RNA elements that are found in the genomes of numerous representatives within the same virus family provide new opportunities to expand the repertoire of targets for the development of antiviral therapy.
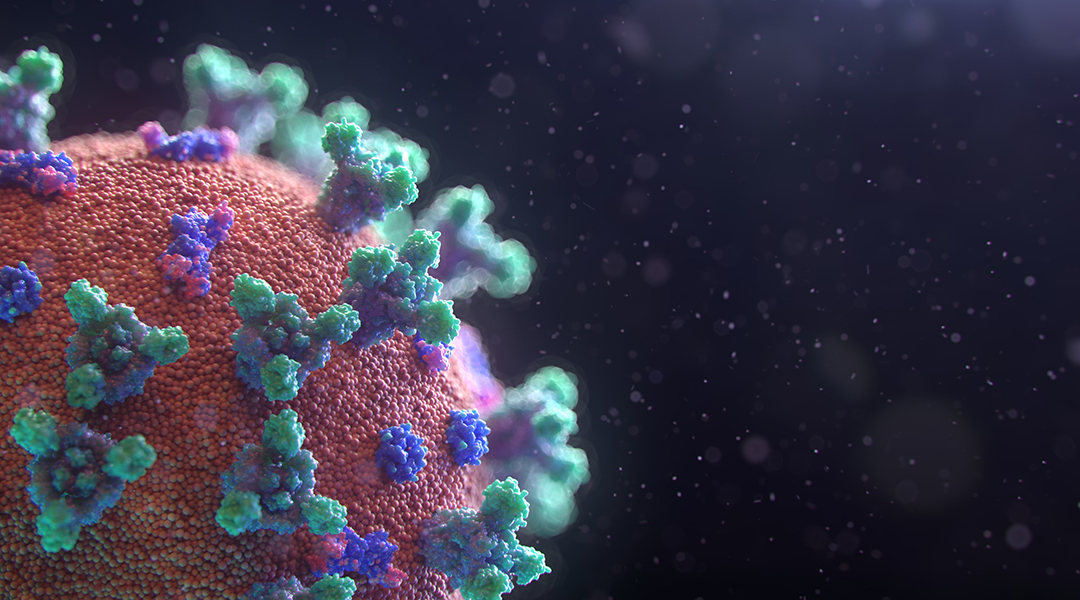

RNA elements that are found in the genomes of numerous representatives within the same virus family provide new opportunities to expand the repertoire of targets for the development of antiviral therapy.
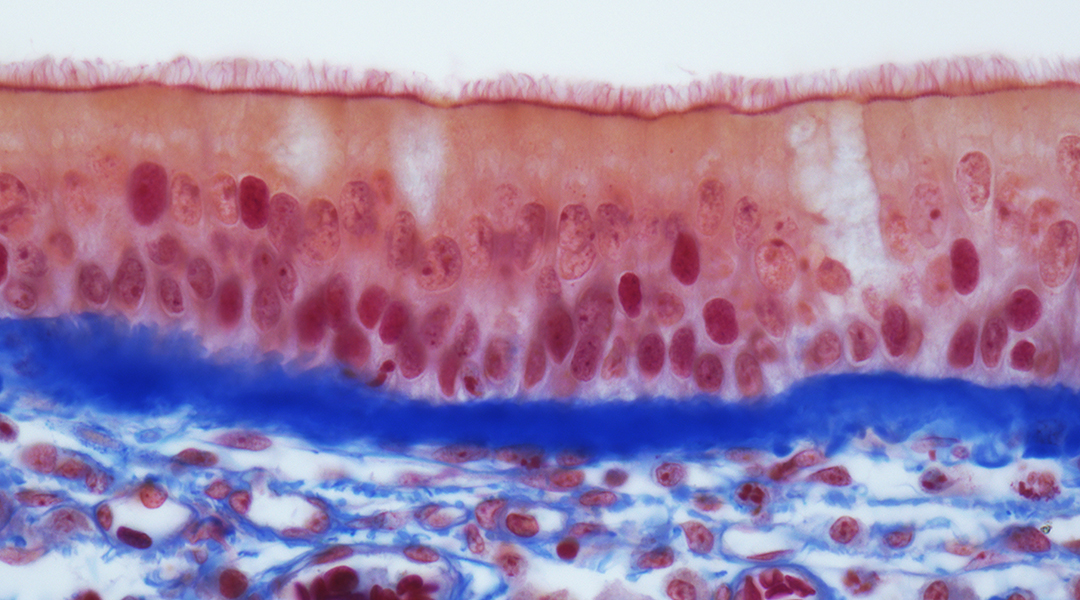
A collaborative team of German scientists identify which lung cells are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 and why infection severity varies in different demographics.
