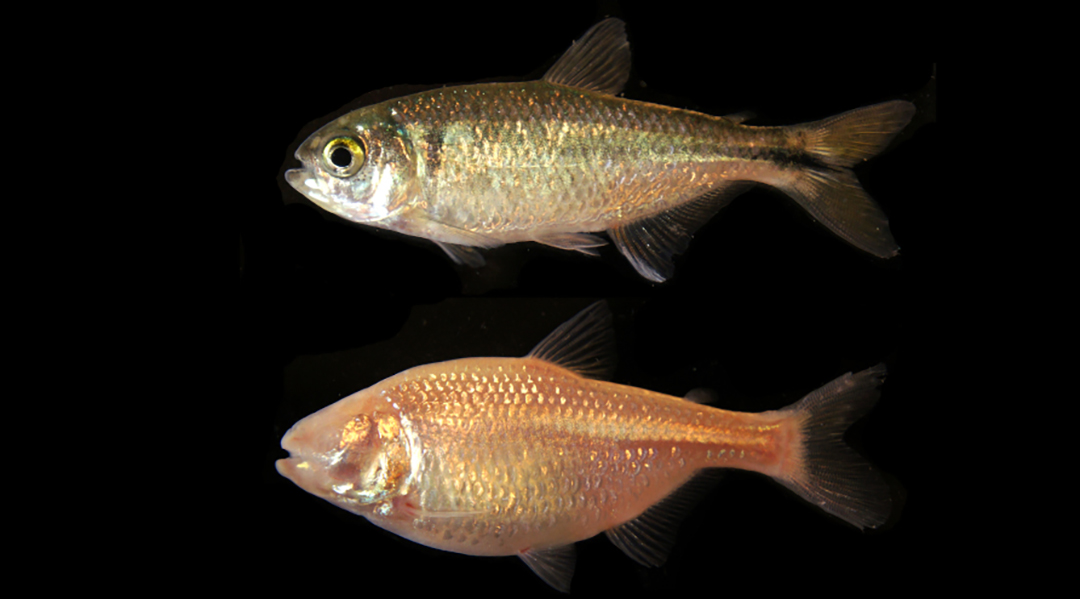

Cavefish studies hint at ketogenic diet’s impact on autism-like behavior, opening new paths for understanding and treatment.
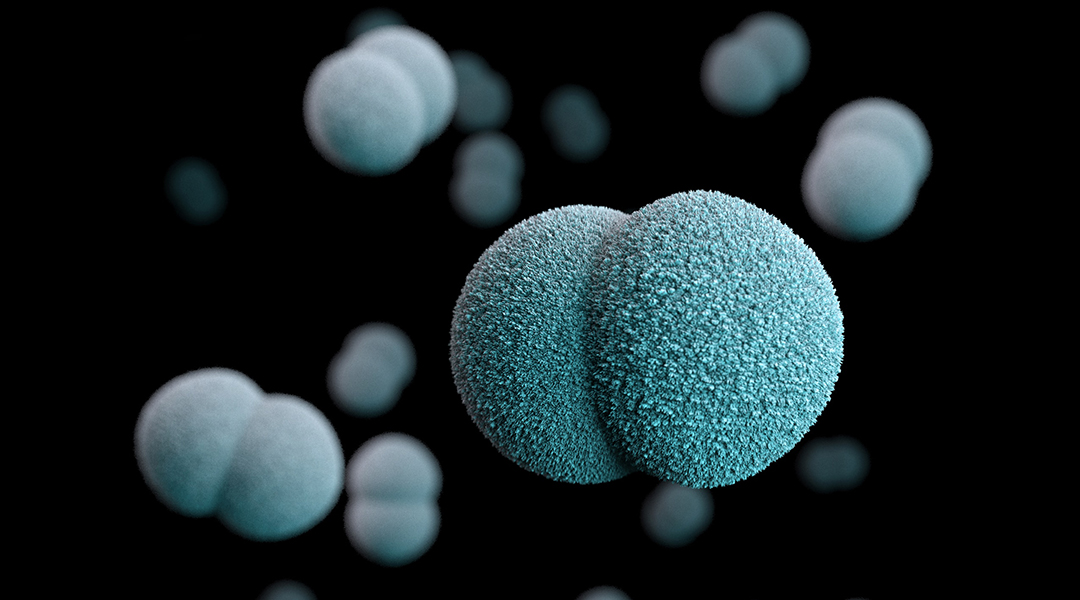
Scientists reveal how antibiotic-resistant genes are spreading around the world, raising concerns about their rapid transmission and the role humans are playing.

