A new tool can diagnose sepsis in less than fifteen minutes, even with a very low concentration of biomarkers.
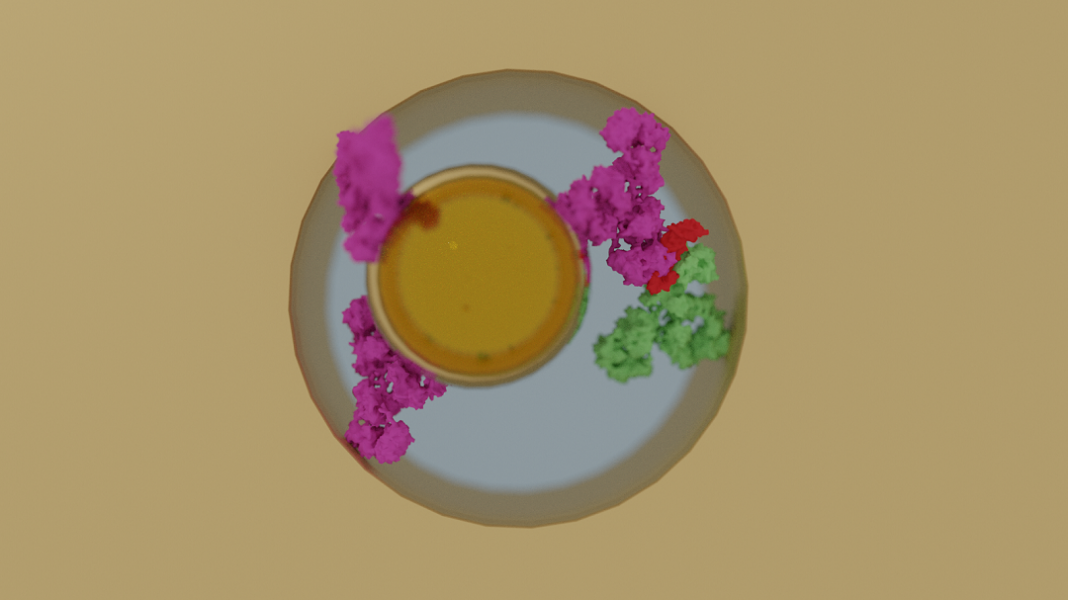


A new tool can diagnose sepsis in less than fifteen minutes, even with a very low concentration of biomarkers.
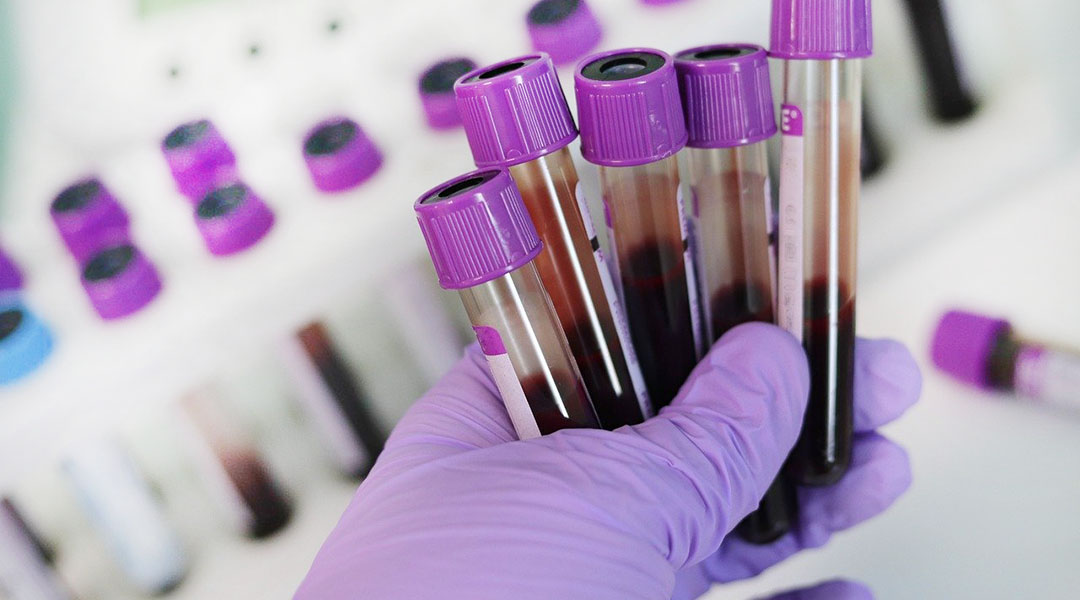
Researchers publish detailed protocol on their new antibody test to be used by researchers and clinicians around the world.
