In response to stress, cells must quickly reprogram gene expression to adapt and survive. This is achieved in part by altering levels of mRNAs and their translation into proteins.
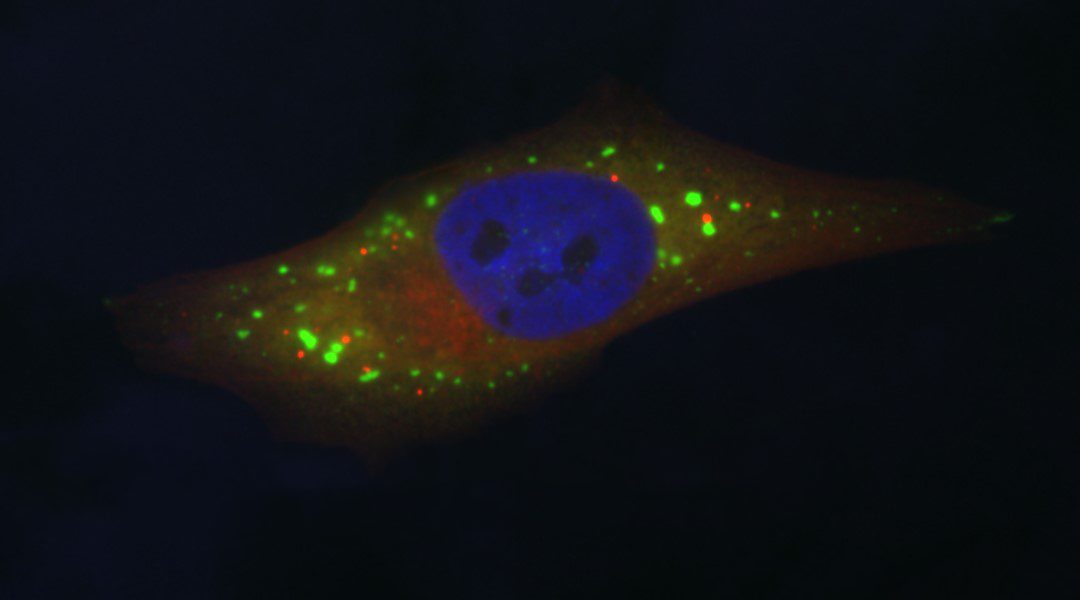


