Nanoparticulate formula together with light augmentation could realize the potential for intranasal vaccines to protect against respiratory viruses.
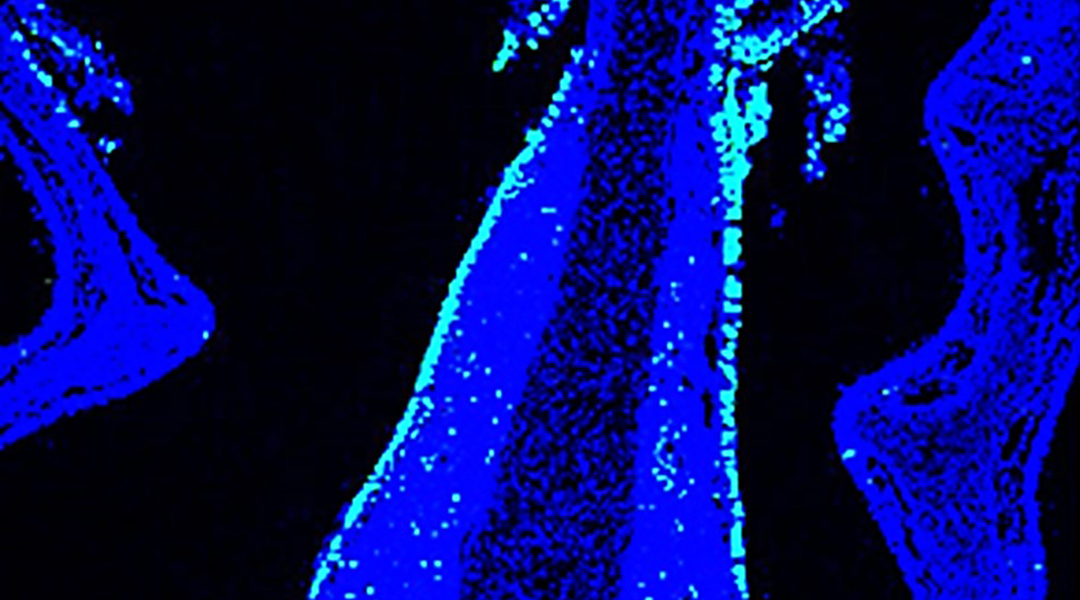


Nanoparticulate formula together with light augmentation could realize the potential for intranasal vaccines to protect against respiratory viruses.
Researchers create a new biocompatible patch that could enhance the clinical treatment of tissue injury by speeding up wound healing.
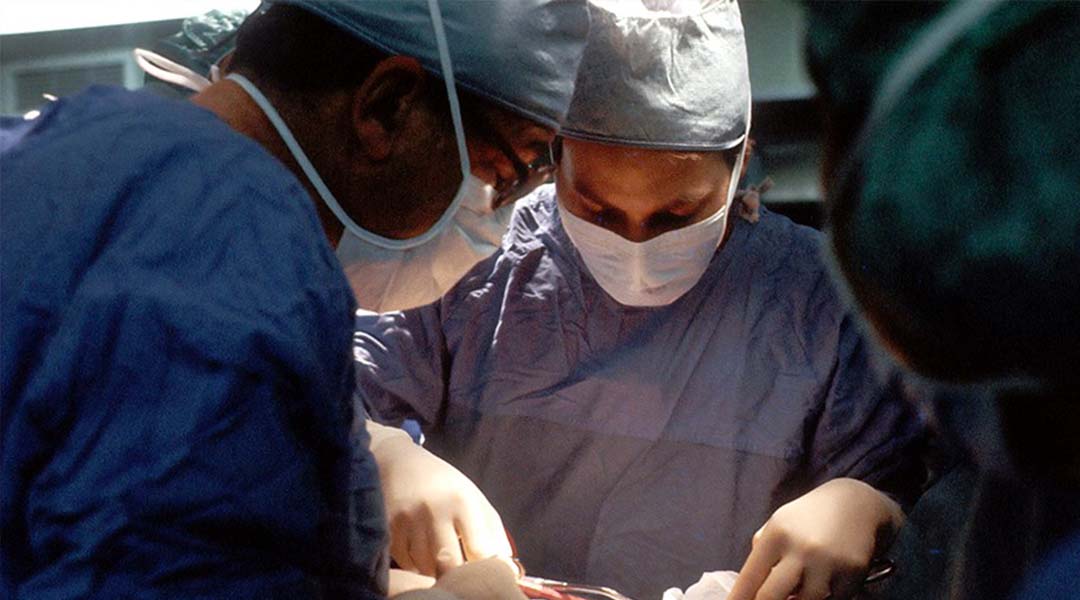
The surgical anesthesia drug, propofol, used in tumor removal, could help promote the spread of cancer by triggering changes in tumor cell properties.
