Using Raman spectroscopy as a means of detection, researchers have built an extensive database of signatures to detect any cancer.


Using Raman spectroscopy as a means of detection, researchers have built an extensive database of signatures to detect any cancer.

Researchers turn to nanotechnology to boost the detection of pathogens, including SARS-CoV-2.
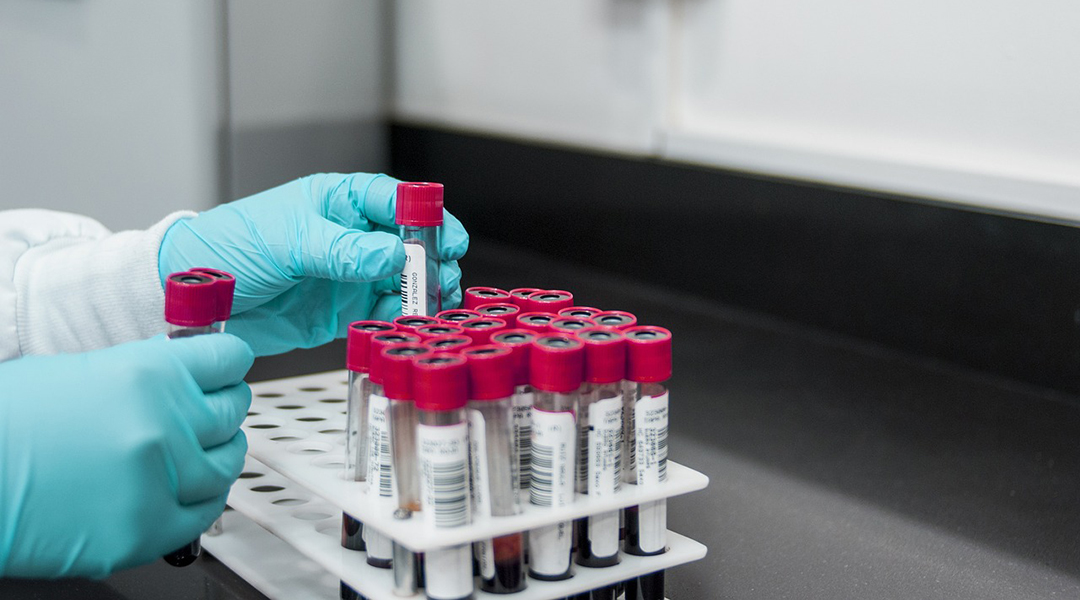
A sensitive blood test has been developed to detect a protein biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease known as brain-derived tau.
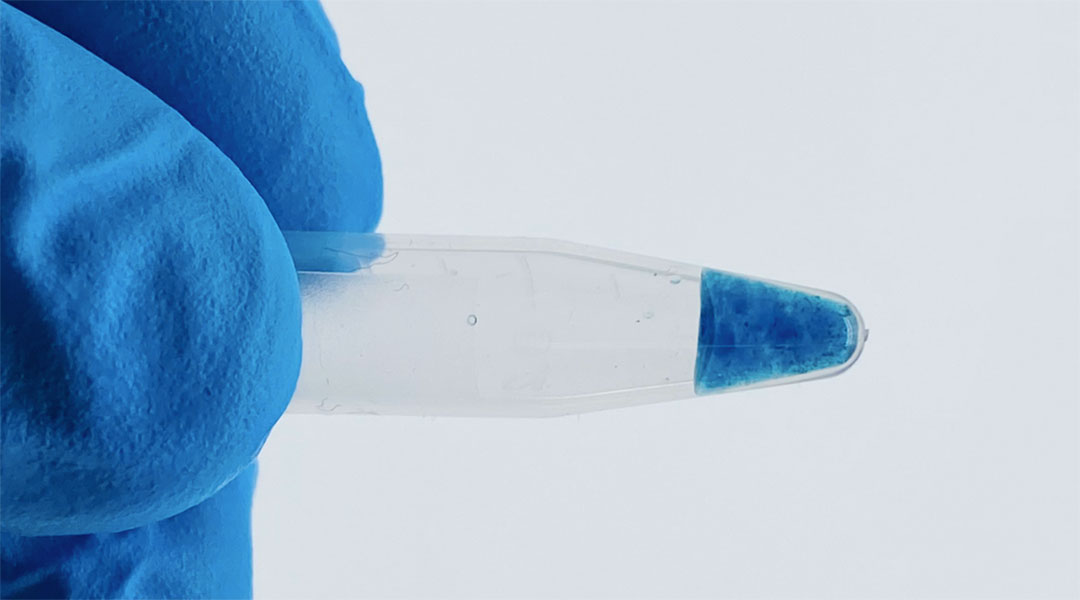
A new hydrogel platform helps monitor chemotherapies in the body in real-time, allowing their side effects and potency to be better understood.