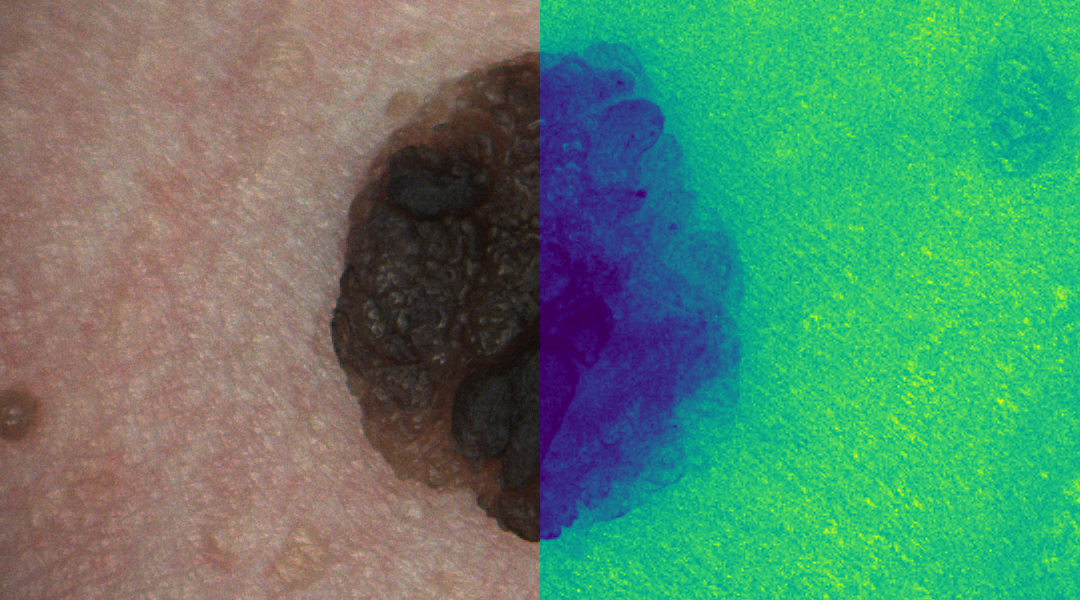
Hyperspectral imaging has the potential to better detect skin cancer to improve the survival rates of patients.
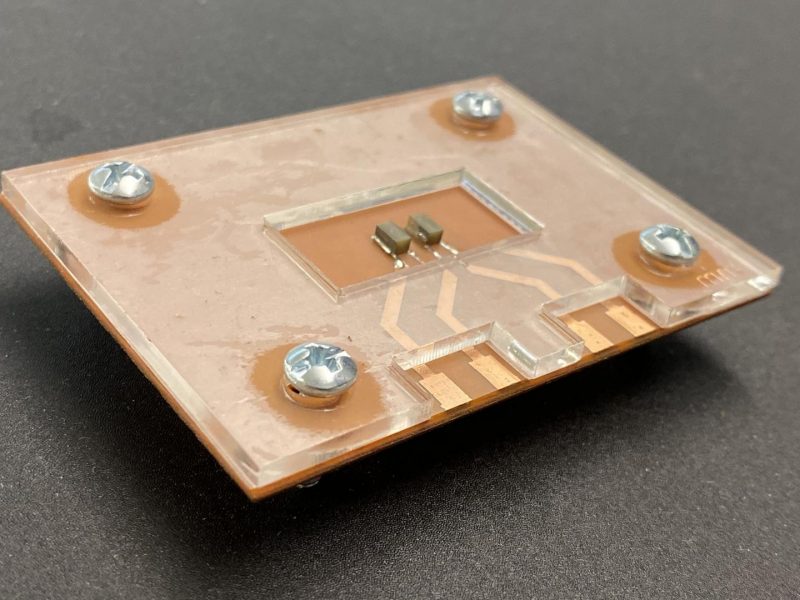
A device uses sound waves to detect the stiffness of an extracellular matrix, a structural network that contains cells, which researchers find can indicate the spread of disease.
