Clumping proteins act as vaccine adjuvants, activating immune signalling pathways triggered by cell stress.

Clumping proteins act as vaccine adjuvants, activating immune signalling pathways triggered by cell stress.
With more research, there is a potential for vaccines to have both adaptive and trained immunity to fight different diseases.
A new in situ, personalized cancer vaccine captures molecules from growing tumors to activate the body’s immune cells against them.
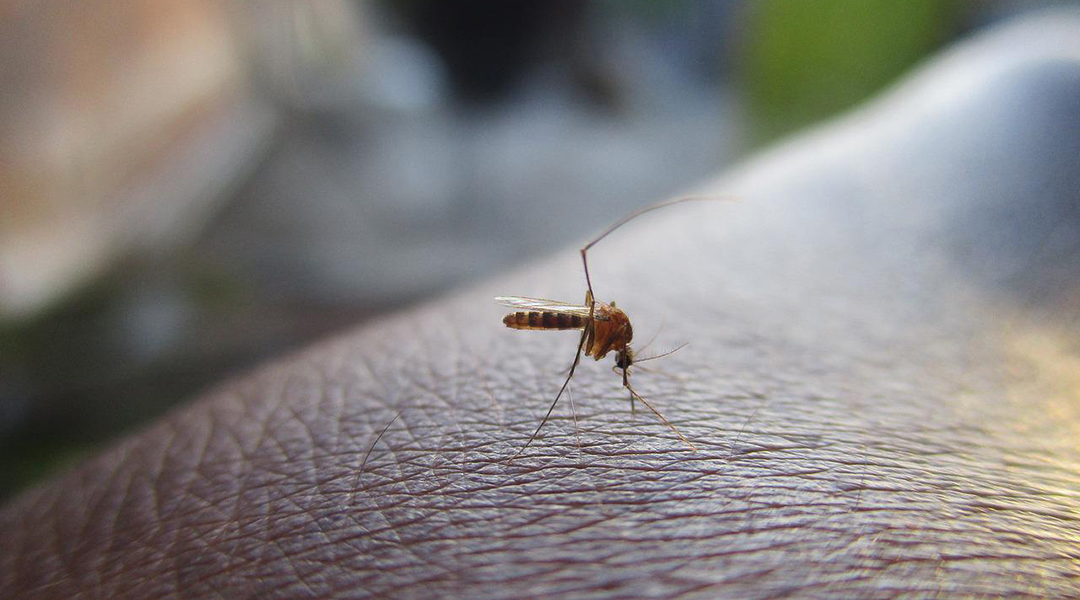

Dengue and Zika take control of a protein responsible for body odor, but a simple treatment helps reverse the process.
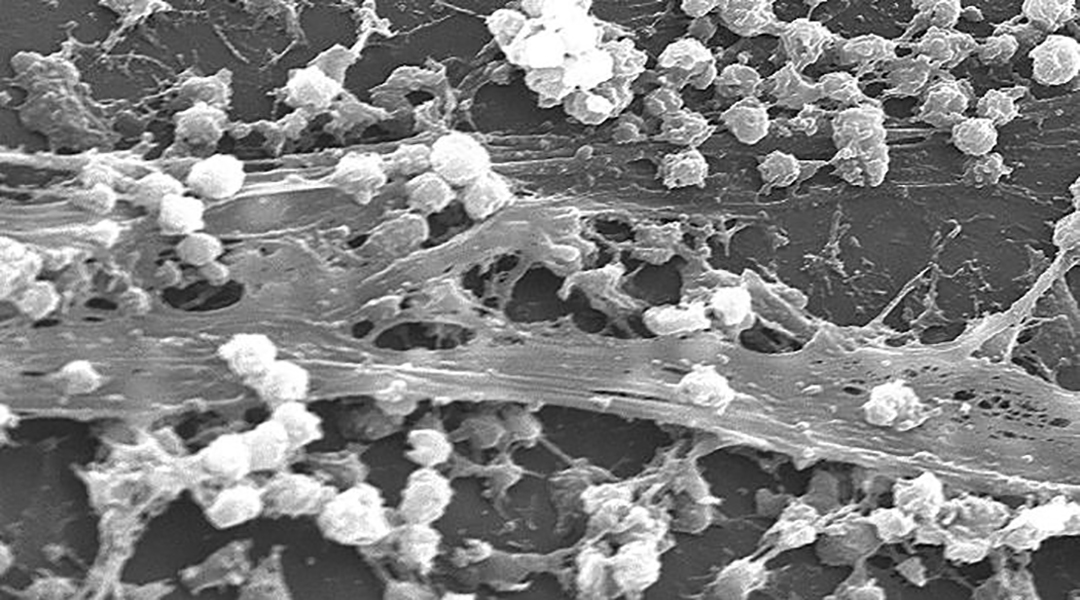
A new antibacterial surface treatment could help improve the safety of medical devices by minimizing the risk of infection during their use.
