Shrouded in the language of computers, the key is to figure out how to work with, and not blindly rely on, AI.



Shrouded in the language of computers, the key is to figure out how to work with, and not blindly rely on, AI.
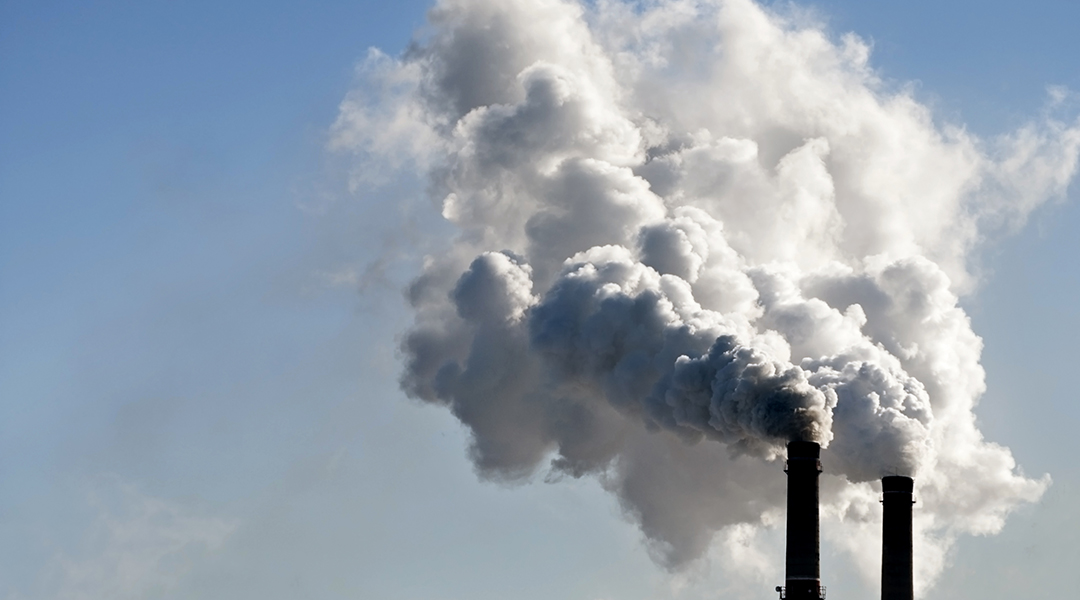

An innovative new material called CALF-20 has found success in an industrial pilot-scale carbon capture project.

Exploring how scientists can develop efficient, solar-powered reactions to convert carbon dioxide to useful chemical feedstocks.

An all-hands-on-deck initiative aims to fast track innovative technologies to remove atmospheric carbon dioxide.

A biorefinery built on the Red Planet could help produce rocket fuel required for a return journey, but some snags need to be worked through first.
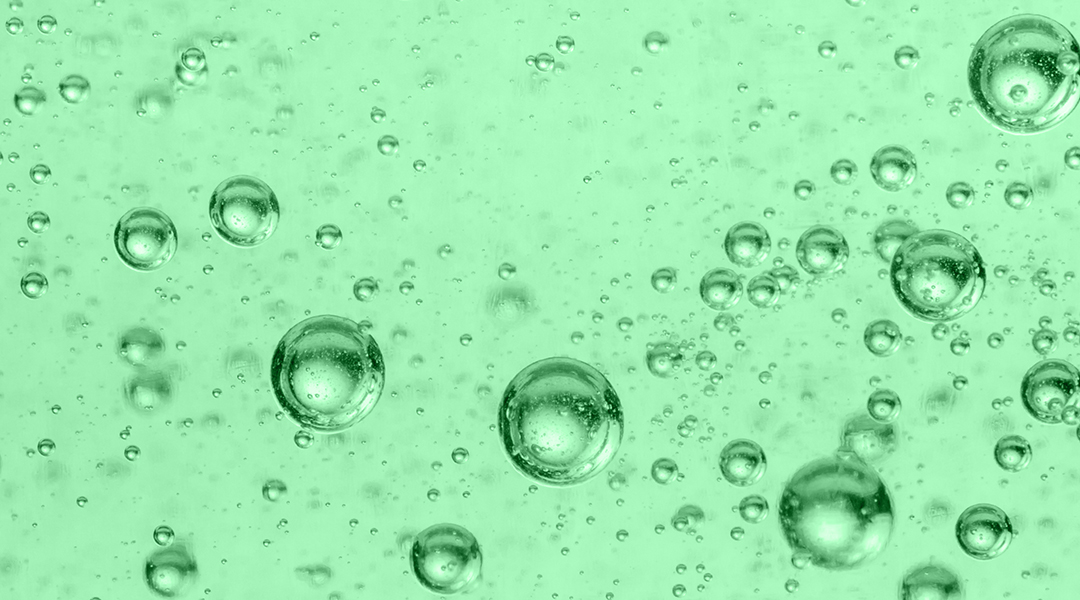