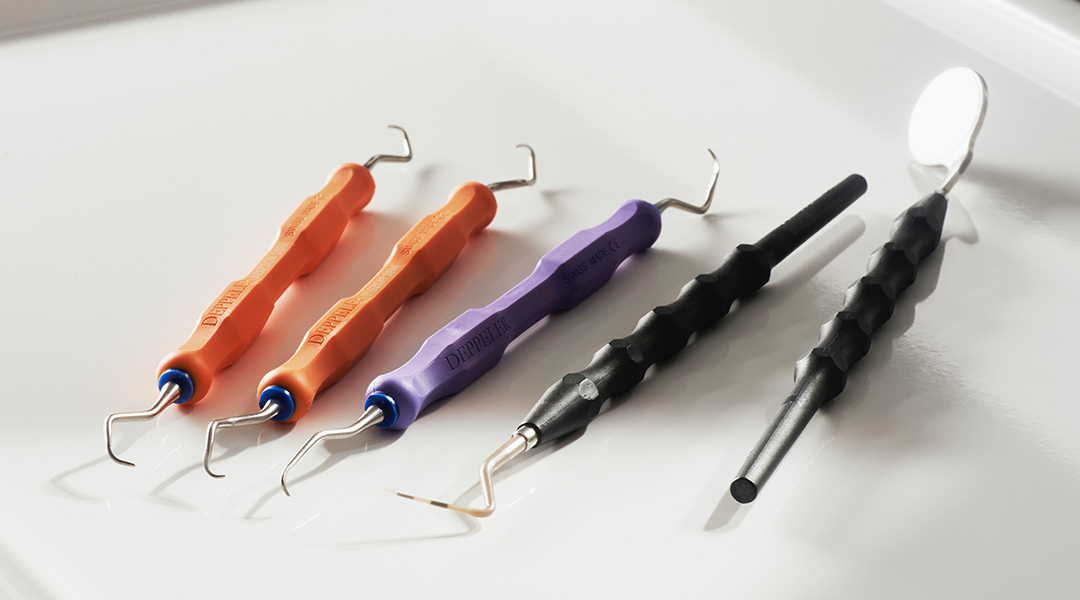

A charged microneedle patch for pain-free delivery of anesthetics could replace anxiety-inducing needles in dental work.

Wearable devices and gadgets have surged in popularity, but researchers say that current ethical frameworks need to catch up with research to protect study participants.
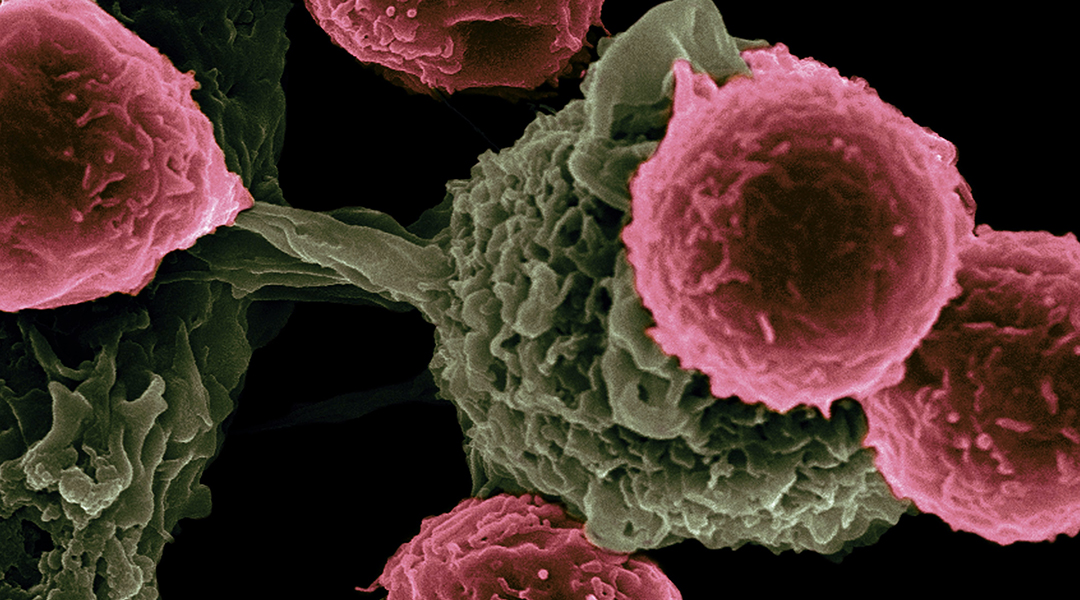
Nanovesicles that directly attack tumors and promote sustained tumor killing by resident T cells could enhance the effectiveness of tumor immunotherapy.
