A simple approach to create high performance thermoelectric materials, which would allow one to turn their body heat into electricity.
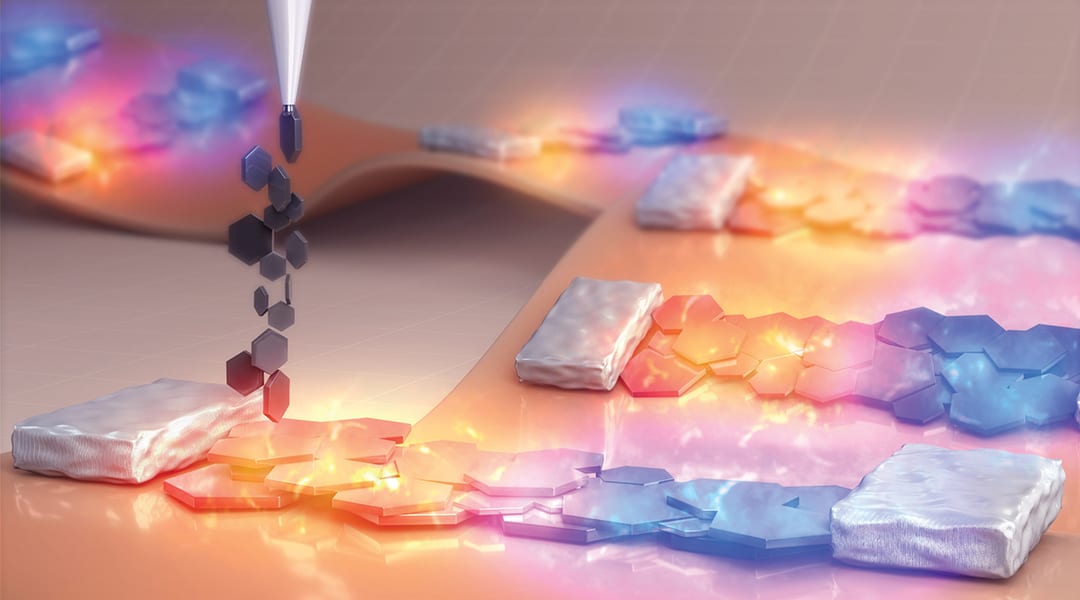

A simple approach to create high performance thermoelectric materials, which would allow one to turn their body heat into electricity.

A low temperature water-splitting protocol uses microwave power in lieu of concentrated solar energy.

Researchers have developed an innovative method to make advanced coating materials for “smart” sub-ambient radiative cooling in large-scale building applications.
While superconductors are not considered an energy material, the energy savings arising from resistance-free transmission and distribution of electricity are potentially massive when considered on a global scale.

Researchers combine waste vegetable oil and sulfur to create an eco-friendly, sturdy and lightweight cement substitute that can be remelted as often as desired.
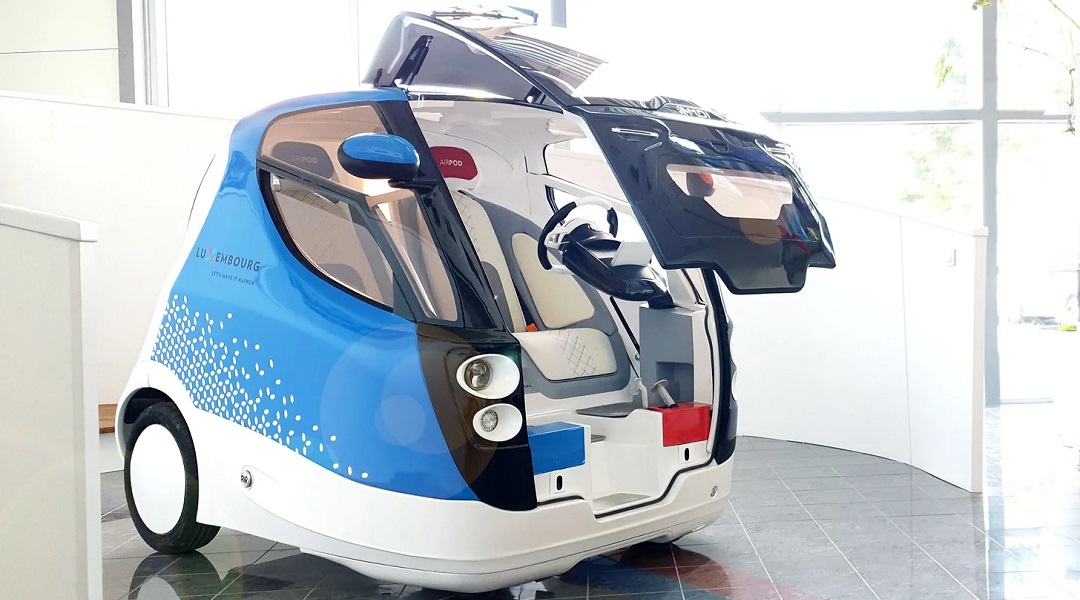

Researchers have increased the efficiency of compressed air cars with the aid of phase change materials for heat recovery, making them a viable carbon-free alternative for future passenger cars.