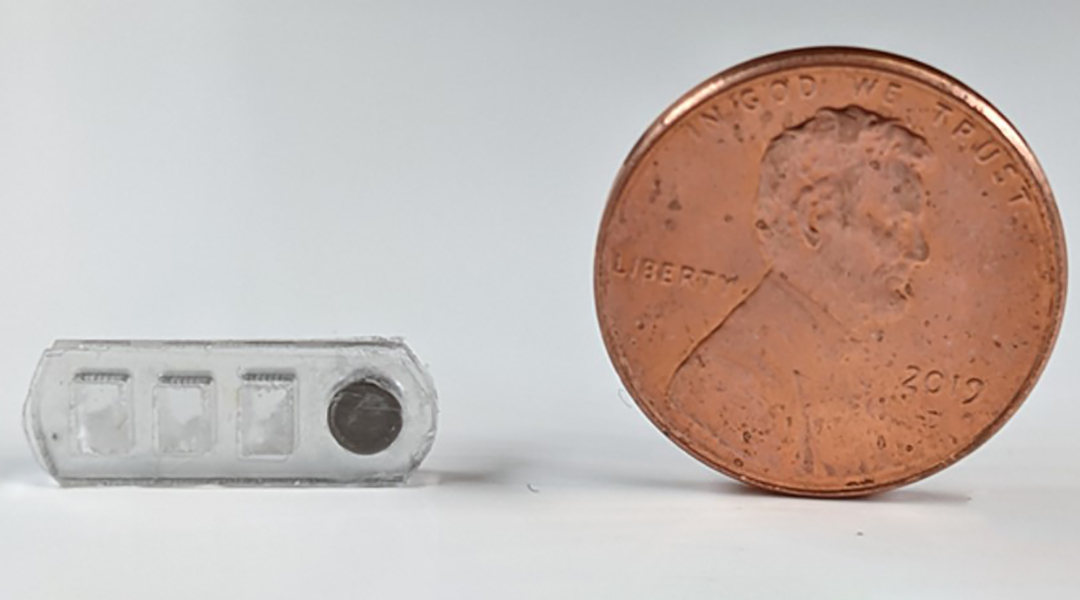
A robotic pill capable of collecting biomarkers, including proteins and bacteria, from the gut provides an easy-to-use disease screening tool.
