Using Raman spectroscopy as a means of detection, researchers have built an extensive database of signatures to detect any cancer.



Using Raman spectroscopy as a means of detection, researchers have built an extensive database of signatures to detect any cancer.
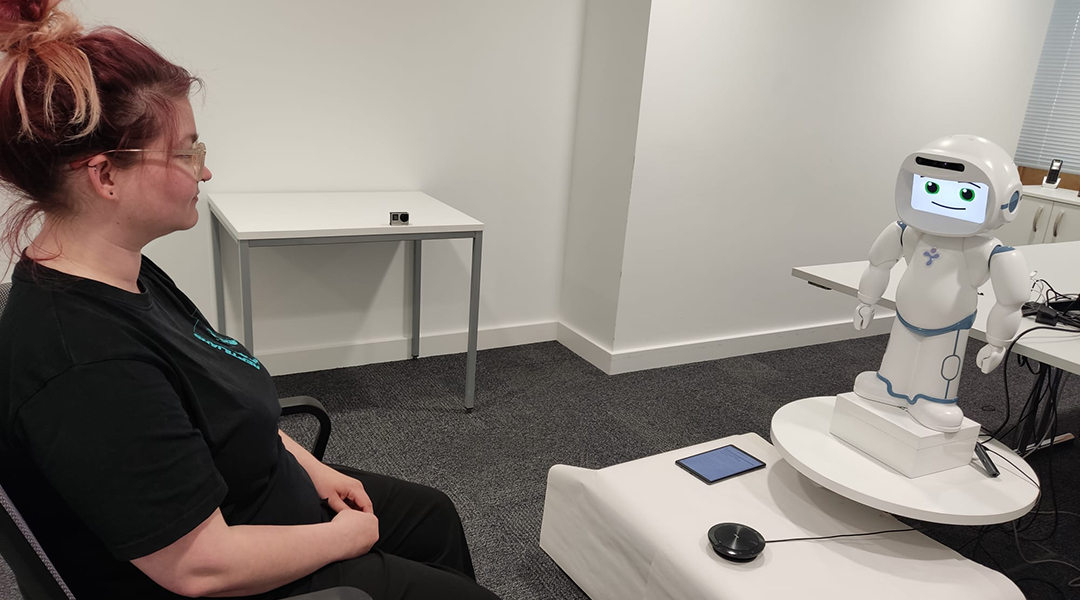

Just like successful therapist or coach relationships, machine-human relationships require engagement and trust if robots are to be useful.
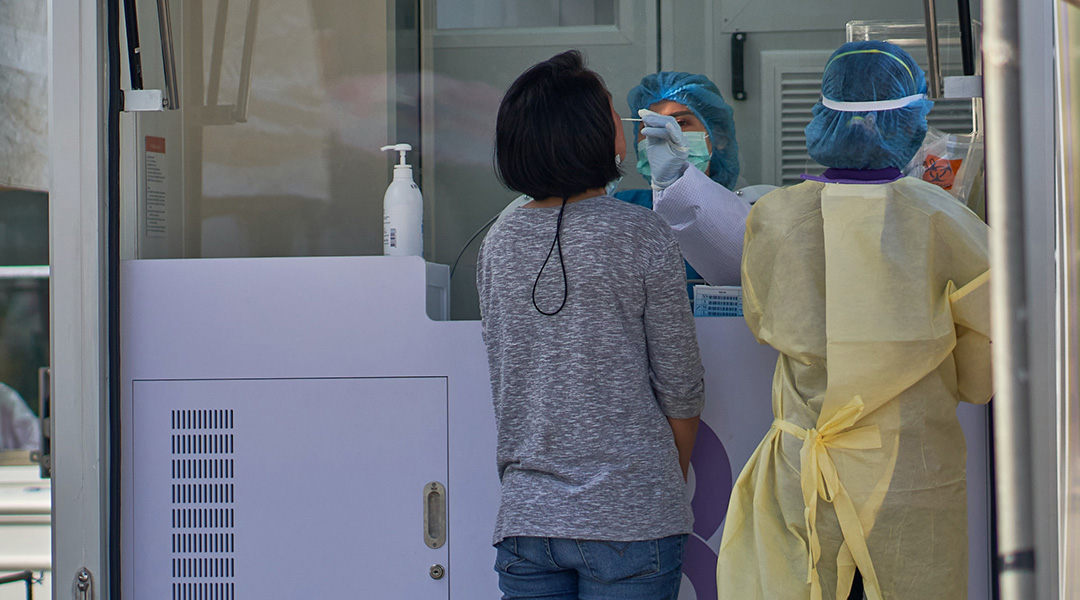

Researchers turn to nanotechnology to boost the detection of pathogens, including SARS-CoV-2.
