Self-healing of a phase change memory device with a metallic surfactant layer opens up new pathways in storage class memory.



Self-healing of a phase change memory device with a metallic surfactant layer opens up new pathways in storage class memory.

A hybrid thermochromic window coating with excellent visible transmittance and thermochromic performance at room temperature, opens new directions in plasmonic coatings.

Researchers design a bio-inspired batoid robot from non-toxic hydrogels operated with Au microelectrodes.
A new biomimetic strategy provides a platform for the synthesis of ligand-targeted nanovesicles that can mediate selective drug delivery to specific tissues.
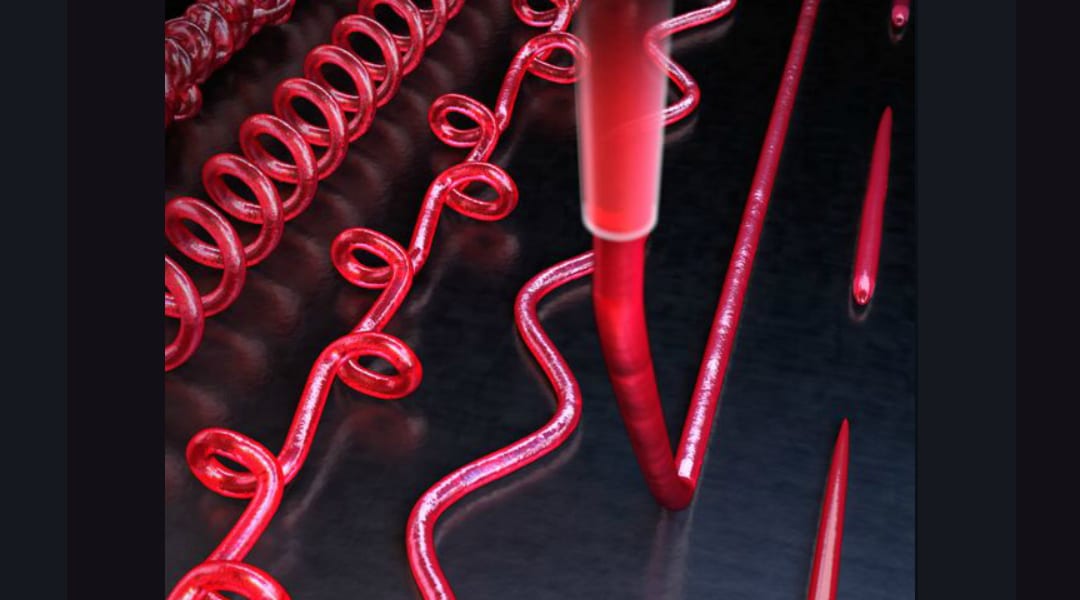

