Researchers have identify a series of ‘Big Data Approaches’ (BDAs) with the potential to shed new light on the complexities and challenges surrounding coastal flood risk management.
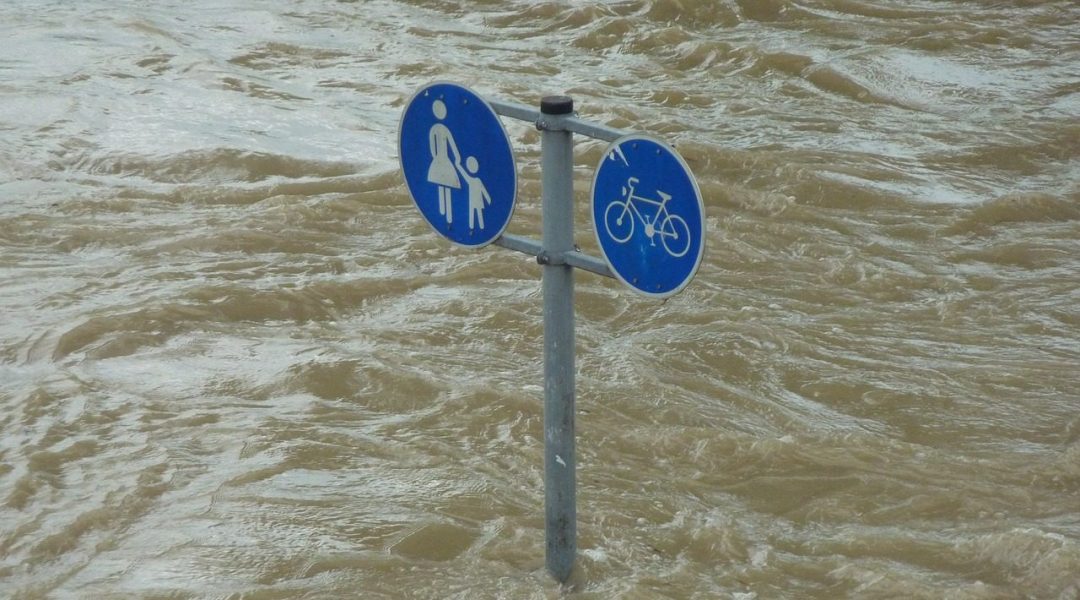



Researchers have identify a series of ‘Big Data Approaches’ (BDAs) with the potential to shed new light on the complexities and challenges surrounding coastal flood risk management.

An exploration of how travel can also be understood as something intimately connected to historic, economic and cultural influences.
Machine Learning (ML) is a well‐known paradigm that refers to the ability of systems to learn a specific task from the data and aims to develop computer algorithms that improve with experience.

Quantitative systems modeling aims to integrate knowledge in different research areas with models describing biological mechanisms and dynamics to gain a better understanding of complex clinical syndromes.
There are striking similarities between the structure of natural river networks and others found in systems as diverse as brains, roads and the communication technologies. Using a series of examples, the authors illustrate how a suite of graph theory-based metrics derived from diverse disciplines can be used to provide new insights into the structure and kinematics of braided river networks.
Could stumps from managed forests provide sustainable biomass in a future bio-economy or are they all needed in the forest to support other ecosystem services and biodiversity?

Light is perhaps the main environmental cue (zeitgeber) that affects several aspects of physiology and behaviour, such as sleep/wake cycles, orientation of birds and bees, and leaf movements in plants. Temperature can serve as the main zeitgeber in the absence of light cycles, even though it does not lead to rhythmicity through the same mechanism as light.

The statistical methods currently in use to estimate past changes in climate are reviewed.

An investigation into how pioneer factors interact with closed chromatin to influence chromatin landscapes and generate differentiated cells.

Silk’s highly tunable range of mechanical properties, degradation rates and material formats arise from subtle changes at the microscopic level.