In a proof-of-concept study, authors in Italy have demonstrated electric field-controlled switching between stable states in a porous material containing nematic liquid crystals.
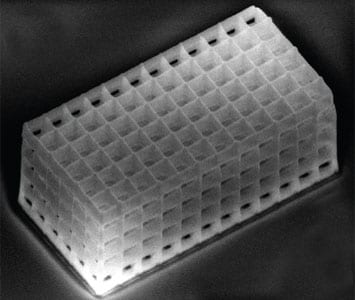


In a proof-of-concept study, authors in Italy have demonstrated electric field-controlled switching between stable states in a porous material containing nematic liquid crystals.

Professor Molly Stevens has become a recognised role model in science. She has won award after award and built a large and successful research group at Imperial College London.

The first thing I noticed about our new Editorial Board Member for Advanced Materials is that Professor Ariga is very on top of his emails. I was then delighted to discover his great sense of humour…
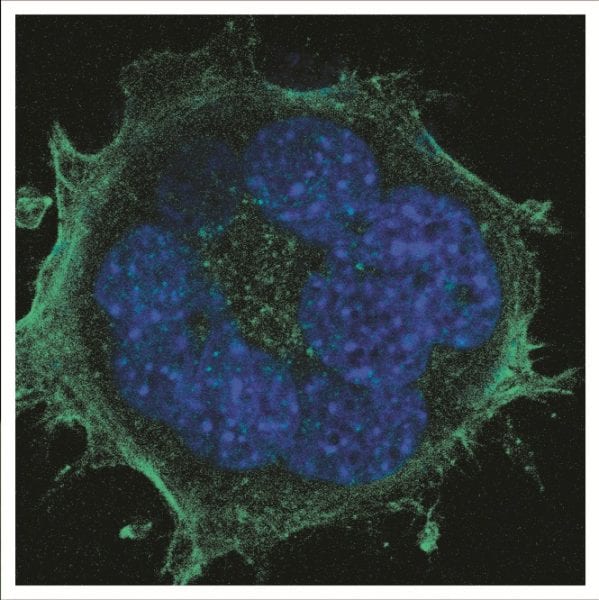
Bigger is not necessarily better: when it comes to culturing fibroblasts on nanowire substrates, there are several reasons to reconsider the use of long nanowires.
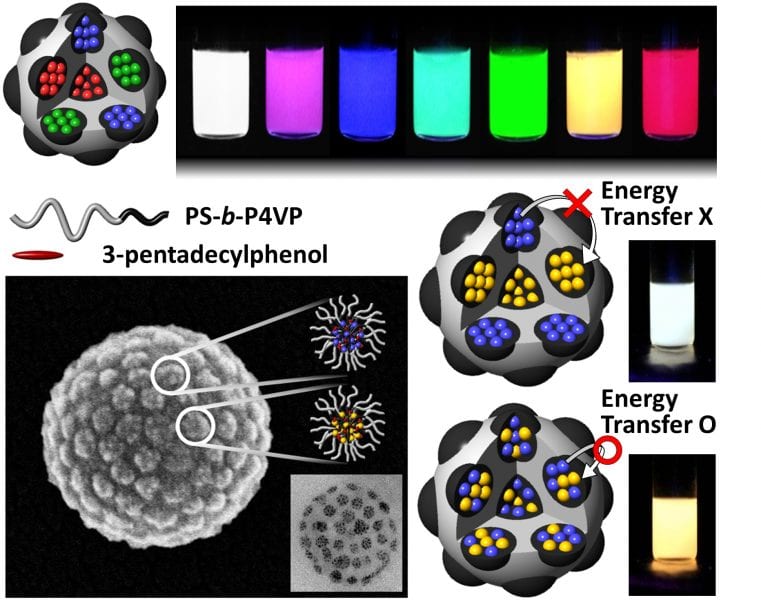
Controlled physical placement of quantum dots inside block copolymer microspheres determines the combined emission characteristics.
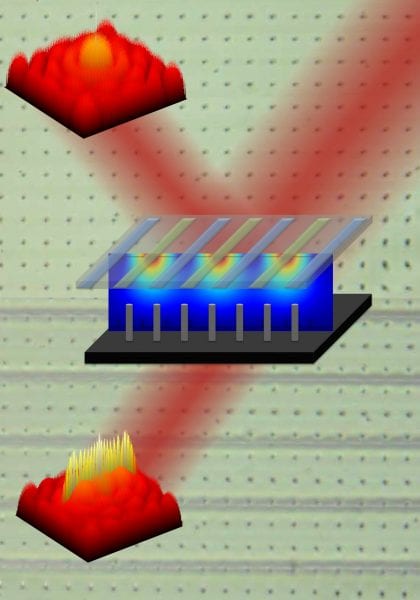
Voltage-dependent diffraction switching makes a hybrid liquid crystal–carbon nanotube device a good candidate for high-resolution displays.
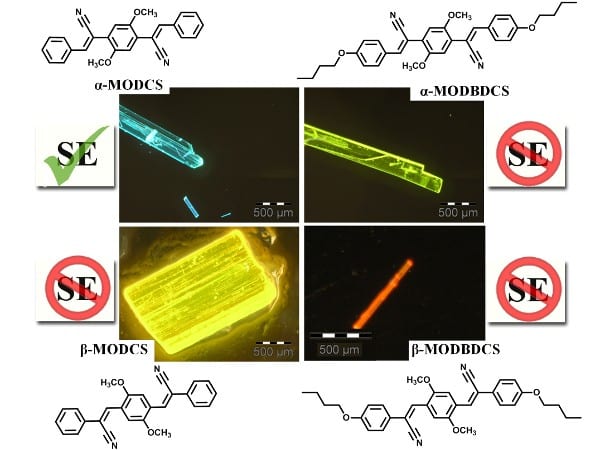
Structure–property relationships of single crystals are analysed such that their spontaneous and stimulated emission properties can be quantified based on their crystal structures.
Nanomaterials have so much to offer – the sooner we uncover their interactions with biological systems and the mechanisms behind them, the sooner we can apply nanomaterials to safe, effective, advanced technologies. That’s why this special issue on Nanotoxicology in Small was just too big to publish as a single issue…

This special issue on low-dimensional carbon materials for Small is dedicated to the 20th anniversary of the Center for Nanochemistry at Peking University.
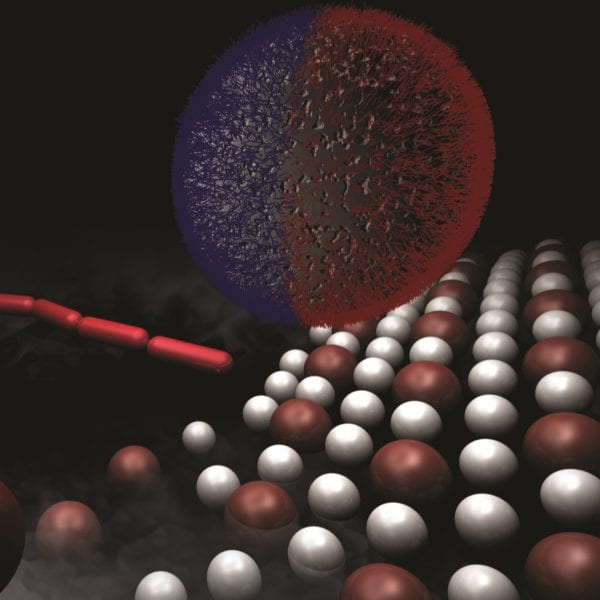
Patchy particles, and Janus particles in particular, already have such broad application potential that it’s hard to believe they are a relatively young concept to nanoscience.