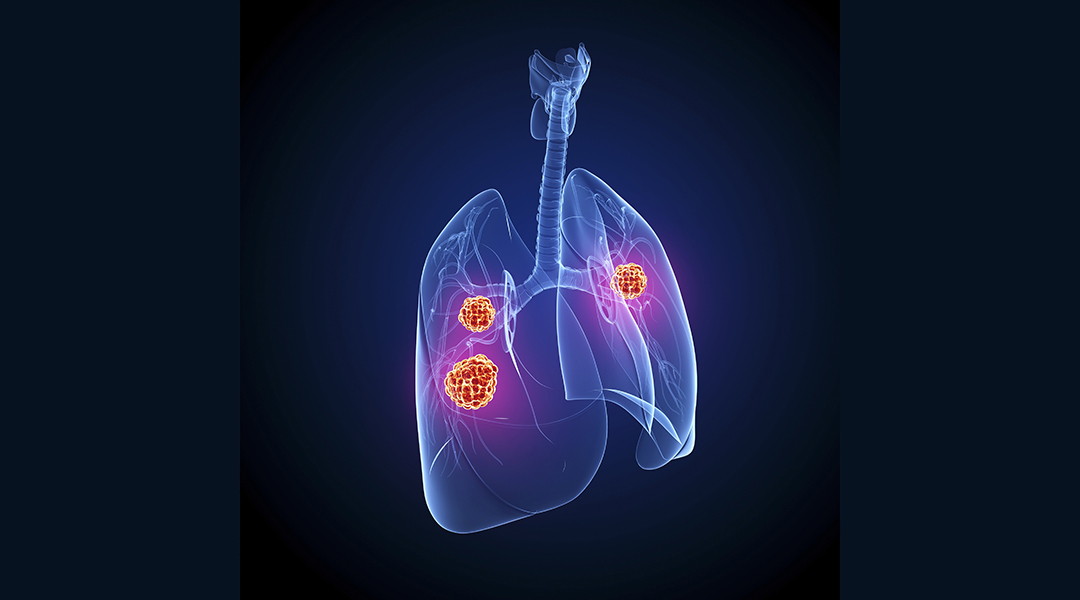
A new class of biocompatible protein-based nanoparticles that have outstanding near-infrared emission for deep tissue imaging.
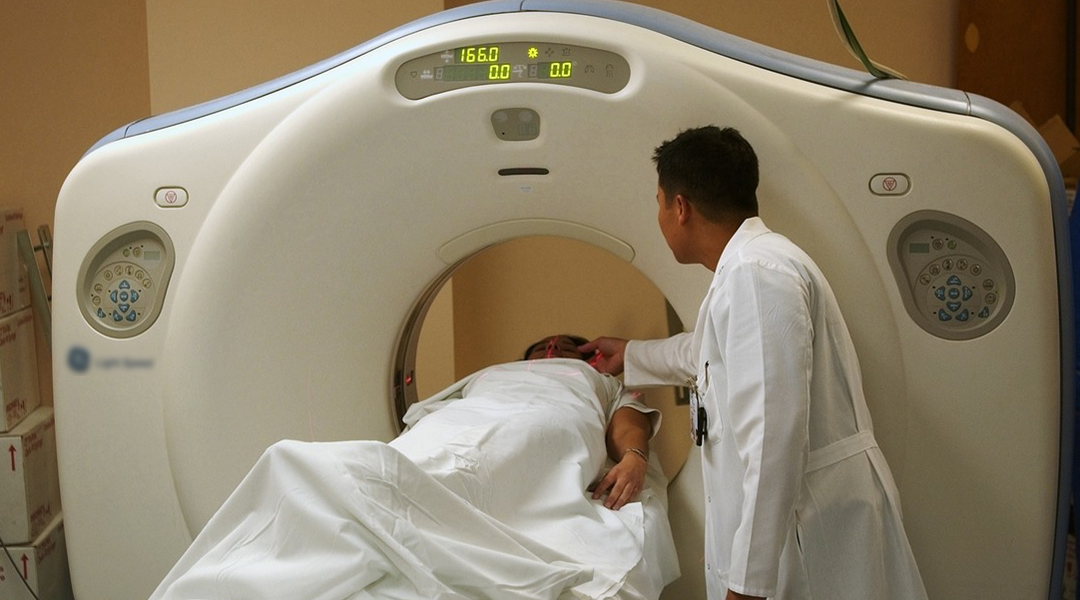
Doctors in Wuhan show that a chest CT is a more sensitive test for COVID 19 than the current standard.
Cardiac models are becoming increasingly accurate as predictive power improves.