With innovations in biosensors, Internet of Things, and machine learning, a collective effort could offer a way to overcome an impending shortage.
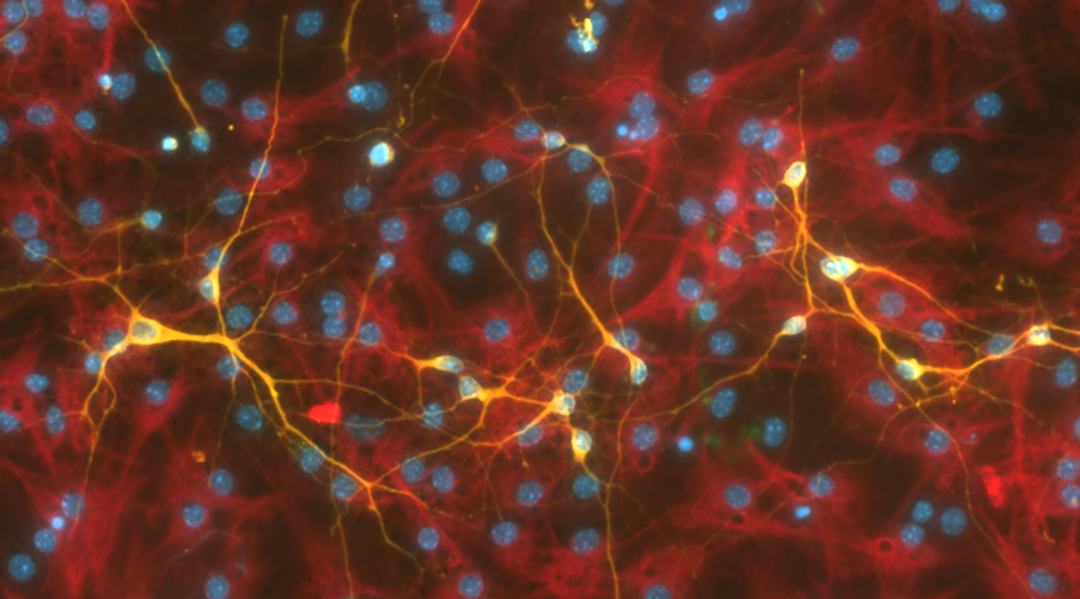
When activated by mechanical stress, a piezoelectric material efficiently stimulates the differentiation of stem cells into new neurons.
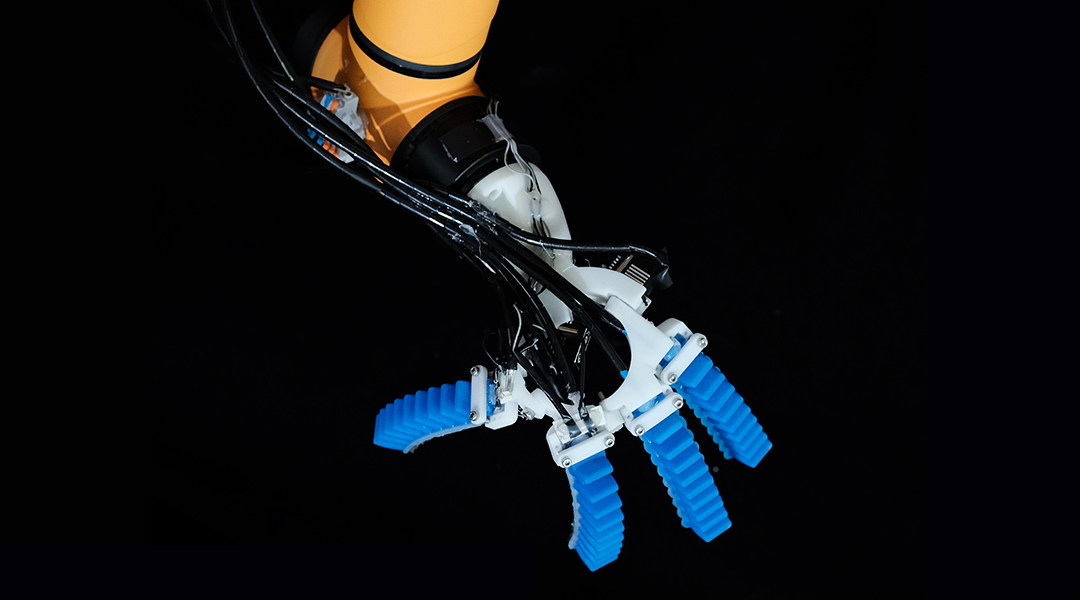