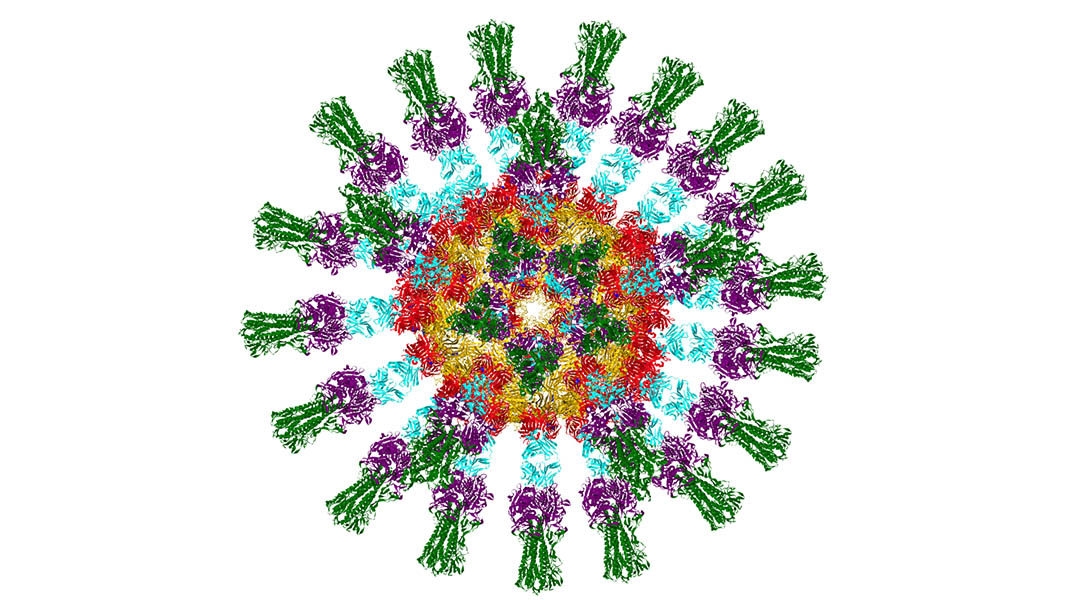
To create a flu vaccine that doesn’t require annual tweaking, researchers develop a nanovaccine that uses an inverted hemagglutinin protein.
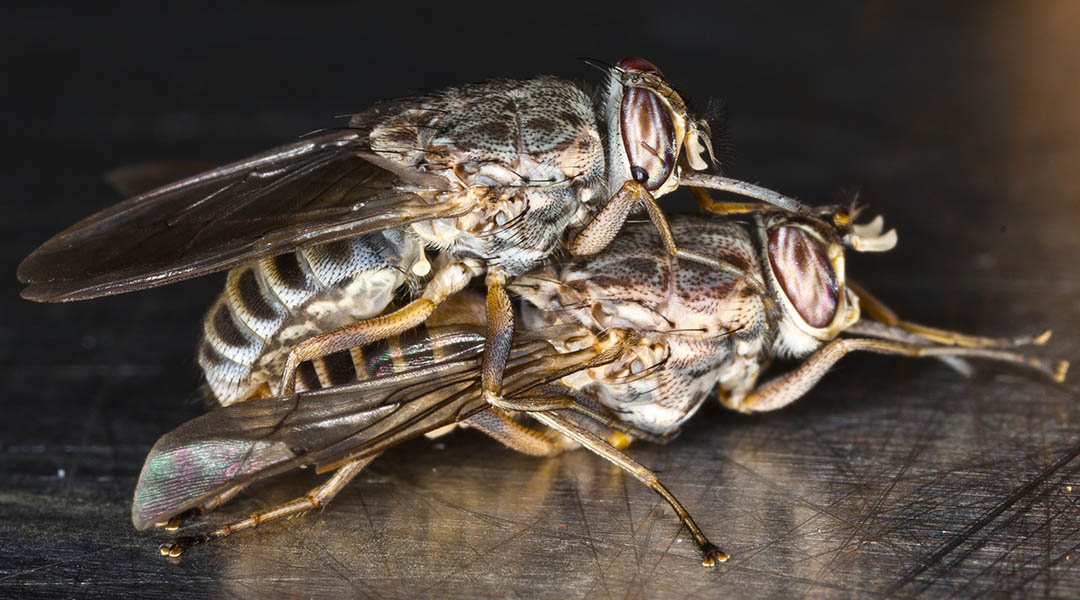

Understanding the chemical language of love used by tsetse flies helps combat the spread of a lethal human parasite.
