Human microbiota, blood group antigens, and disease, a look at the ways that microbiota interact with the human body.


Human microbiota, blood group antigens, and disease, a look at the ways that microbiota interact with the human body.

The award-winning WIREs (Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews) series combines some of the most powerful features of encyclopedic reference works and review journals in an innovative online format. WIREs are designed to promote a cross-disciplinary research ethos while...
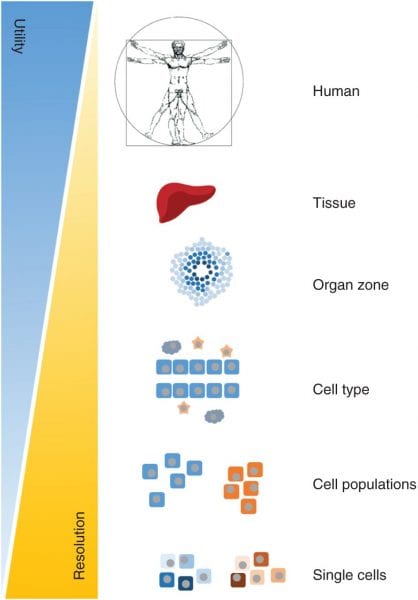
Genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs) are relatively new tools for studying the metabolic changes associated with many diseases. GEMs are reconstructions of the metabolic networks of cells, sometimes able to represent an organism’s whole body.
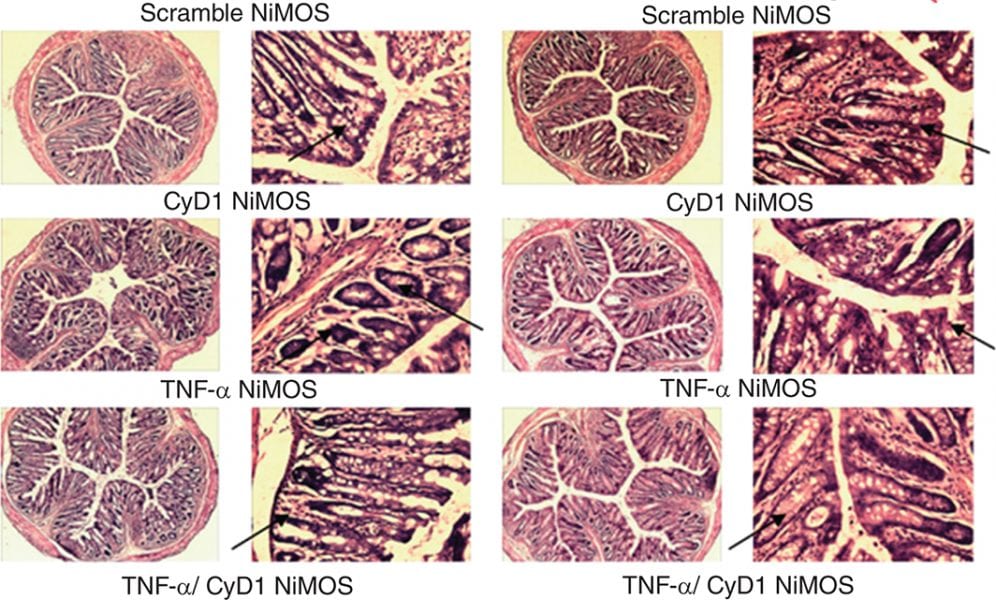
DNA and RNA (nucleic acids) interference therapies have the potential to treat many human diseases.
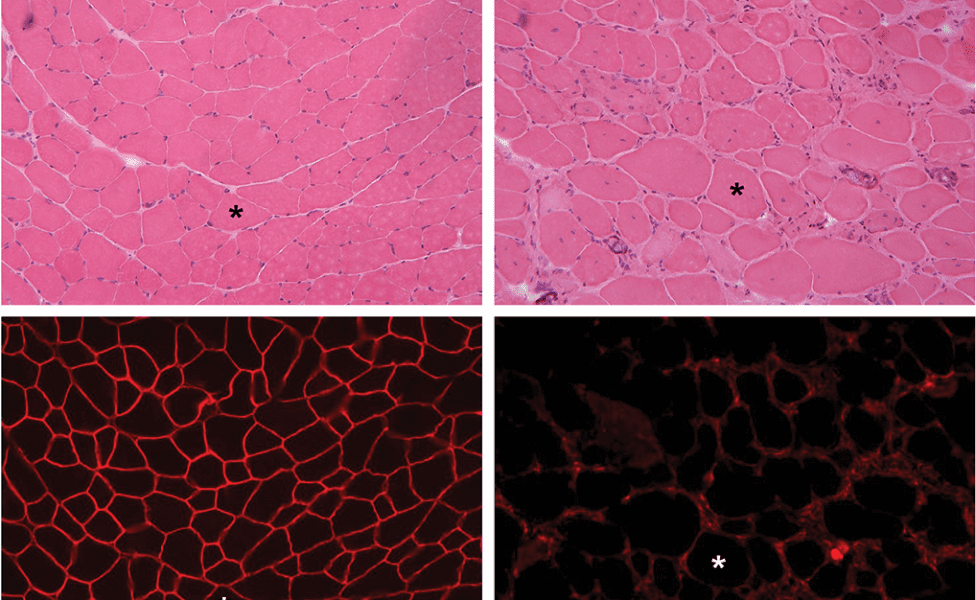
A recent review discusses the emerging nanomedications and therapies with potential to alter Duchenne’s fatal outcome.

While women are more likely to express concerns about climate change and to accurately grasp its science, they are also more likely to underestimate their knowledge.
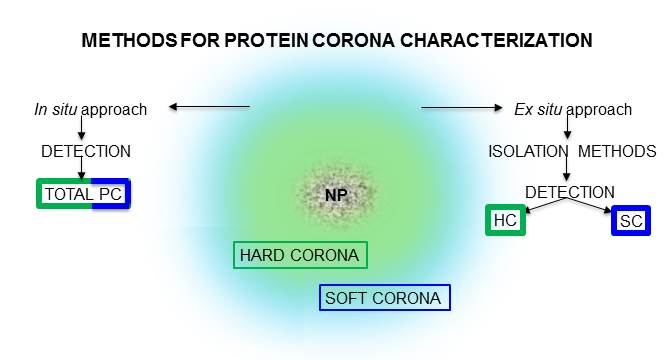
The application and the clinical development of nanomedicines strongly requires a deep study on the complex dynamics that happen after in vivo administration. Particularly, plasma proteins tend to associate to nanoparticles, forming a new surface named the “protein corona” that can have a strong impact on biodistribution, targeting efficacy, and toxicity.