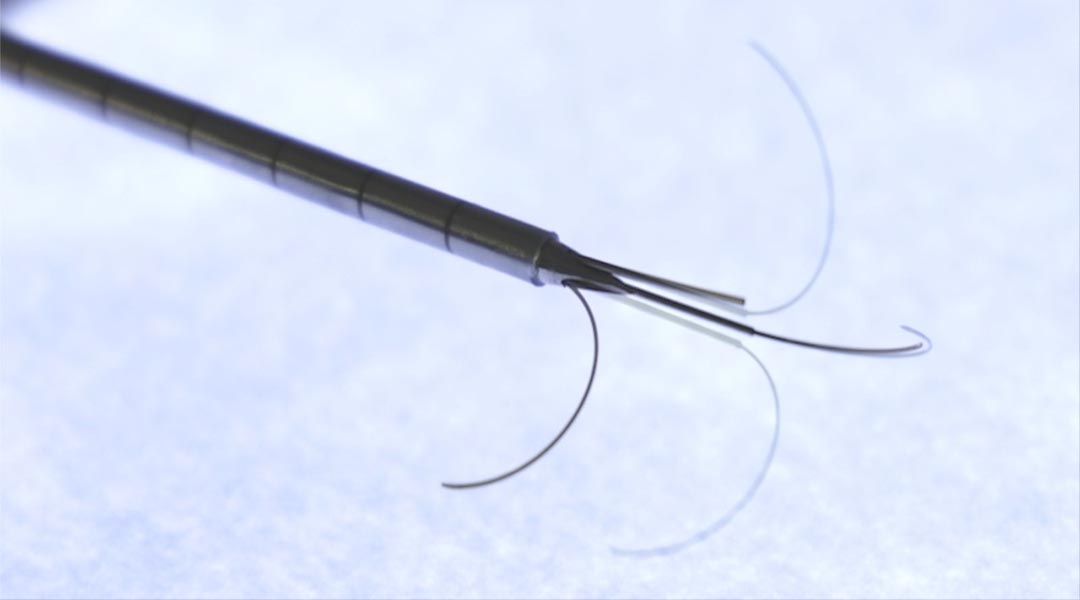
A new proof-of-concept cancer therapy safely and accurately destroys cancerous cells with precisely delivered heat.
