A novel fuel cell prototype forms part of Nissan’s on-going commitment to the development of zero-emission vehicles. The Japanese car builder already sells the world’s highest-volume zero-emission car, the LEAF, and is establishing mobility systems that will be deployed in a range of vehicles over coming years.

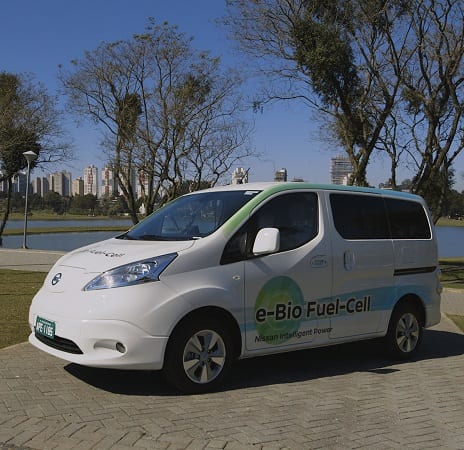
Prototype vehicle of the Nissan e-bio fuel-cell on public roads in Brazil. Source: Nissan.
The new e-bio fuel-cell prototype vehicle runs on 100 % ethanol to charge a 24 kWh battery that enables a cruising range of more than 600 km, according to the company. Nissan will conduct further field tests on public roads in Brazil using the prototype.
President and CEO Carlos Ghosn said: “The e-bio fuel-cell offers eco-friendly transportation and creates opportunities for regional energy production… all the while supporting the existing infrastructure. In the future, the e-bio fuel-cell will become even more user-friendly. Ethanol-blended water is easier and safer to handle than most other fuels. Without the need to create new infrastructure, it has great potential to drive market growth.”
The car builder pledges that the powertrain is clean, highly-efficient, easy to supply, and runs on 100 % ethanol or ethanol-blended water. Its carbon-neutral exhaust gas is as clean as the atmosphere, while the e-bio fuel-cell features low-running costs equivalent to an electric vehicle, with a driving range of a gasoline-engine vehicle.
Bio-ethanol fuels are mainly sourced from sugarcane and corn. These fuels are widely available in countries in North and South America, as well as Asia, with solid infrastructure in those markets.
Due to the easy availability of ethanol and low combustibility of ethanol-blended water, the system is not heavily dependent or restricted by the existing charging infrastructure, making it easy to introduce to the market – at least in these countries.