Ammps, a new cost-effective, sensitive and non-invasive clinical assay, for the detection and monitoring of bladder cancer.


Ammps, a new cost-effective, sensitive and non-invasive clinical assay, for the detection and monitoring of bladder cancer.
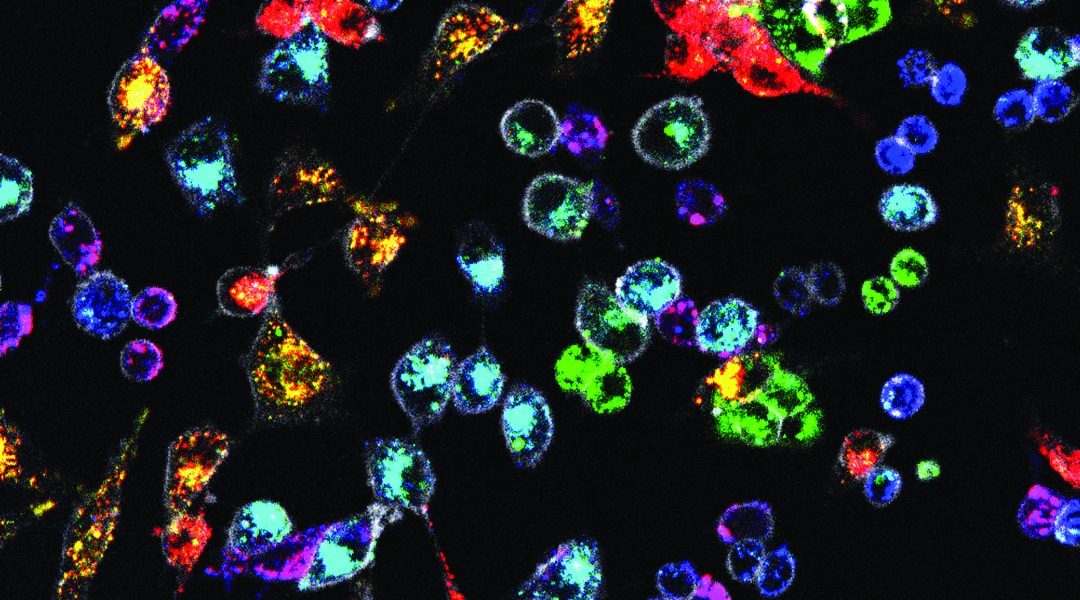
A method that allows the long-term labeling of different cell populations in tens of different colors using fluorescent nanoparticles.
A flexible self-powered ultrasensitive pulse sensor (SUPS) based on a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) is presented.
Two new, Special Sections dedicated to imaging technologies.

This week’s Advanced Healthcare Materials cover manuscripts.
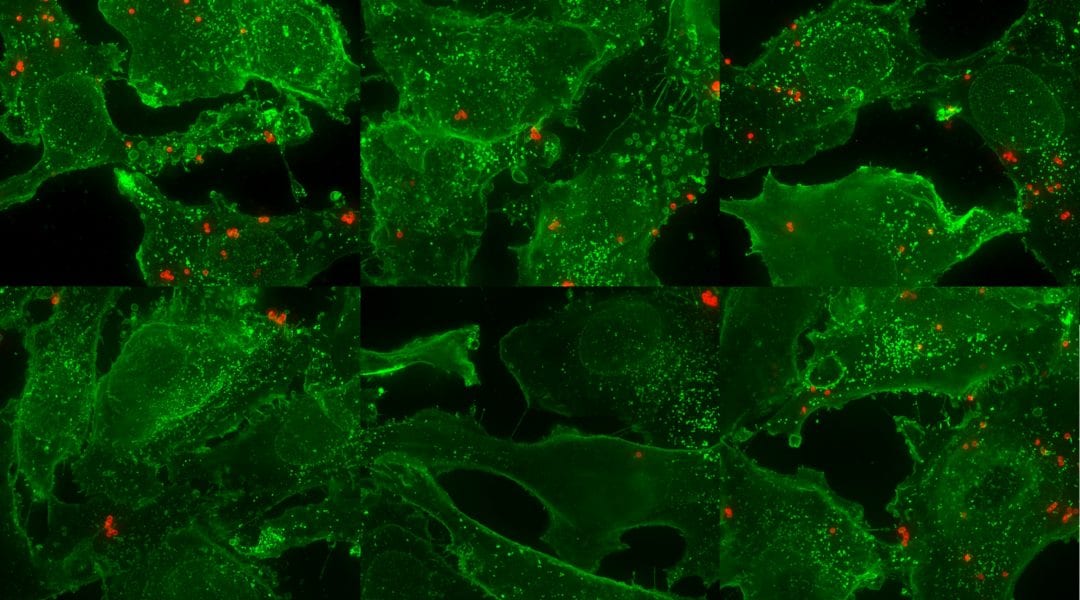
Parameters that affect the biological performance of particles and highlight strategies for improved targeting ability of particles.
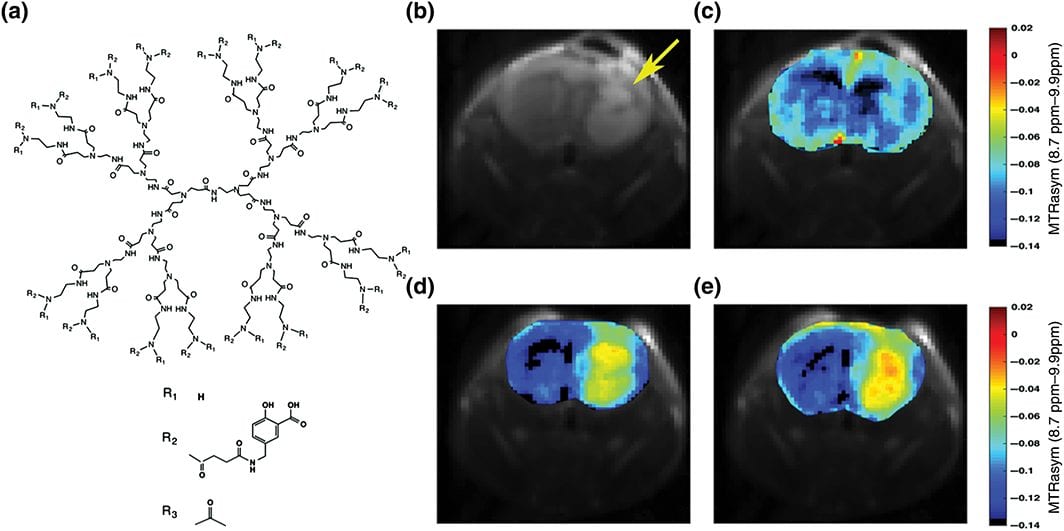
A vast number of metallic and non-metallic labels can be conjugated to the dendrimer surface in order to transform them into MRI agents. Due to their multiple branches and high payload they can be readily detected, for example, following local delivery to a brain tumor.