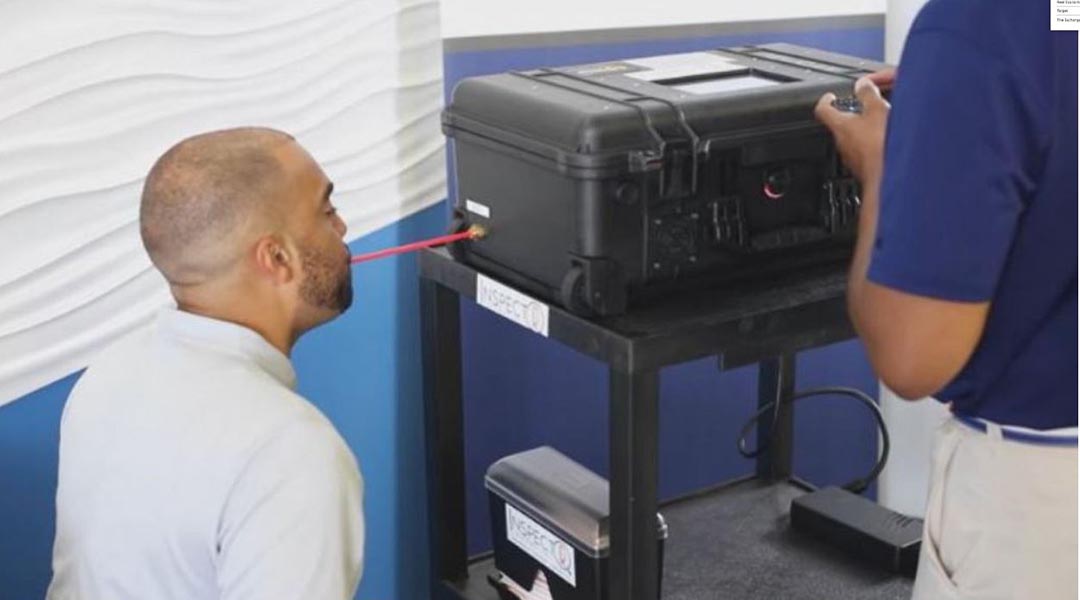

Using a chemical signature in the breath, a newly approved COVID-19 breathalyzer could provide an easy and rapid means of testing.
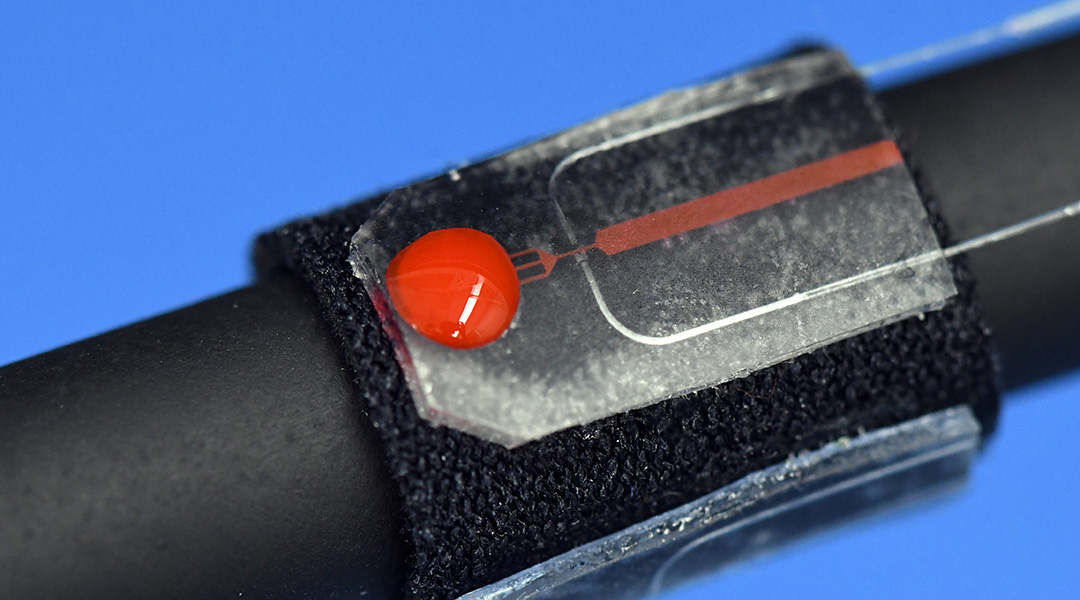
A new blood sensor utilizes miniaturized channels to monitor for accidental bleeding during colonoscopies.