Researchers from MIT present a strategy to increase printing resolution beyond the nozzle size, while drawing diverse complex patterns with a linear nozzle path.
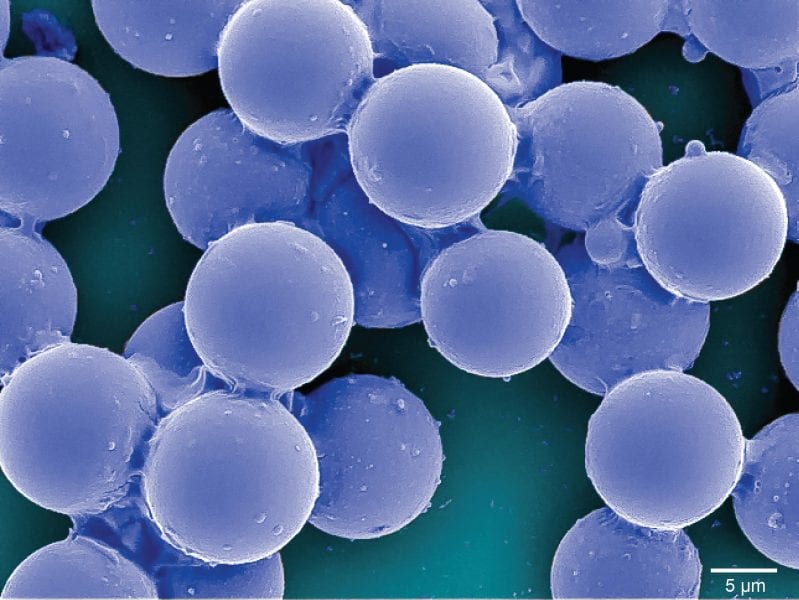
A simple and convenient method to fabricate thermoresponsive gel particles with tunable size across multiple size scales opens new directions in biomaterials, optics, and pharmaceutics.
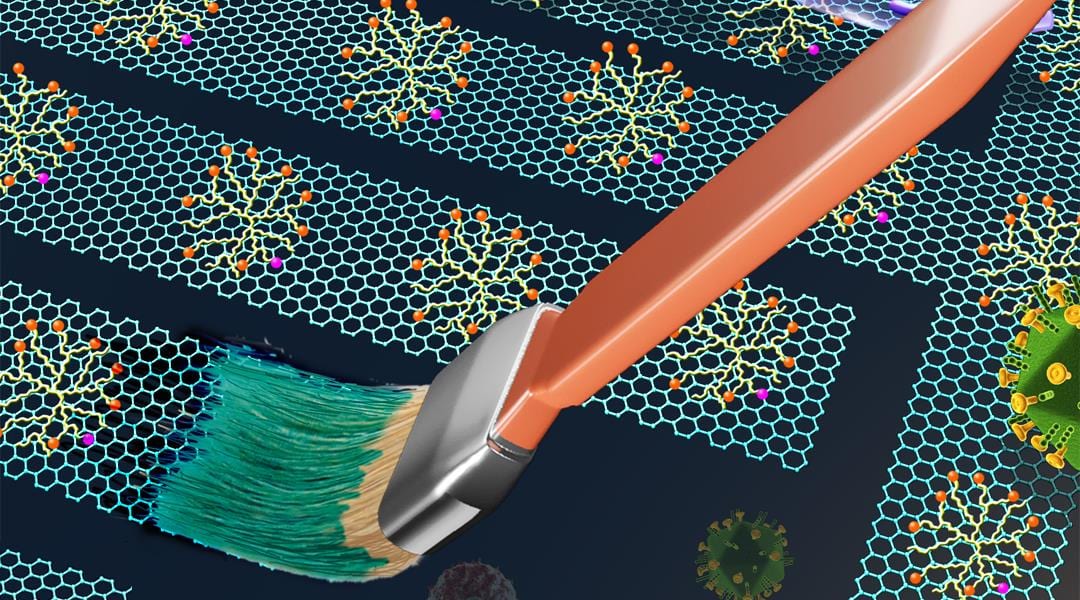
Flexible graphene nano-inks with an excellent bioactivity pave the way for next generation biomedical applications.
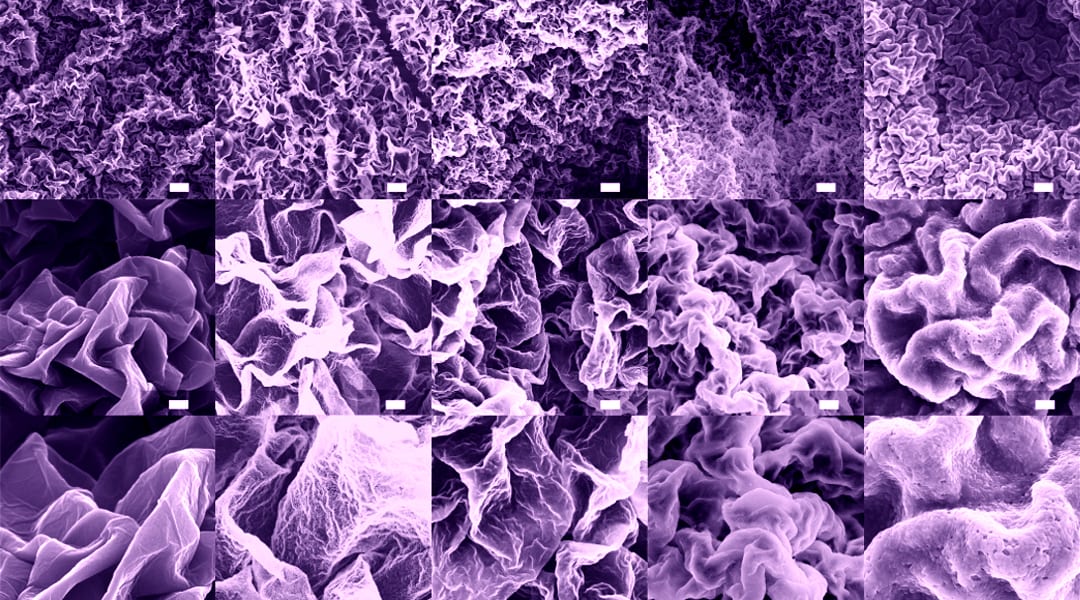

Metallized graphene inks open new directions in film patterning since dense ceramic films with the micro- and macrostructure of a graphene host were produced for the first time in Brown University
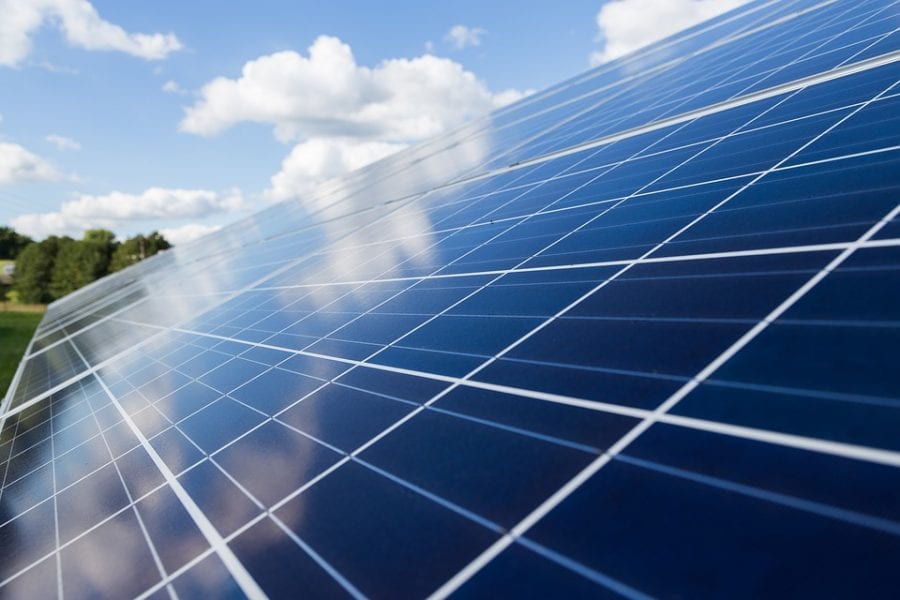

A new technique renders the low-cost process of sputtering a highly competitive fabrication method for photovoltaics.