Scientists develop a light-driven carbon capture system using photoacids, creating an energy-efficient method to remove atmospheric carbon dioxide.


Scientists develop a light-driven carbon capture system using photoacids, creating an energy-efficient method to remove atmospheric carbon dioxide.
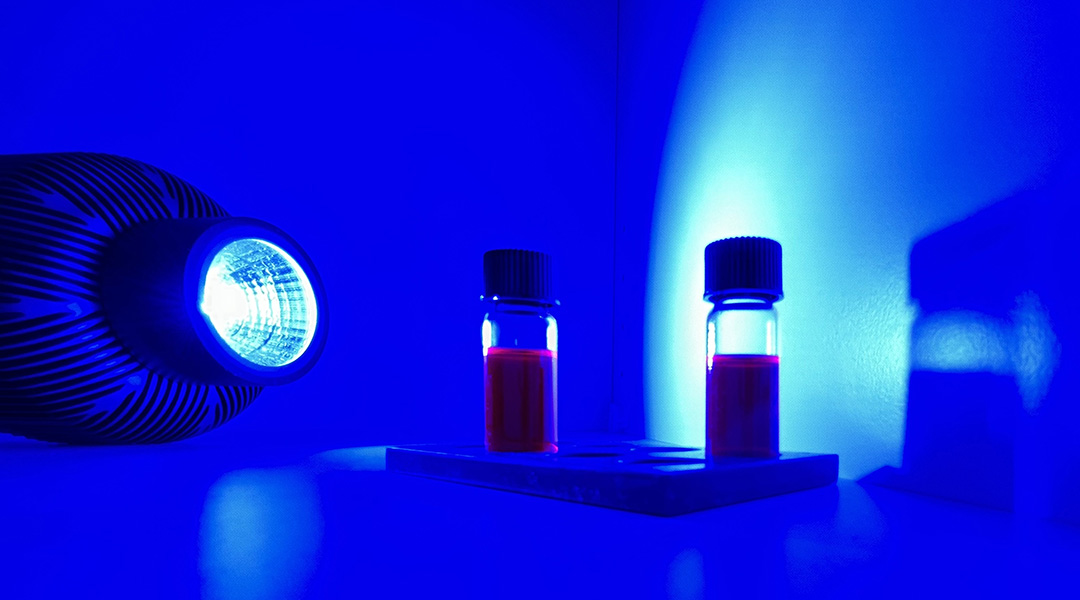

Researchers use photocatalysis to edit molecules, adjusting carbon-based ring sizes for versatile structures.
Scientists pioneer mixed-valence molecules in quantum-dot automata for faster, room-temperature operation, overcoming transistor limits.
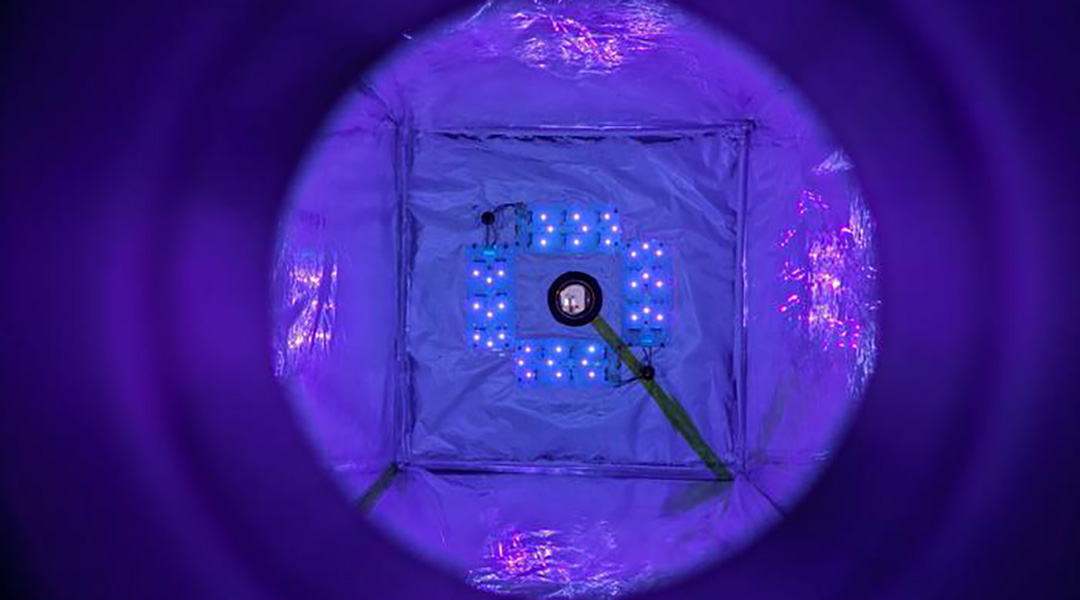