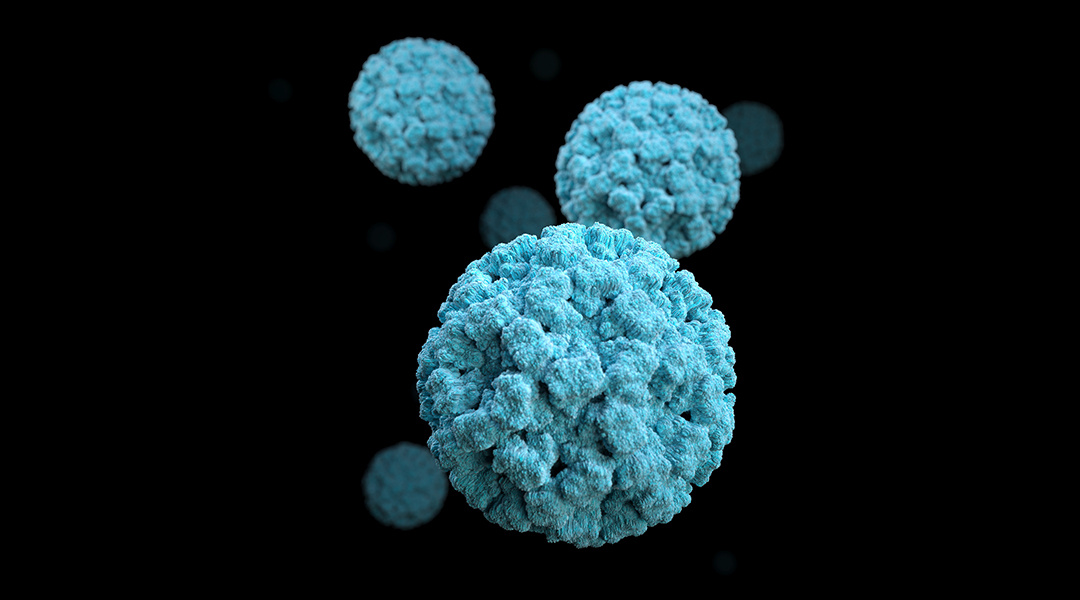
Scientists engineer a virus known to be be harmless to humans to stimulate an immune response against the coronavirus family in mice.
A new case study monitors the evolution of testing guidelines in the face of a growing global pandemic.
Potential vaccine against COVID-19 could begin human trials after FDA approval.

The convergence of four broad but easily identifiable networked conditions, or “Four Horsemen”, are hurtling civilization towards potential self-destruction triggered by the current pandemic.
SARS-CoV-2 is being added to VirScan’s library, a virus scanning tool that can identify thousands of past and present pathogens in a single drop of blood.
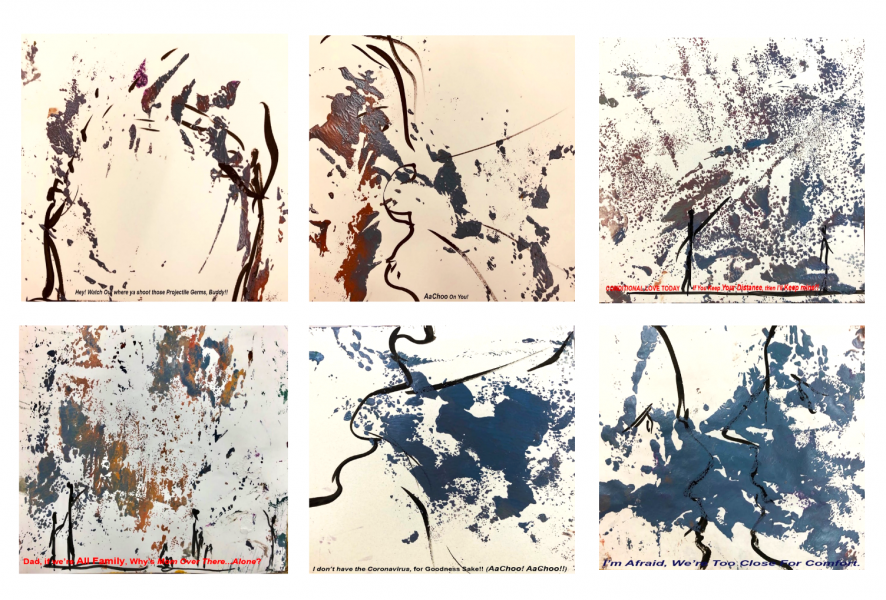
In facing a pandemic of this magnitude, coming together and seeking connection is more important than ever before.
Researchers at UT Austin hope their computer model of COVID-19 can help other scientists in developing new drugs against the virus.
Researchers provide evidence for the effectiveness of isolation and quarantine measures in minimizing the spread of COVID-19.