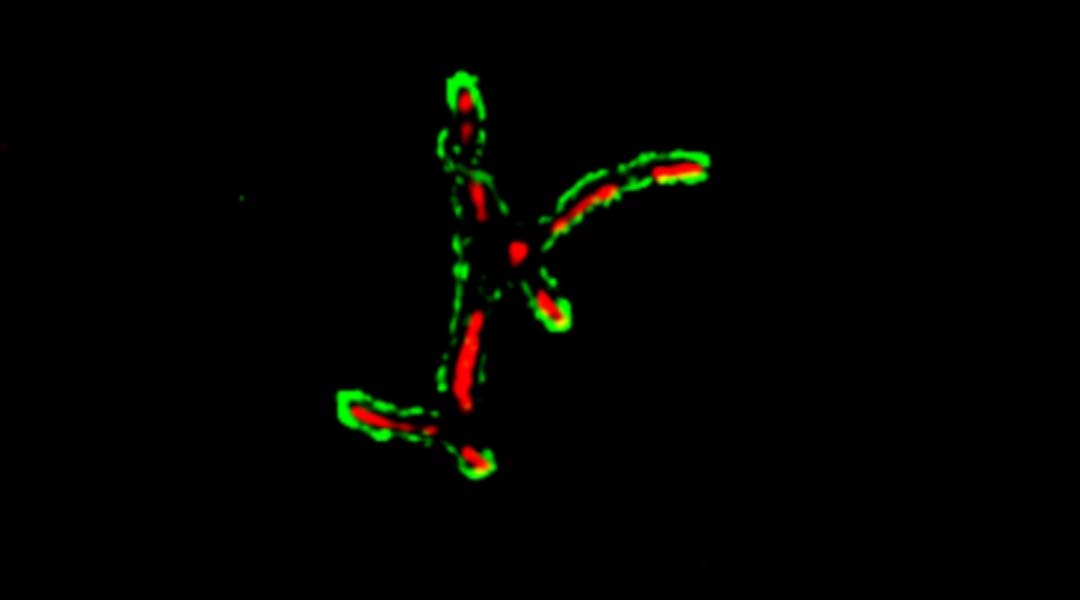
A new fluorescent probe for detecting tuberculosis can now identify disease-causing bacteria in extra-pulmonary tissue for better diagnosis.
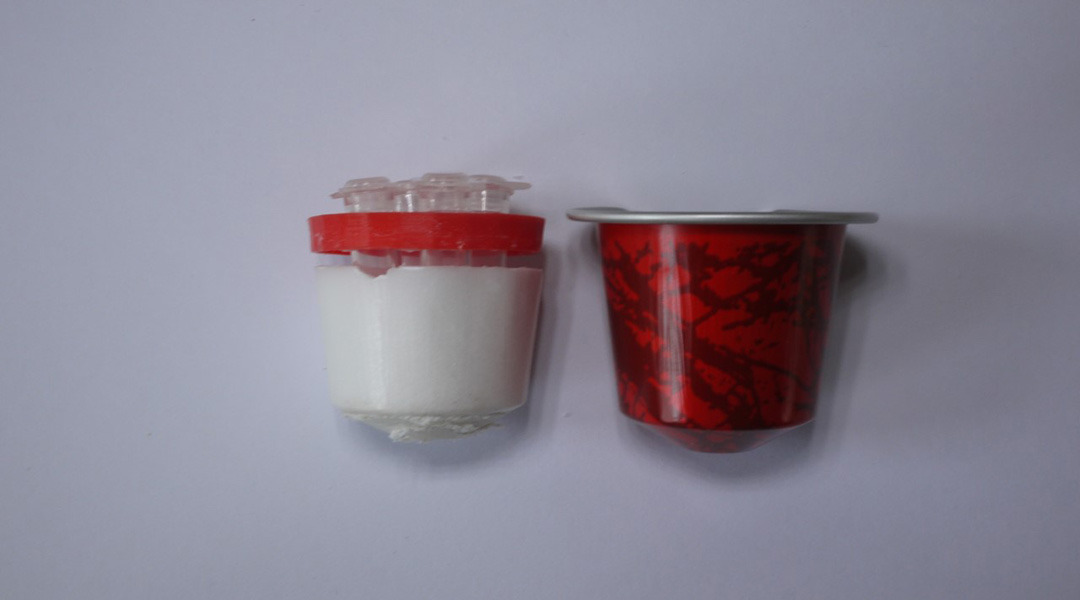

Using materials found around the house, researchers stuck at home created an accurate test to detect COVID-19.
Tin mono-sulfide nanosheets prove to be effective and sensitive soft X-ray detectors with potential to monitor biological systems in real time.