In response to stress, cells must quickly reprogram gene expression to adapt and survive. This is achieved in part by altering levels of mRNAs and their translation into proteins.
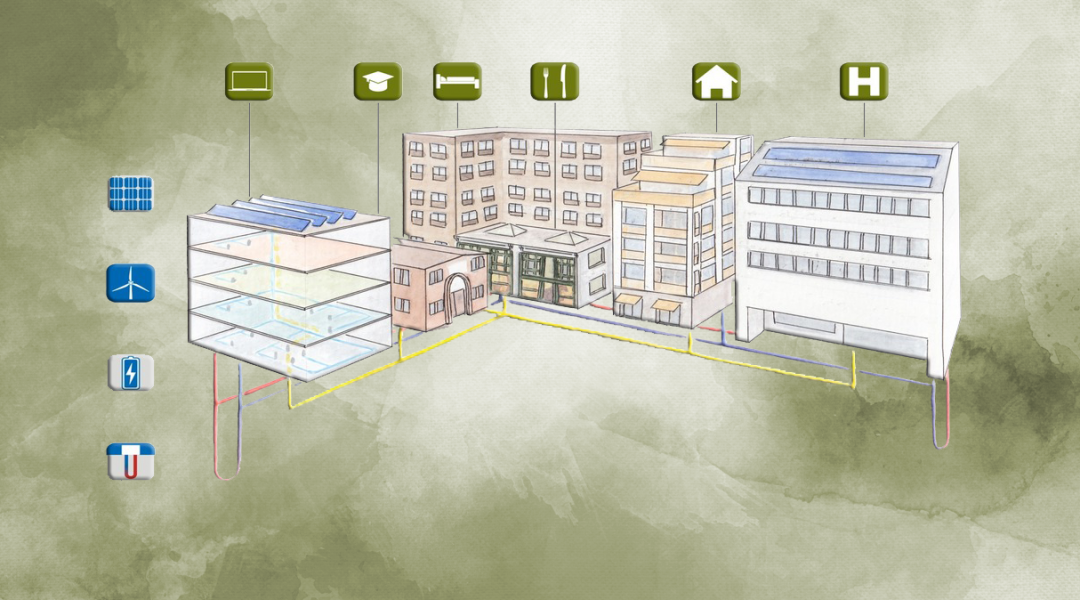
Decentralized renewable energy systems are promising options to cope with the challenge of balancing local production and energy consumption.
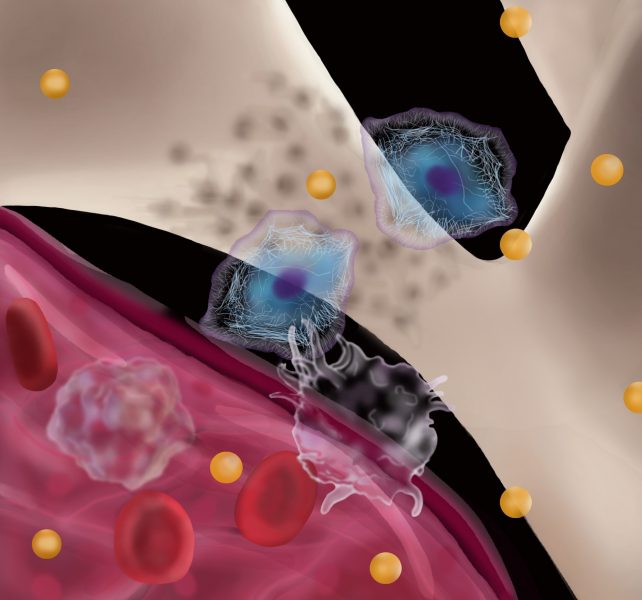
“Off the shelf” allogeneic stem cell transplants and stem cell nano‐composites are being used for the treatment of degenerative bone diseases. However, major and minor histocompatibility antigens of therapeutic cell transplants can be recognized as foreign and lead to their rejection by the host immune system.
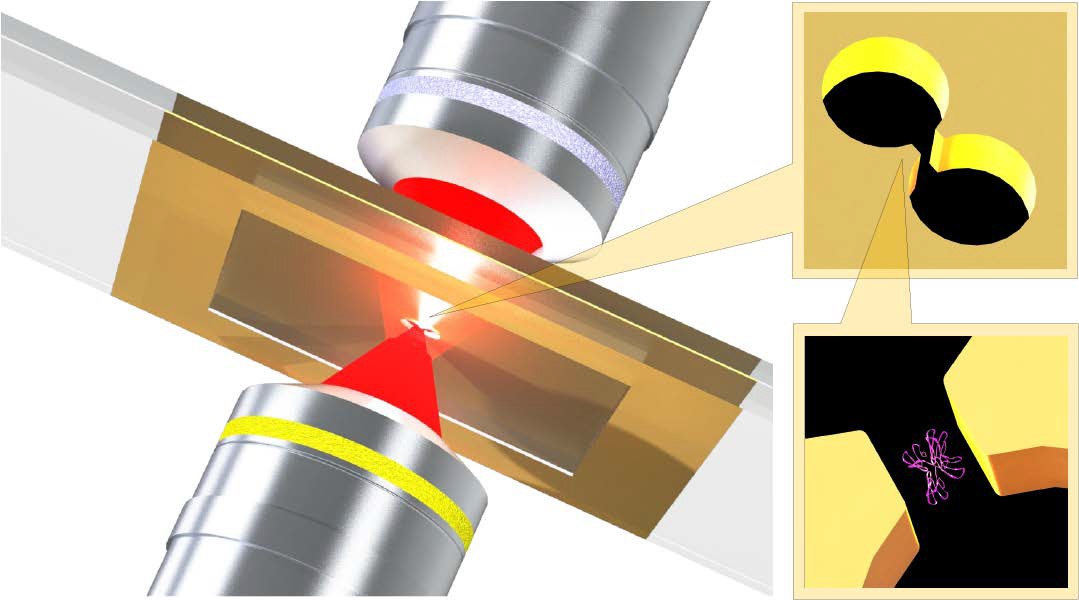
Recent advances in single‐molecule techniques have led to new discoveries in analytical chemistry, biophysics, and medicine. Understanding the structure and behavior of single biomolecules provides a wealth of information compared to studying large ensembles.