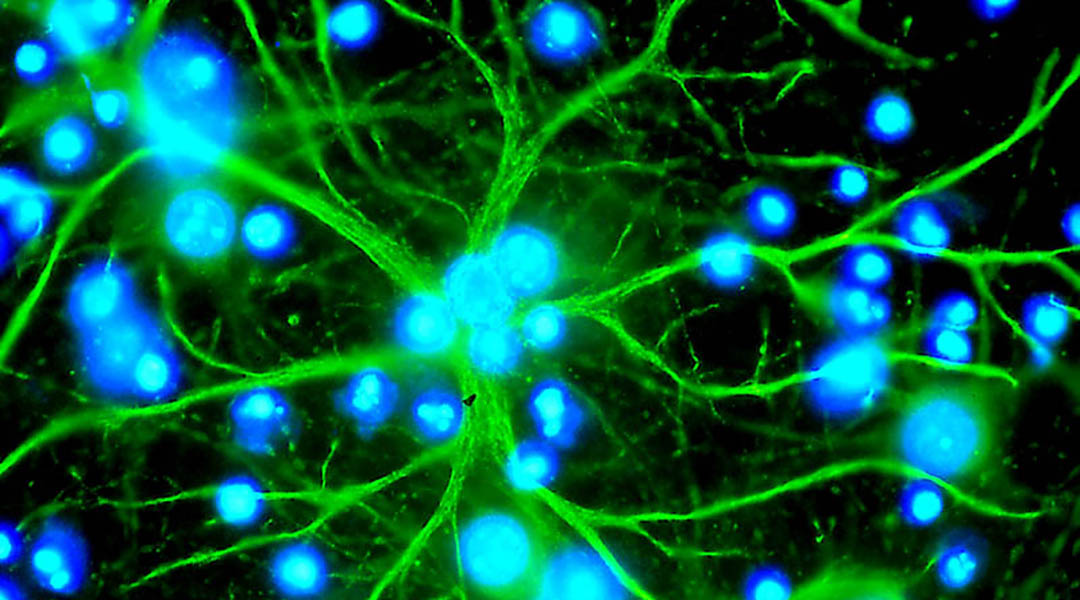
A group of brain cells called astrocytes might be involved in how information is conveyed within the brain’s neural networks.