Directly integrated photovoltaic–electrochemical devices could provide a viable path toward a green hydrogen economy.
The effects of some of the world’s blackest materials on our atmosphere.
While AI has proven itself to be extremely capable in discerning optimal chemical structures, synthetic feasibility remains a challenge.
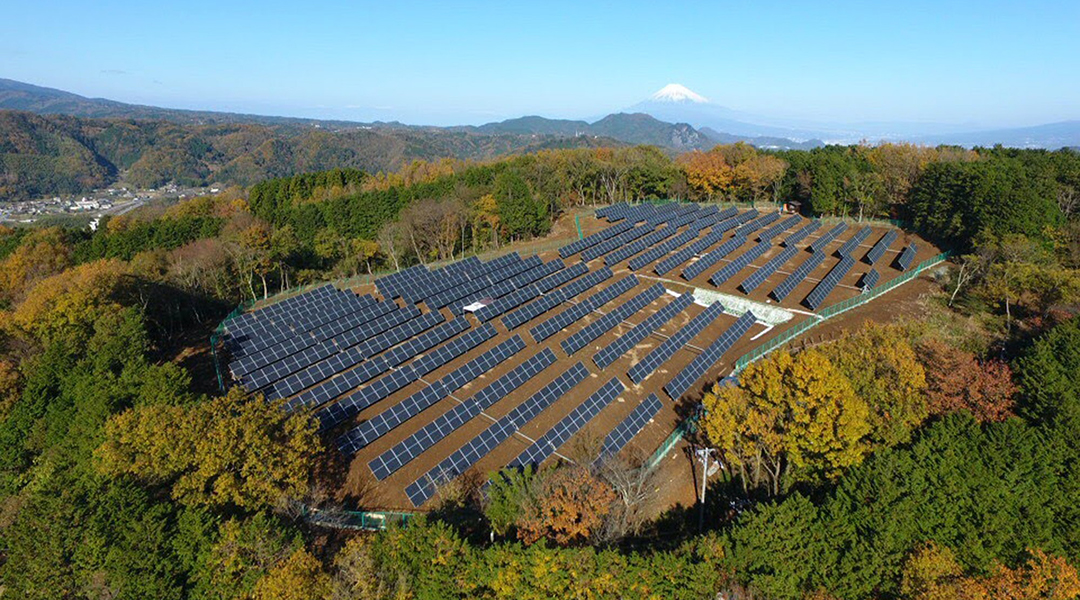

There needs to be more transparency to judge how diligent our governments, corporations, industries, and power generators are really faring in the green energy transition.
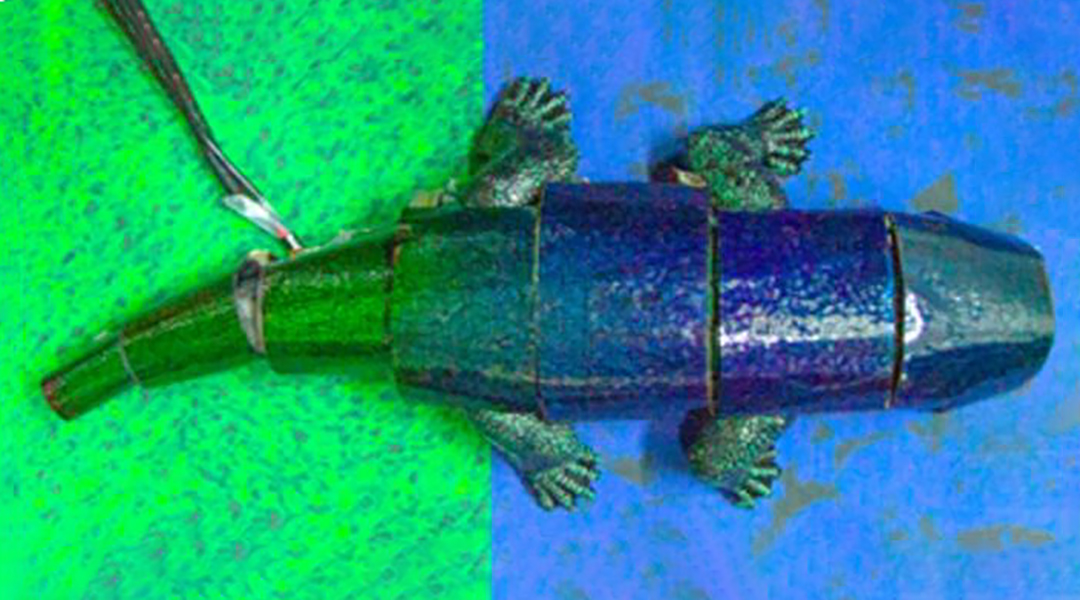

Using advanced sensors and a thermally responsive skin, a new robotic chameleon demonstrates mastery over color.