A transparent and breathable microfluidic contact lens that could help to diagnose and treat eye disease is developed.


A transparent and breathable microfluidic contact lens that could help to diagnose and treat eye disease is developed.

A wearable soft microfluidic device with sequentially filling reservoirs can collect, store, and analyze sweat in situ from almost any part of the body.
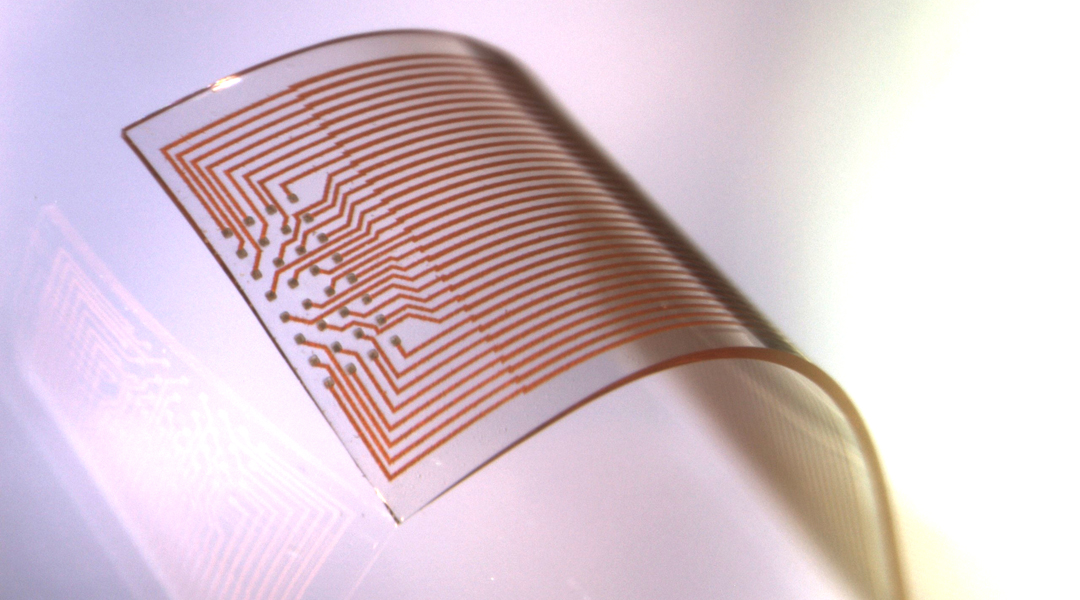
High-density stretchable electrode grids based on a material that can resolve high spatiotemporal neural signals from the surface of the cortex in freely moving rats with stable recording quality during 3 months of implantation.

Graphene sensors with high-resolution features are produced on flexible tapes for wearable electronics via a simplified drop-cast-and-transfer process.

A team of North American researchers demonstrated a label-free and more direct way to observe and quantify microvascular and metabolic healing mechanisms, and the biological response to a topical treatment, utilizing a multimodal microscope equipped with OCT and FLIM.

Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences has published this year’s installment of the annual reviews series The Year in Diabetes and Obesity, edited by Rexford Ahima (The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine).
Multipartite designer nanoparticles are formed from the phage lambda decoration protein and can be used in a variety of theranostic applications.

A new international journal covering innovations in the science & engineering that underlie medical devices and medical sensors now accepting submissions.
Latest Advanced Healthcare Materials covers.
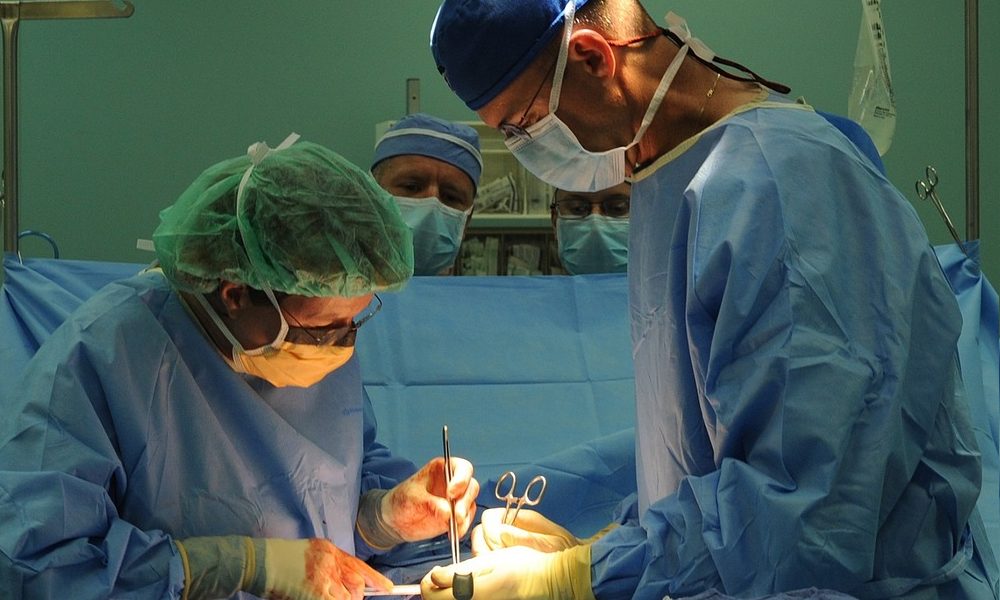
Research into how to better visualize tumor cells during surgery is underway, with a hope of limiting the occurrence of positive surgical margins.