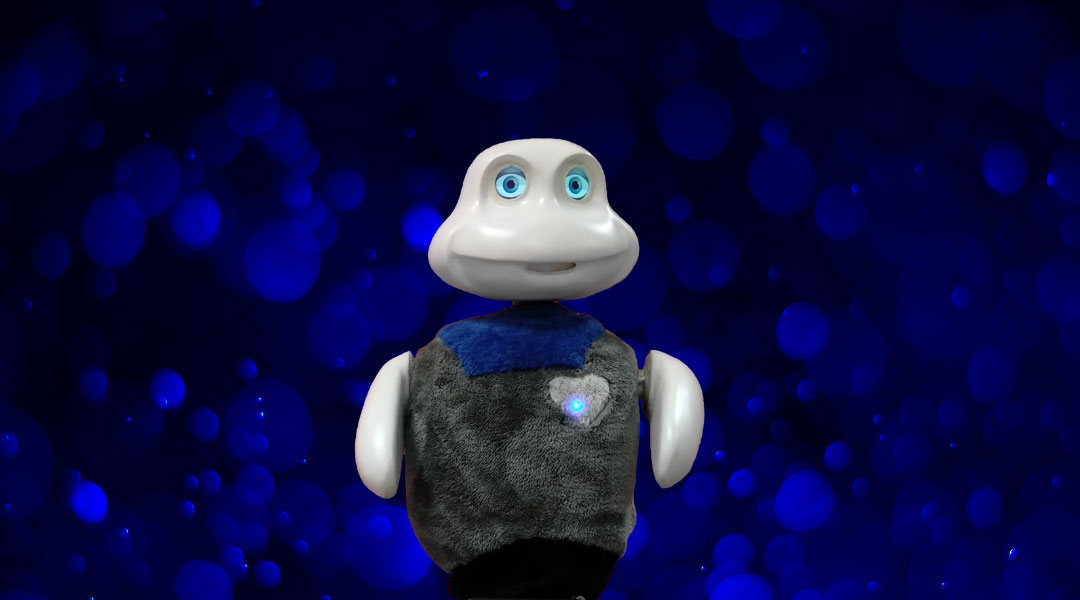

Modeling involuntary aspects of human behavior, such as blinking or even jet lag, might help build trust in robot-human interactions.
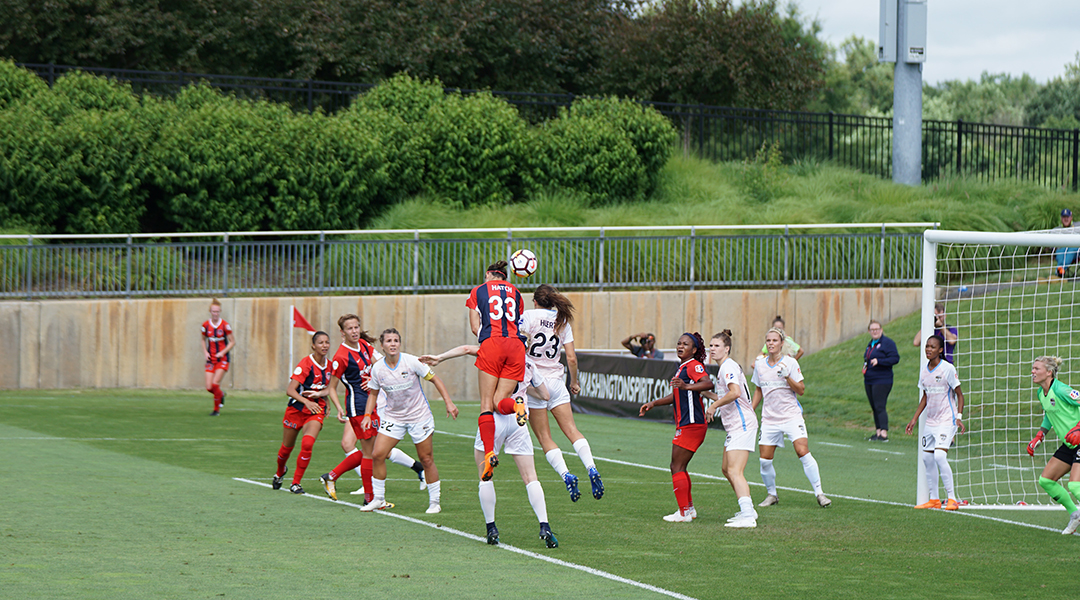

Even light blows from heading a soccer ball can contribute to long term brain injury, highlighting the need for collecting precise data.
