Members of the Max Planck Research Network in Synthetic Biology put together a special issue on synthetic cells for Advanced Biosystems.

Members of the Max Planck Research Network in Synthetic Biology put together a special issue on synthetic cells for Advanced Biosystems.

Artificial biomotors for in vivo therapeutic applications.

Bacteria are able to build biofilm bridges to connect with adjacent bacterial colonies.
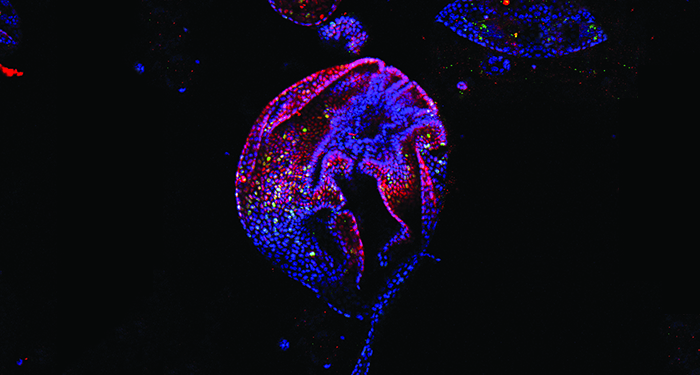
Intact whole-mount immunostaining of organoids after growth for 14 days.
Arsenic trioxide is a promising novel latency-reversing agent to achieve the goal of eradicating HIV-1.
Upon viral infection, a tug of war is triggered between host cells and viruses to gain control of vital cellular functions.

Hundreds of RNA‐binding proteins and their associated RNAs have been revealed, which enables the large‐scale prediction of RNA–protein interactions using machine learning methods.
This review focuses on classical and state‐of‐the‐art methods for the identification and quantification of RNA molecules in a variety of subcellular locations.

Fruit flies are ideal for modeling complex genotypes and phenotypes and have significant potential in drug screening.
Photodynamic therapy combines light and a photosensitizer to generate reactive oxygen species to induce cellular damage.