Groundbreaking soft sensors enable robots to both see and feel, paving the way for robots that can autonomously interact with and understand their environment.
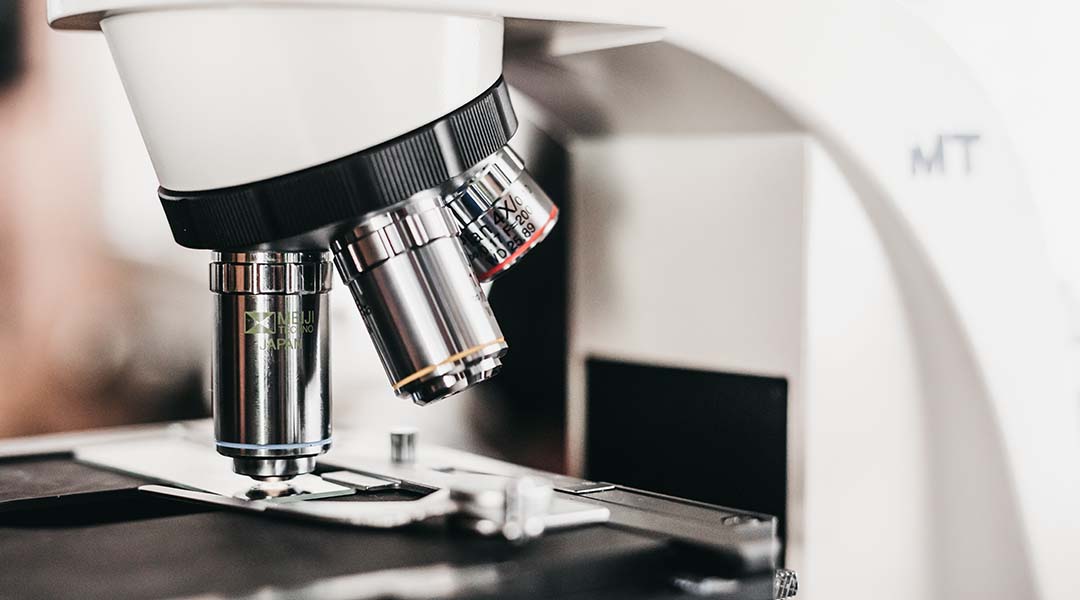

A modification to conventional microscopes pushes the limits of their resolution and enables high-precision observation of difficult-to-observe pathogens.
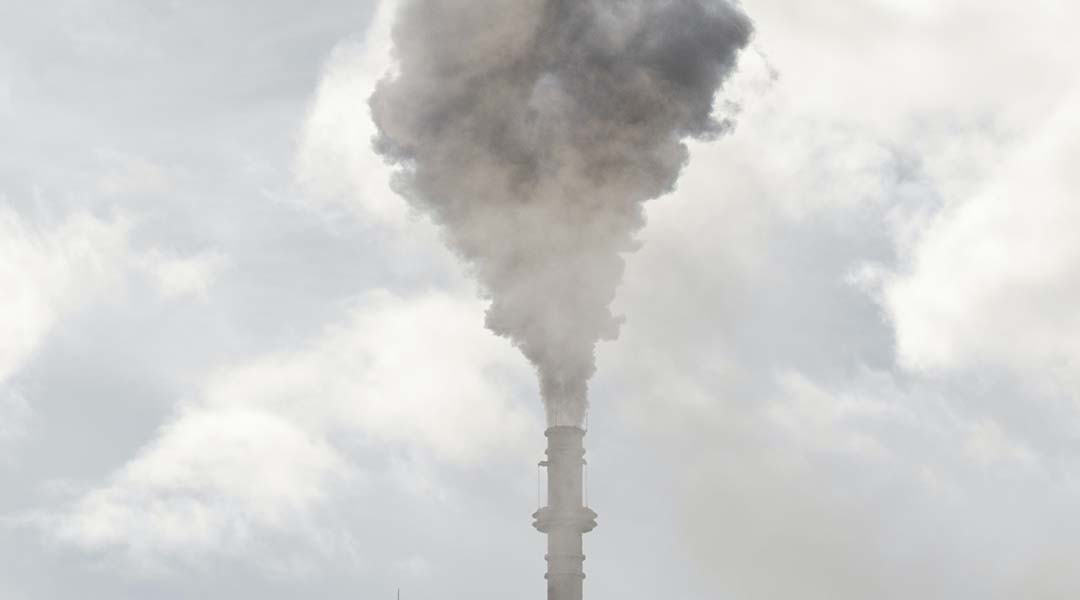

A renewable, carbon-based absorbent is challenging MOFs in carbon capture technology, offering sustainable solutions for emissions reduction.

Using Raman spectroscopy as a means of detection, researchers have built an extensive database of signatures to detect any cancer.