A team of German scientists used fast spontaneous Raman and Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) combined imaging to study the distribution and composition of lipids related to cardiovascular disease.
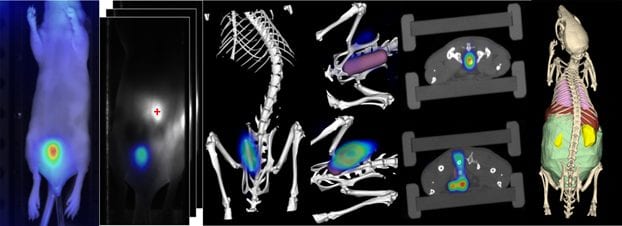
German scientists recently developed an improved FMT reconstruction for the imaging of deep tissue regions which could be beneficial in imaging colon cancer and inflammatory bowel disease.
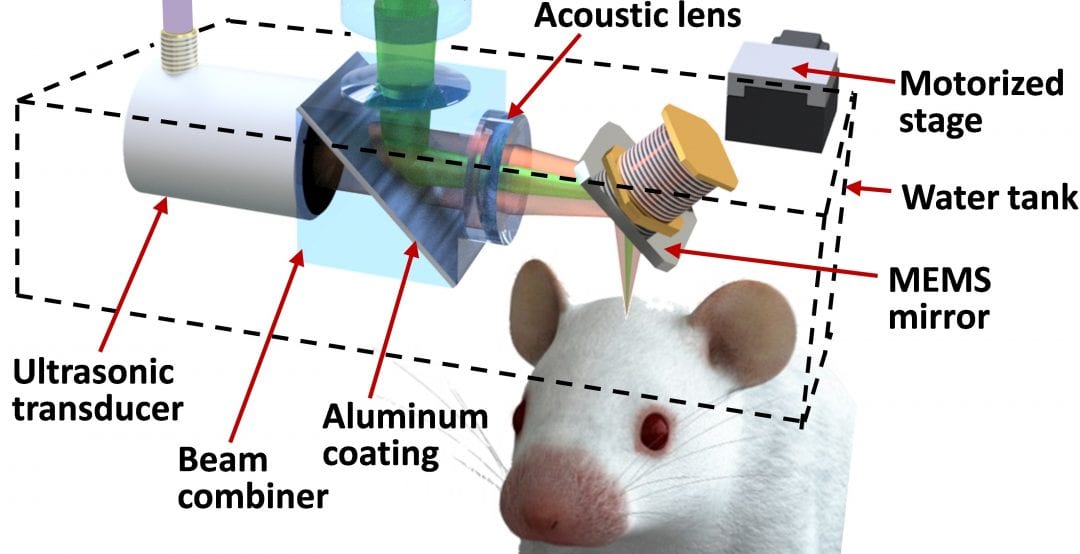
American neuro-scientists recently demonstrated getting a small step closer to creating a better understanding of so-called mini-strokes, which are related to cognitive decline and dementia, using high-speed optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy.