Understanding the interactions, permeability, and partitioning of drug delivery systems in ocular tissues can improve the drug retention time and bioavailability.


Understanding the interactions, permeability, and partitioning of drug delivery systems in ocular tissues can improve the drug retention time and bioavailability.

A team of researchers demonstrated the capability of RSOM for detailed, cross‐sectional visualization of microvascular changes in the skin in the volar and dorsal aspects of the human forearm in response to local hyperthermia.
Physical, chemical, and synthetic virology work together to reprogram viruses as controllable nanodevices.
All organisms are subject to large amounts of genetic and environmental variation and have evolved mechanisms that allow them to function well in spite of these challenges. This property is generally referred to as robustness.
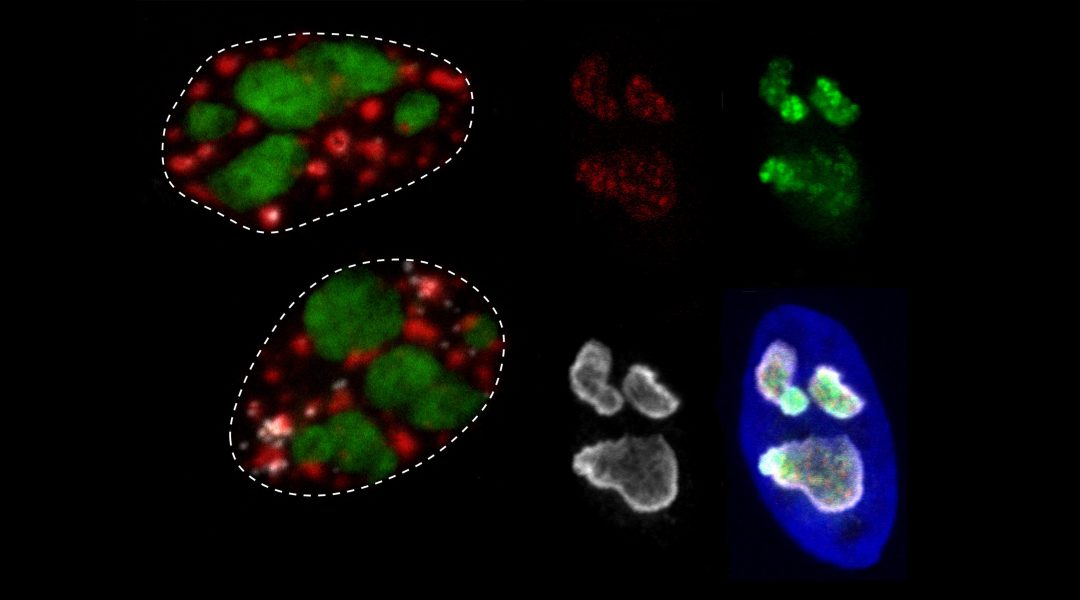
An analysis of nuclear body protein disorder that suggests MLO proteomes are significantly more disordered than structured cellular features.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is well recognized as a primary cause for lower respiratory infection or bronchiolitis in infancy, but how many events coded as bronchiolitis are actually attributable to RSV?
![Overcoming Organ Transplant Rejection with Hydrogels [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/adma201805018_ASN_image.jpg)
Researchers devise an effective method to reduce transplant rejection following surgery.

Ali Khademhosseini and his co-workers take a detailed look how engineering approaches can contribute to the field of precision medicine.

Joanna Aizenberg talks about the people who inspire her, her advice to early-career researchers, and her hopes for the future of scientific research.
Single stranded RNAs with a free 5′ monophosphate end are susceptible to rapid degradation. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are stabilized by hairpin structures and by “hiding” their 5′ ends within complex protein structures.