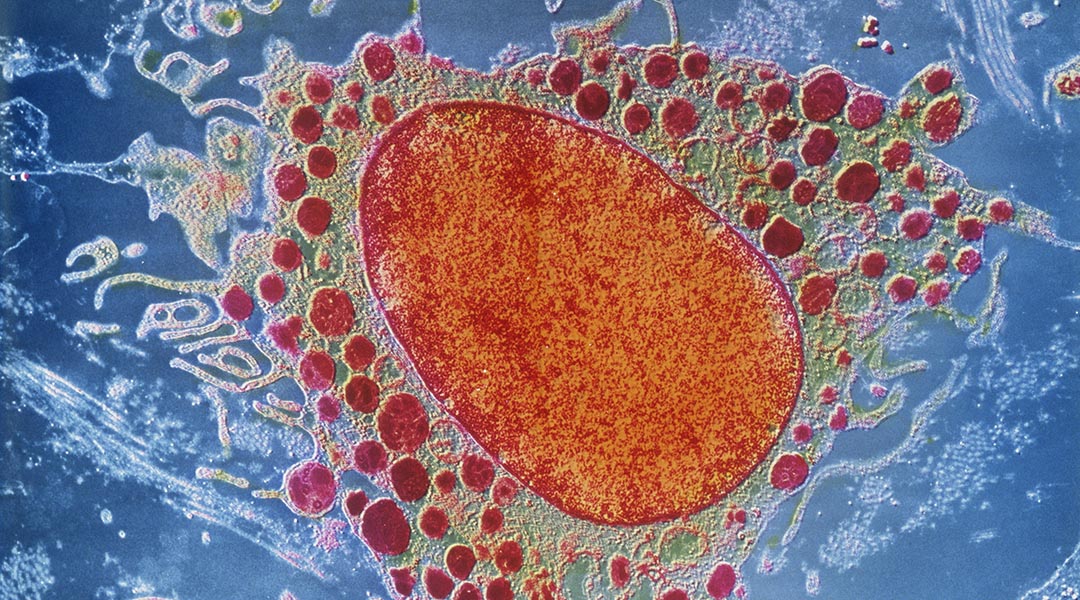
An extensive library of over one million cells could pave the way for new and repurposed treatments for a number of autoimmune diseases.
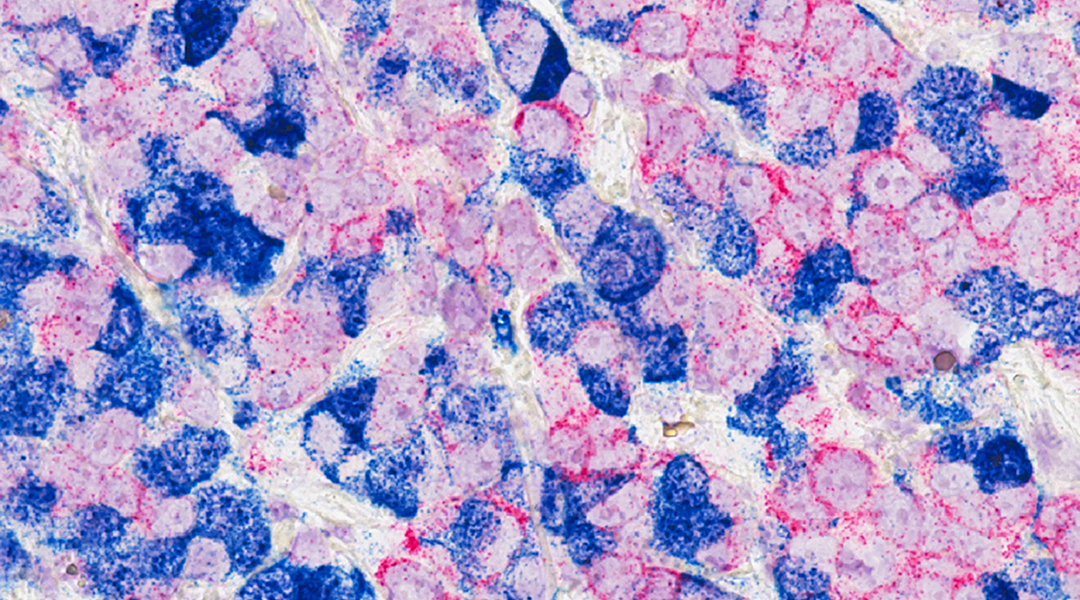
Triple-negative breast cancer has poor survival and few therapeutic options — but with a new approach, things could change.
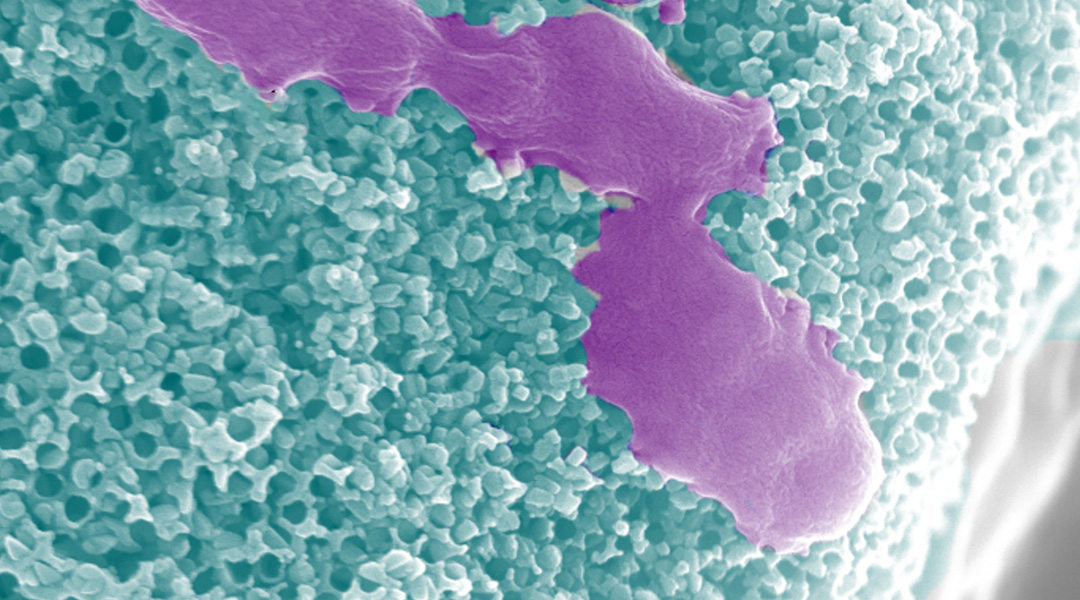
Hybrid microrobots harvest chemical energy from their environment for self-propulsion while releasing reactive species to kill bacteria.
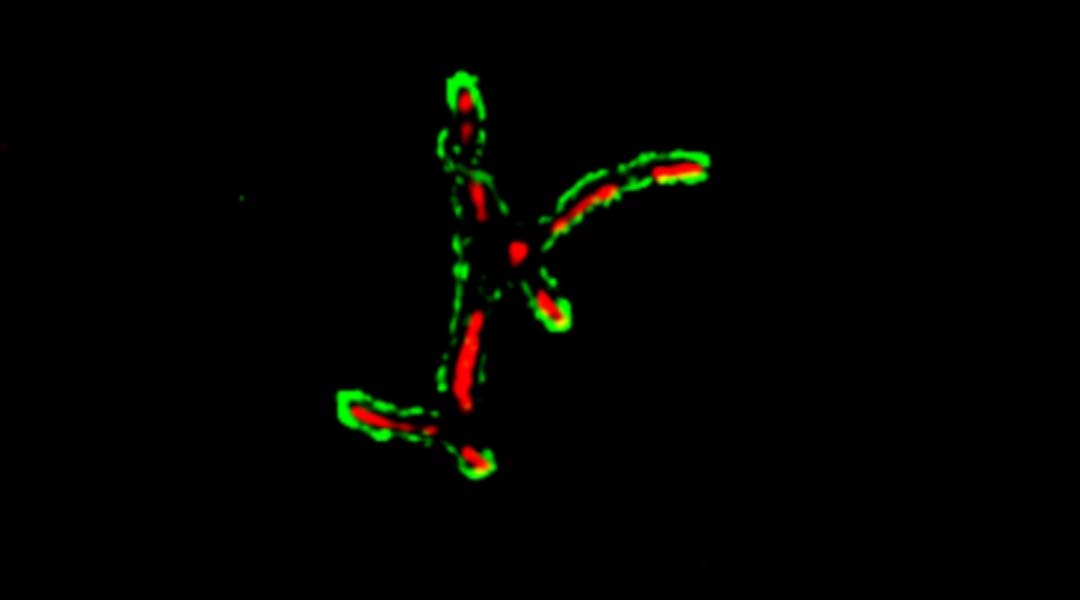
A new fluorescent probe for detecting tuberculosis can now identify disease-causing bacteria in extra-pulmonary tissue for better diagnosis.