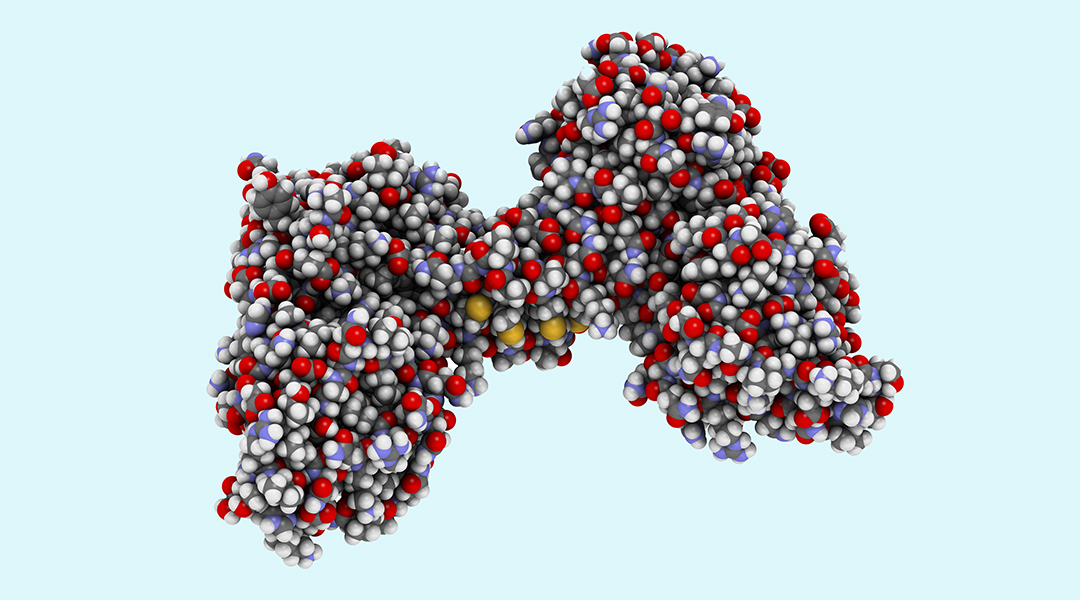
Important findings from an animal study have prompted the exploration of a gene therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy in an ongoing human trial.
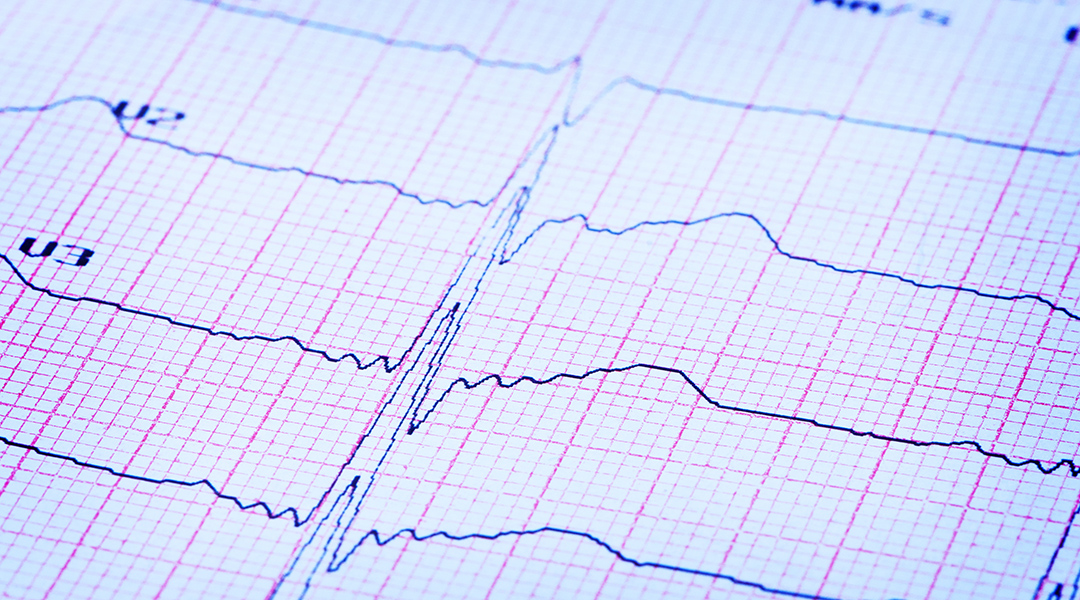
Scientists explore whether macrophages — key players in trauma repair — can sense and respond to damage caused by a heart attack.