Researchers have given an overview of the principal inscription techniques and physical properties of fs pulse written in-fiber gratings for fiber optics.


Researchers have given an overview of the principal inscription techniques and physical properties of fs pulse written in-fiber gratings for fiber optics.
Quantum design strategy pushes high-power vertical external-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VECSELs) beyond the 100 W milestone.
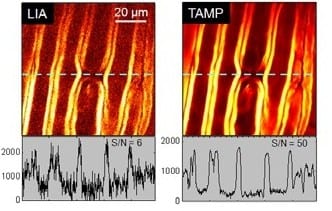
A superior signal to noise ratio for heterodyne detected nonlinear optical imaging can be attained by a newly developed tuned amplifier system in a lock-in free manner, as demonstrated through stimulated Raman scattering imaging of live cells and tissues.

Aside from the classical Gaussian intensity profiles, unconventional laser beam shapes open up new perspectives for technologically relevant areas such as deep-hole drilling, photopolymerization, and nanopatterning.
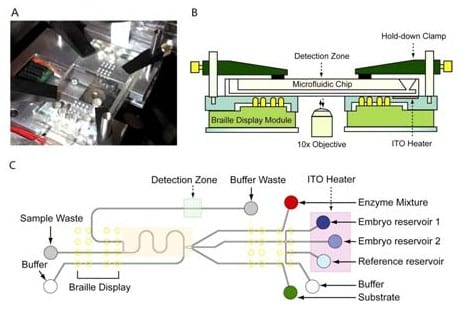
Lab-on-a-chip method, when combined with biophotonics, can be used to assay for metabolites, to separate gametes via optoelectrical tweezers, or to improve the vitrification of oocytes.
Nobel laureate Ahmed H. Zewail has summarized his insights into the physical backgrounds of protein folding.
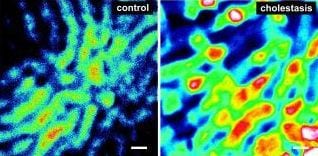
What happens in the liver during cholestasis? A novel in vivo imaging technique based on fluorescence microscopy delivers insight into the hepatic excretory function in rat.
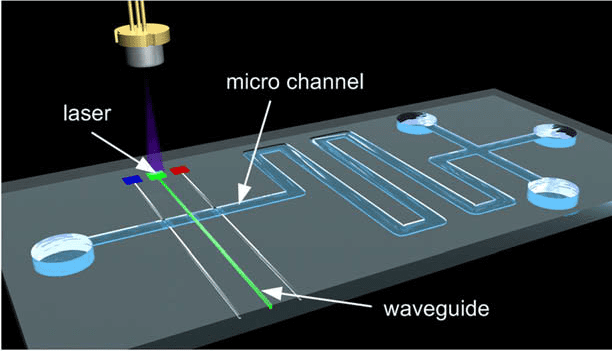
Solid-state organic amplifiers and lasers have evolved into attractive buildings blocks for on-chip integration. They offer low-cost and simple processing combined with high performance.
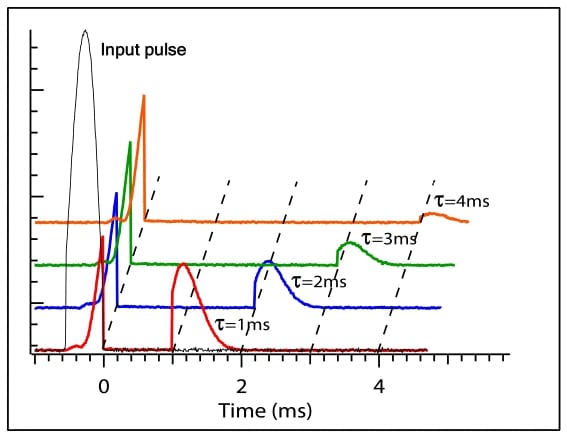
One of the exciting potential applications of electromagnetically induced transparency and slow and stored light is for practical realization of quantum memory, and, ultimately, quantum computing. Recent advances using ensembles of warm atoms in vapor cells have been made.
Coherent Raman scattering methods have one key advantage over spontaneous Raman microscopy: speed. The (sub-)microsecond pixel dwell times offered by narrowband CRS imaging methods have initiated a new era of chemical imaging applications in biology and biomedicine.