A rechargeable aluminum-nitrogen battery serves the dual purpose of not only storing and retrieving energy, but also being able to fix its nitrogen stream as ammonia.

A new titanium nitride sulfur composite reduces the notorious shuttle effect and improves the overall performance of lithium-sulfur batteries.
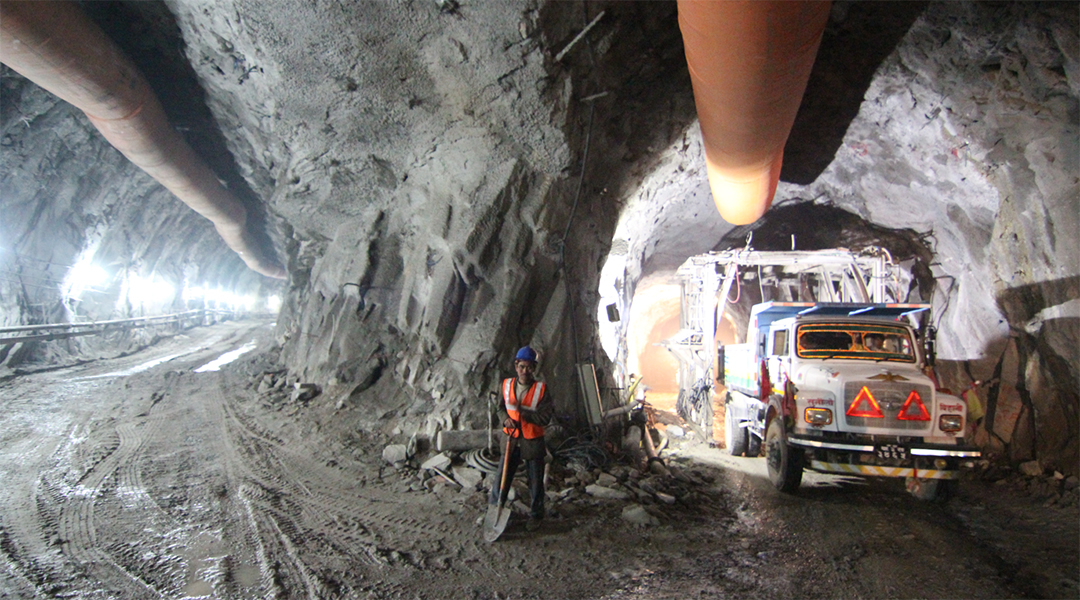

As hydropower projects are built across the Himalayan region, recognizing the temporal politics inherent to hydropower development will become increasingly critical.
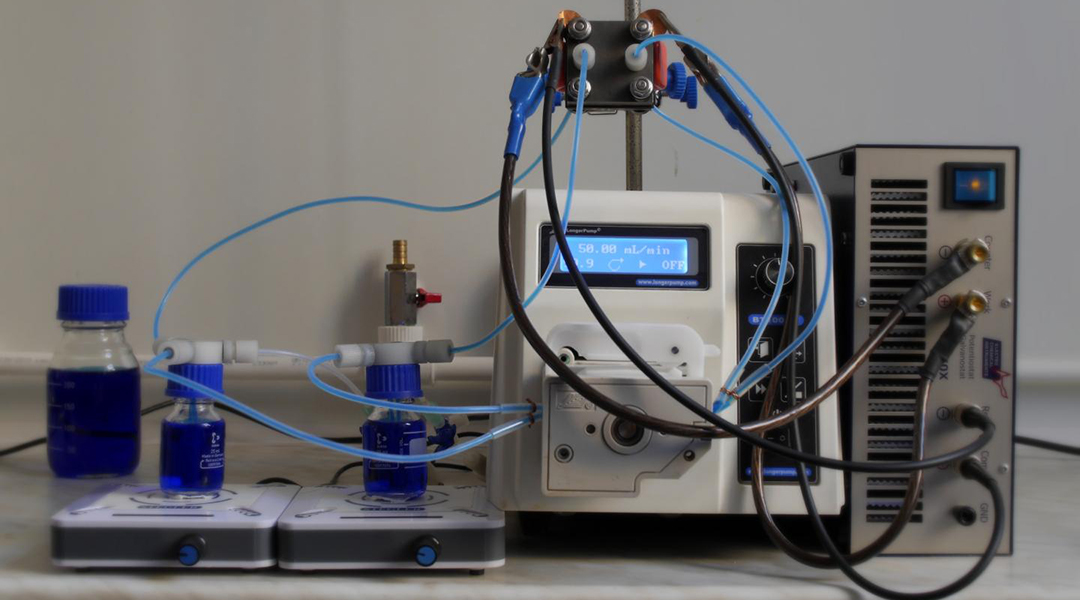
A new design for vanadium redox flow batteries could help fundamental research and accelerate commercialization of this energy storage technology.