The new device pulls methane out of the air and could help tackle emissions from low-concentration sources, like livestock farms.
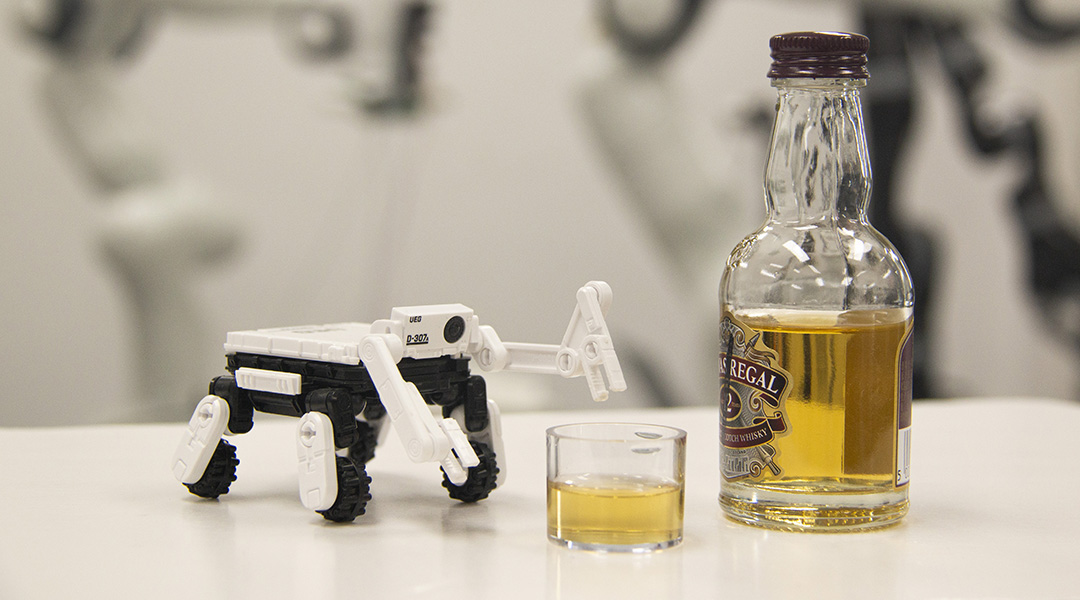

Precisely copying the capabilities of a biological nose with an artificial one is a lofty but potentially world-changing goal.

Click chemistry spins bacterial-produced spider silk into a biomedical marvel, promising innovations in fiber optics, wound healing, and tissue regeneration.

Scientists unlock nature’s green secrets to accelerate drug discovery, delivering eco-friendly pharmaceuticals with exciting potential.

A new frontier in clean energy may be on the horizon with nanoscale generators that capture electricity from molecules.
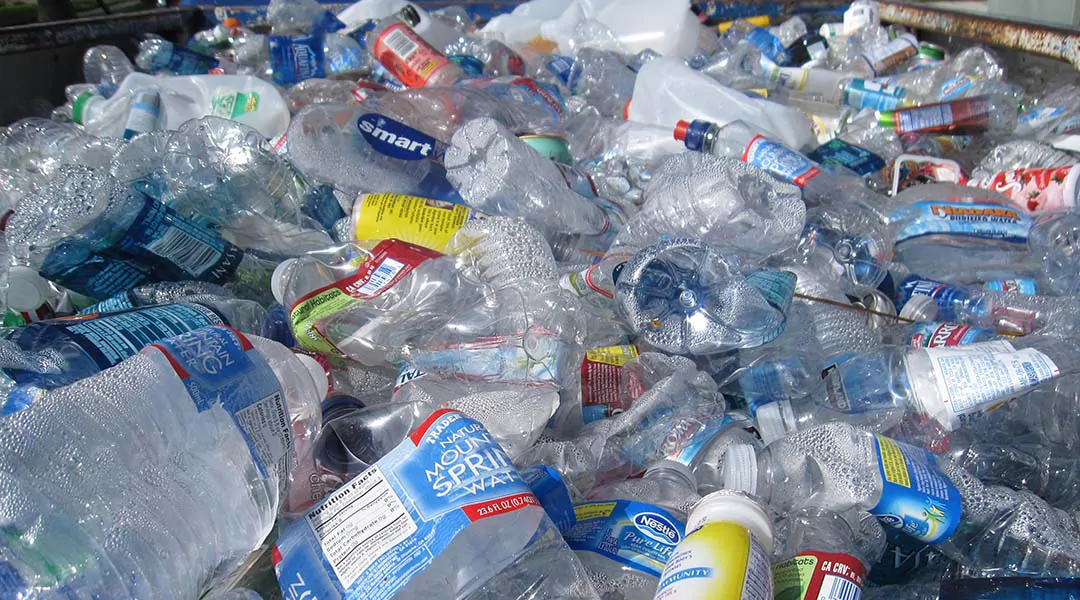

A flash heating technique breaks down plastic waste and converts it to pure hydrogen and graphene with significantly less emissions and at a low cost.
A one-step synthesis of ammonia without thermal, electrical, or solar input could help replace energy-intensive Haber Bosch.