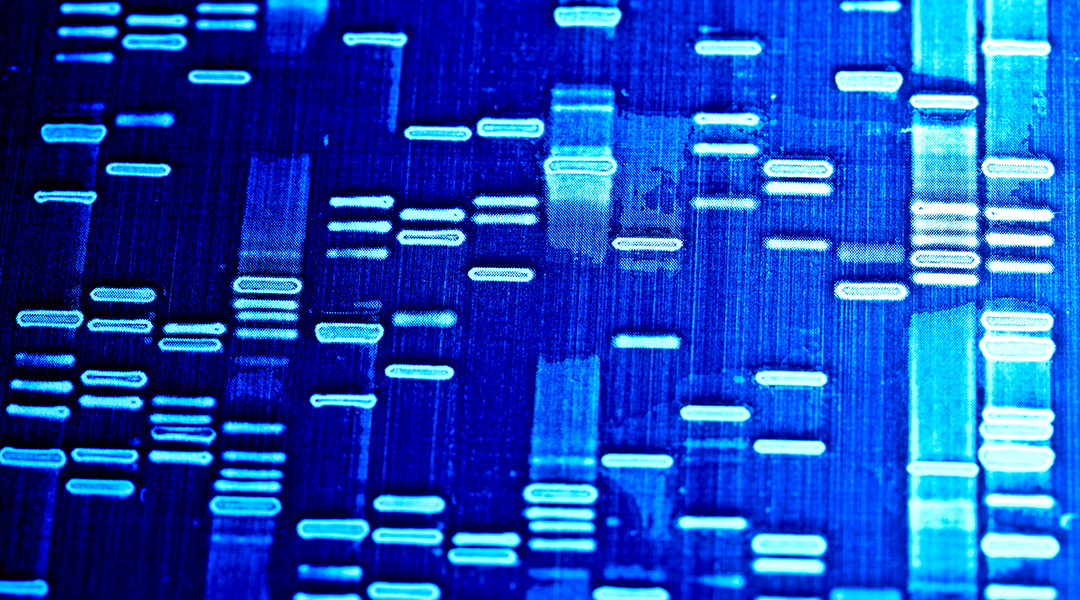

Genomic editing tools can reverse disease causing mutations to provide cures — once we can conquer the remaining barriers.
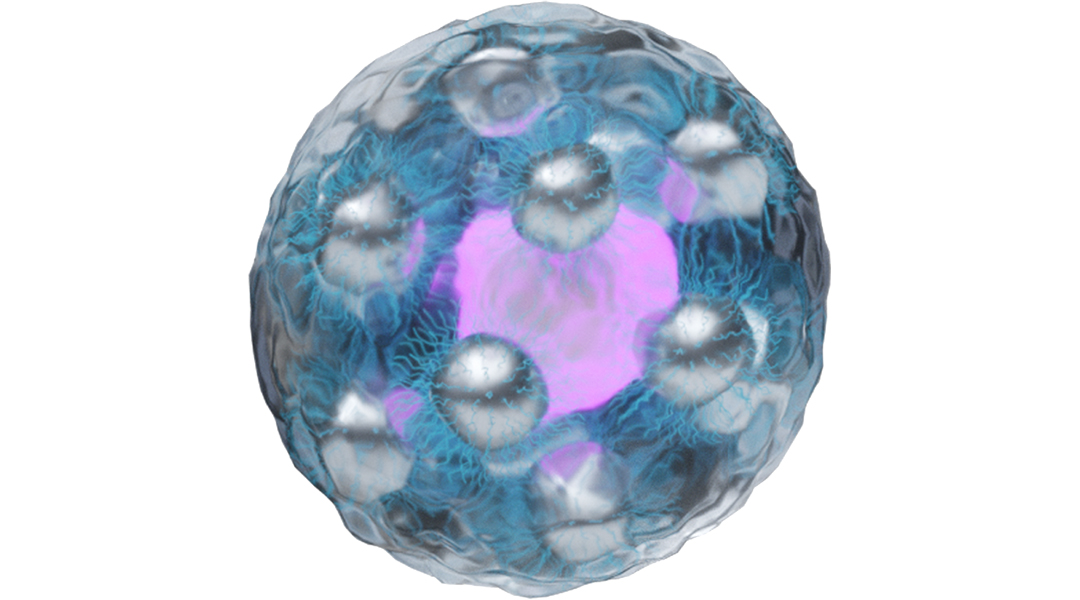
A minimally invasive method holds promise for the treatment of neurological disorders and injury.
