A study that analyzed data from nearly 15 000 patients with COVID-19 receiving four combinations of chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and antibiotics indicates the drug regimen may be doing more harm than good.


A study that analyzed data from nearly 15 000 patients with COVID-19 receiving four combinations of chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and antibiotics indicates the drug regimen may be doing more harm than good.
Scientists identify a cocktail of antibodies from a recovered COVID-19 patient’s blood sample that helped neutralize the SARS-CoV-2 virus in mice.

A new study explores how SARS-CoV-2 damages cells in the nasal cavity, altering infected individuals’ sense of smell.
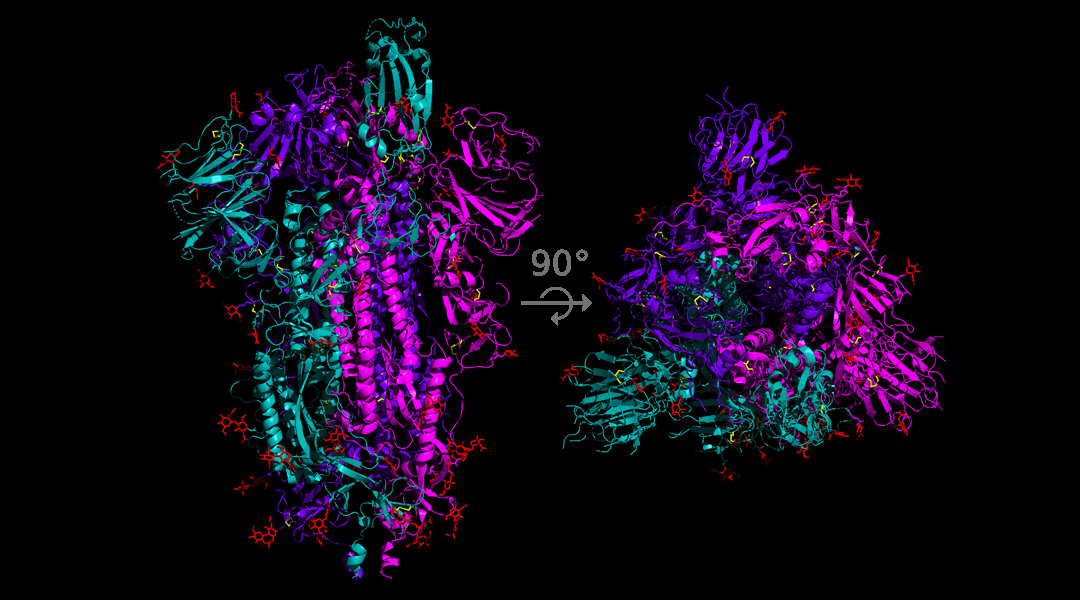
Understanding changes to the spike protein’s structure is critical to the development of an effective vaccine.

The interaction between the innate and the adaptive immune responses to COVID-19 may be impacting disease progression, and the answer might be to suppress them.
Researchers publish detailed protocol on their new antibody test to be used by researchers and clinicians around the world.

The two countries, in separate studies, begin human trials of potential vaccines against COVID-19.

A new AI system can identify optimal combinations of drugs and dosages in a matter of days to help halt viral pandemics before they reach global scales.
Remdesivir, an anti-viral agent known to be effective against MERS, is already in human trials as researchers search for a treatment for COVID-19.

How should doctors navigate murky ethical territory throughout the COVID-19 pandemic?