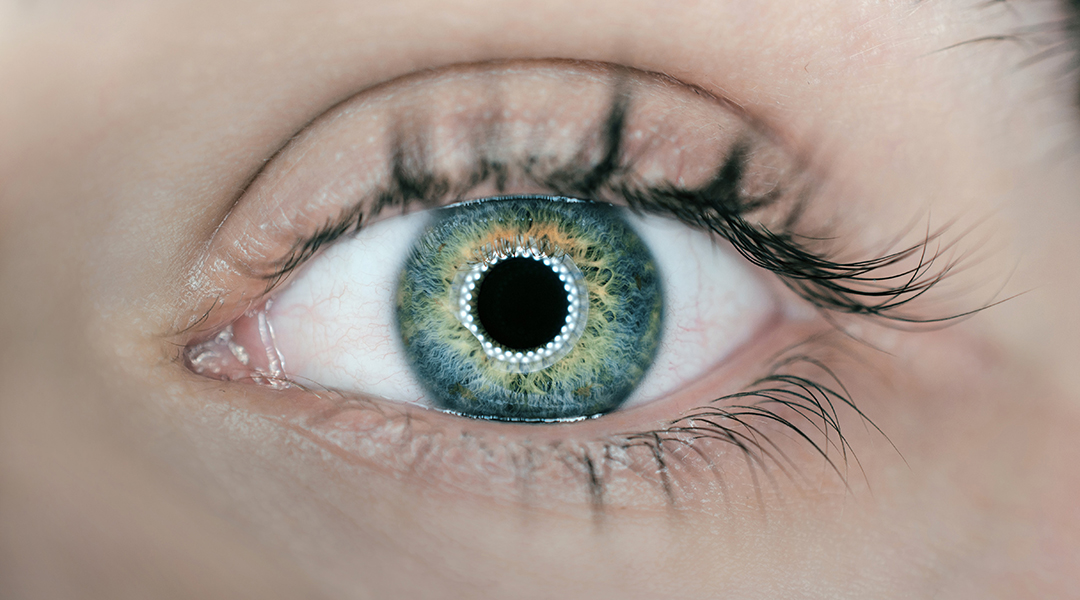

Smart contact lenses could revolutionize the way in which we monitor brain activity and diagnose neurological diseases.

How recent advancements in the developing of photoacoustic contrast agents are creating a better imaging technology.
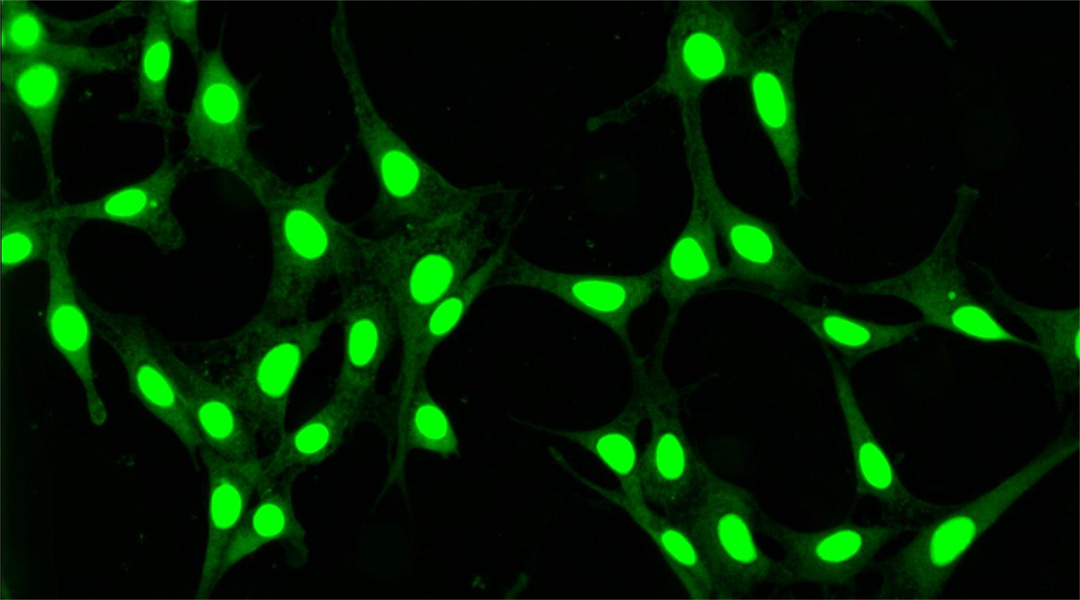
Fluorescent carbon dots could change the way in which we visualize cells.