Specially designed microrobots could help clean plastic waste from water systems.


Specially designed microrobots could help clean plastic waste from water systems.

Scientists at Sarbonne University reveal the chemical secrets behind the Romantic era’s most celebrated artists.

A new algorithm helps researchers search out new molecules for applications in medicine, keeping their synthesis quick and cost-effective.

By simplifying the production steps needed to treat surfaces with antibacterial films, scientists hope they can become more widely adopted in clinical settings and beyond.

Computer-aided drug discovery looks to neural networks that can better predict chemical properties to streamline the search for new therapeutics.

Scientists have developed a polymer-coated glass that can change from transparent to opaque when exposed to sunlight and heat.

Clean-burning synthetic fuels made from renewable ethers could replace carbon-based fuels and contribute to a cyclic carbon economy.
Bioorthogonal hydroamination of activated linear alkynes now suitable in living cells.
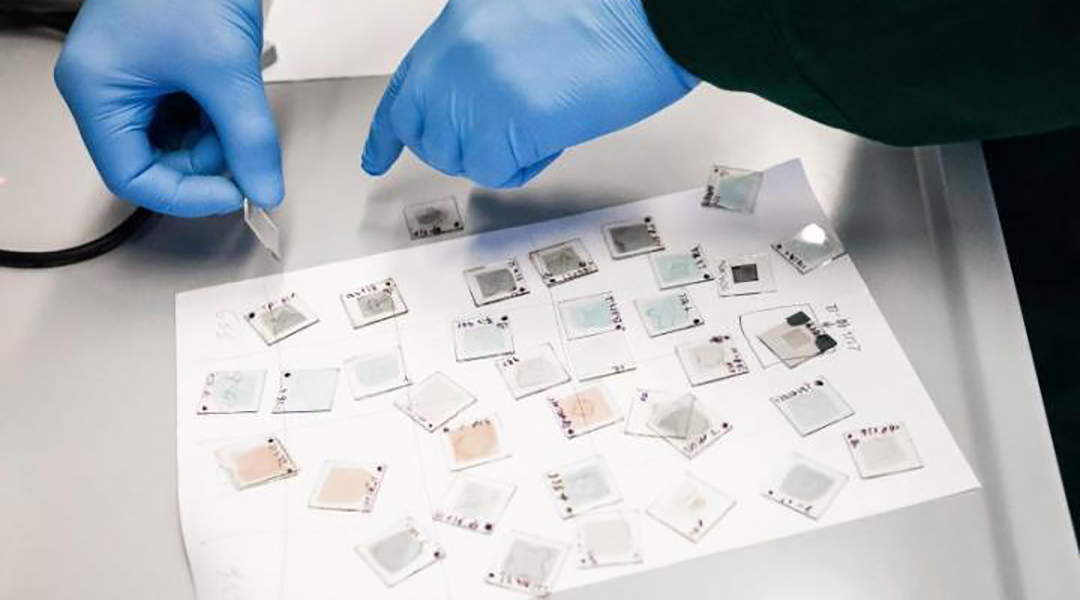

A molecule-thick material is opening doors for the advancement of flexible and recyclable organic solar cells.
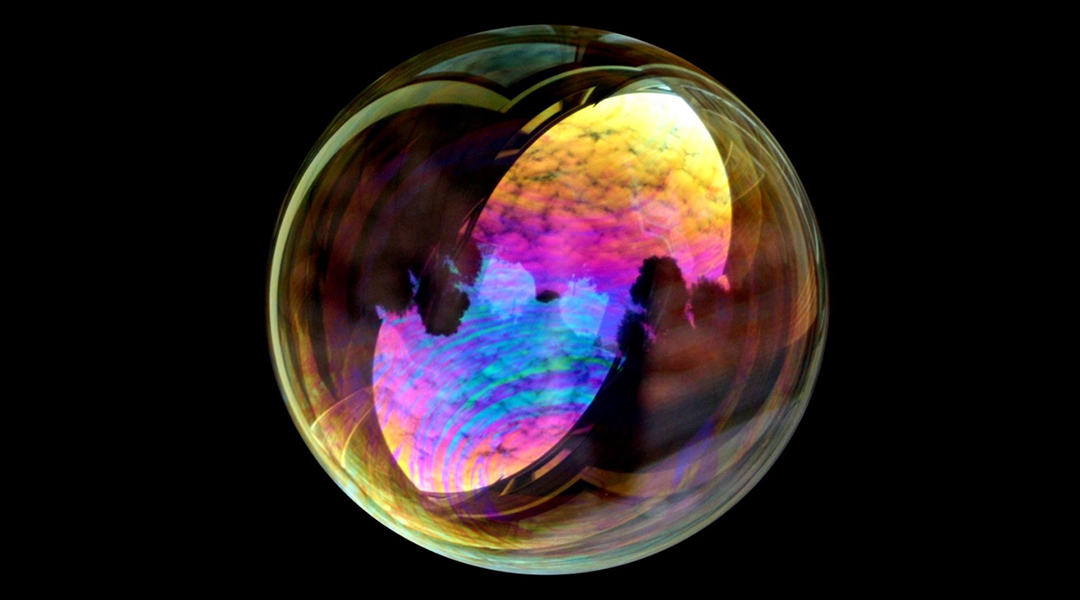

Understanding how bubbles form is vital to both producers and consumers of the world’s most popular alcoholic beverage.