Recent high‐resolution cryoEM structures of various spliceosomal complexes reveal unprecedented details of this large molecular machine.
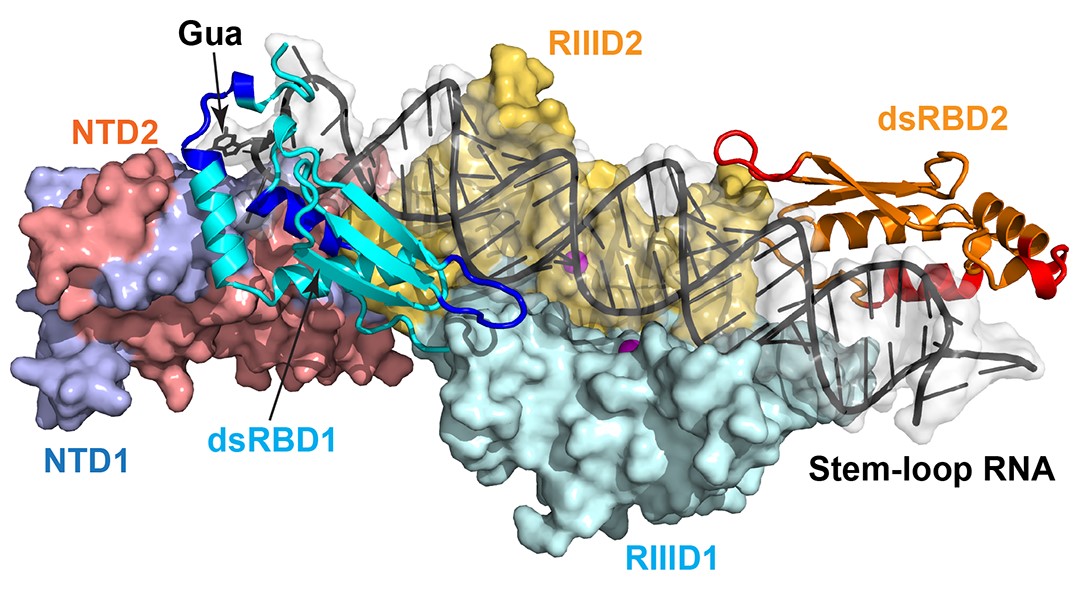
The double‐stranded RNA‐binding protein family controls RNA editing, stability, and function in all eukaryotes.

The more engagement the better?
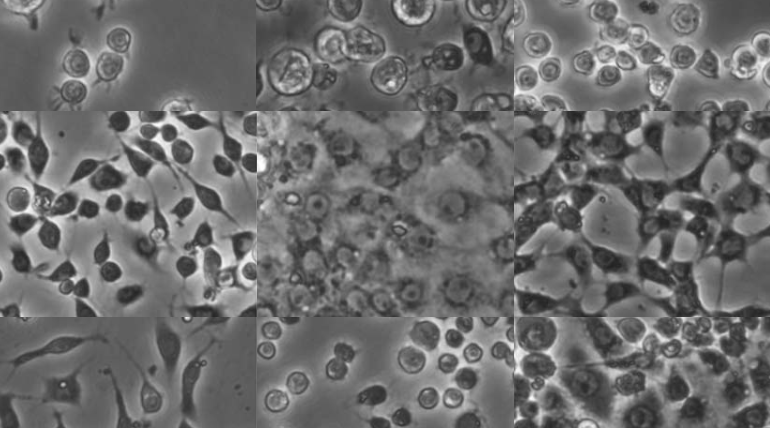
Challenges and opportunities to improve the state of Drosophila cell cultures.

Polymer physics is the basis to models that explain chromatin folding mechanisms.

Adaptability would reduce vulnerability to global climate change, but requires better communication between researchers in the field.