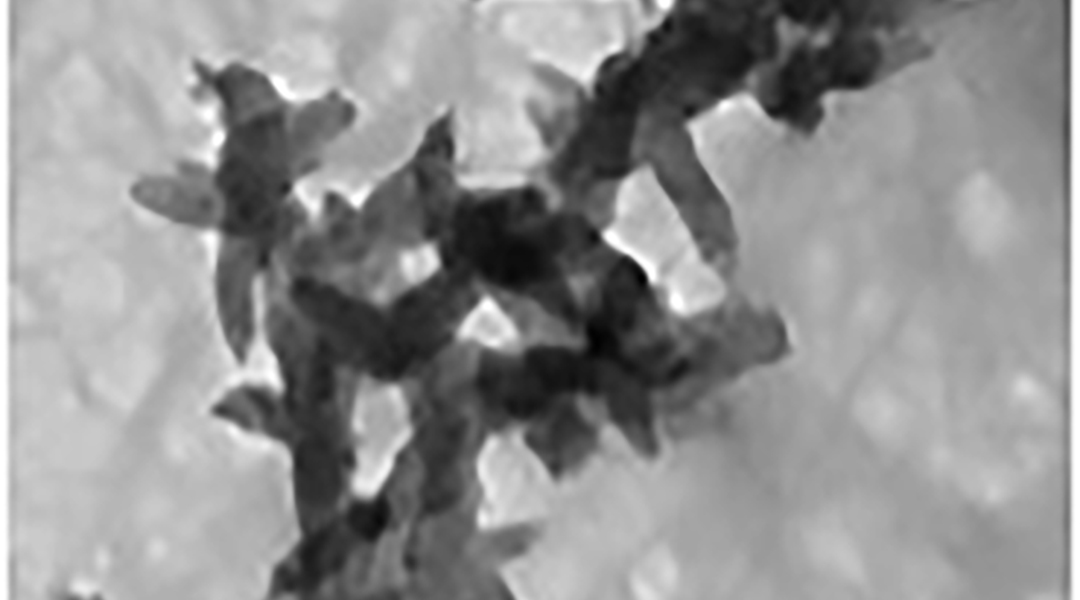
A conductive biomaterial that supports the growth of cardiac muscle cells and facilitates their synchronous beating holds great potential for cardiac tissue engineering.
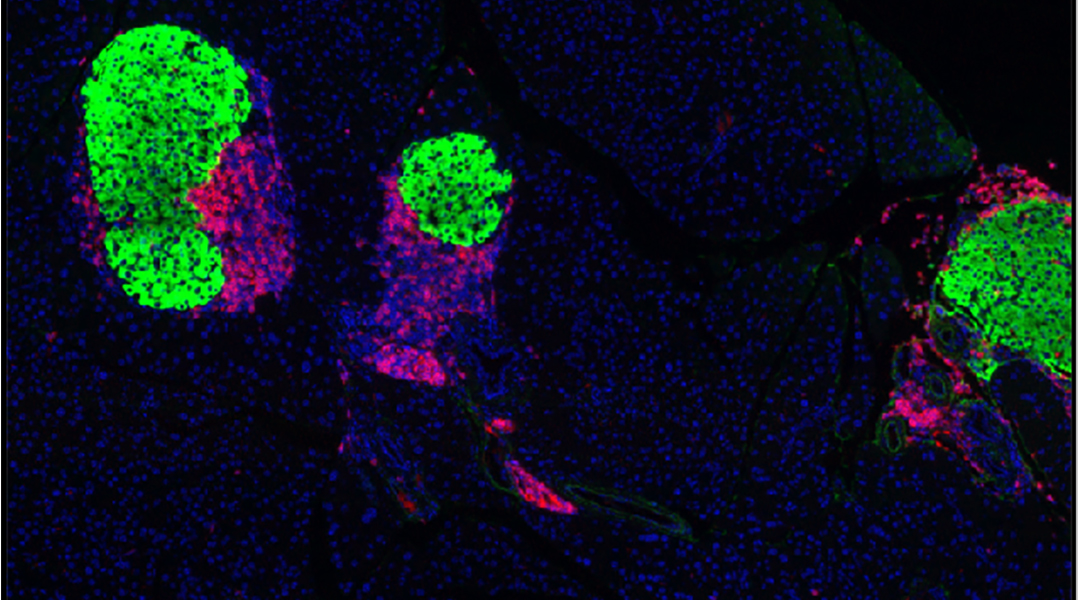
Bioengineered pancreatic beta cells adorned with immune checkpoint proteins prevent the progression of type 1 diabetes.