A non-invasive test uses a combination of lasers and ultrasound to detect red blood cells infected with malaria parasites with acoustics.
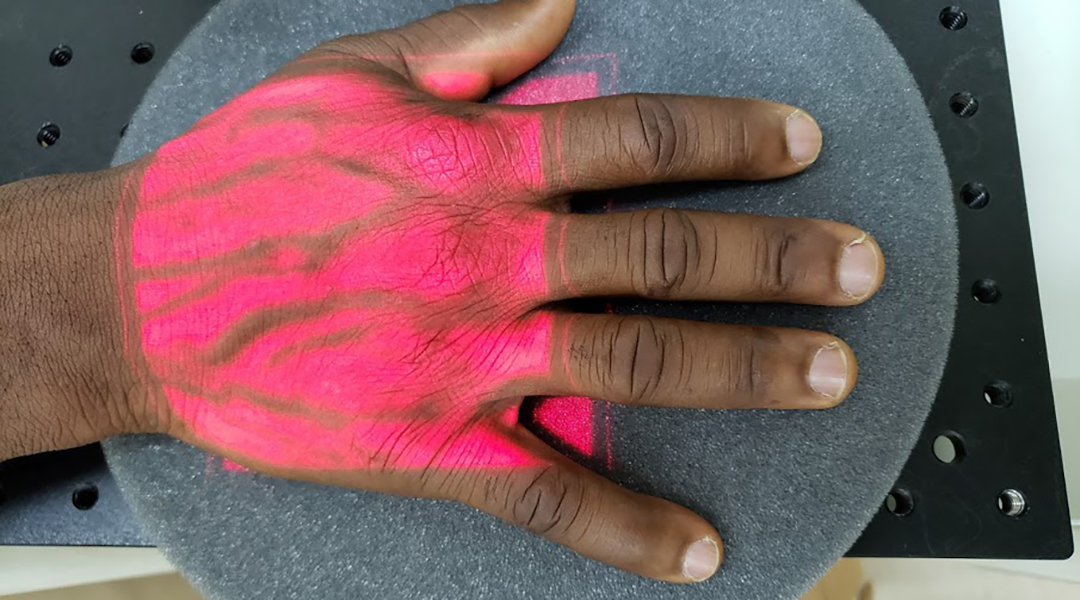


A non-invasive test uses a combination of lasers and ultrasound to detect red blood cells infected with malaria parasites with acoustics.

This new class of antivirals could unlock treatment for viruses beyond just dengue that have been challenging to treat in the past.
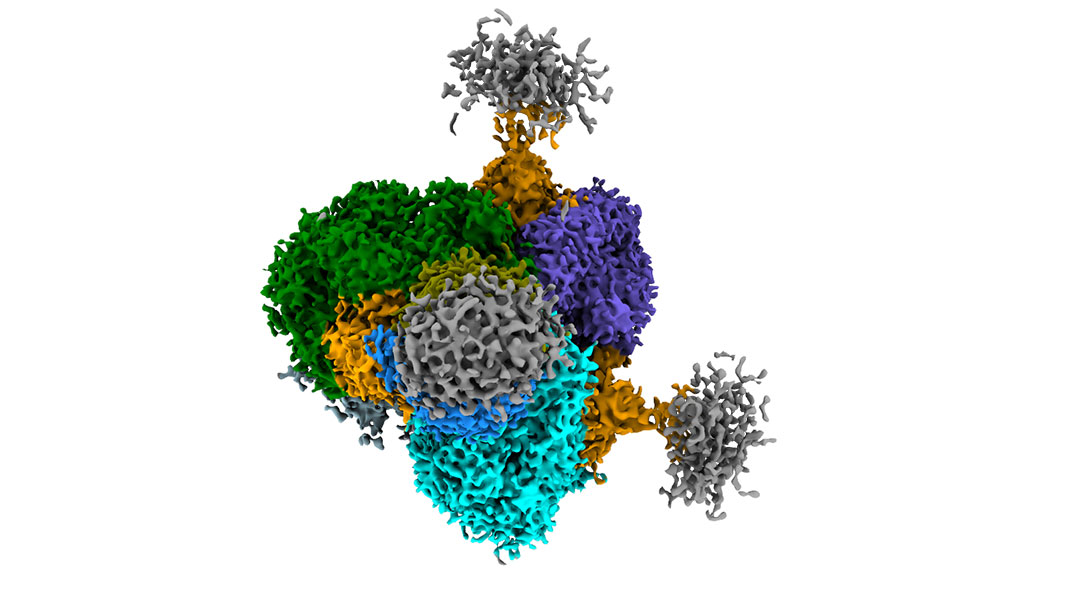
A potent antibody therapy derived from llamas was found to broadly neutralize numerous strains of HIV-1.
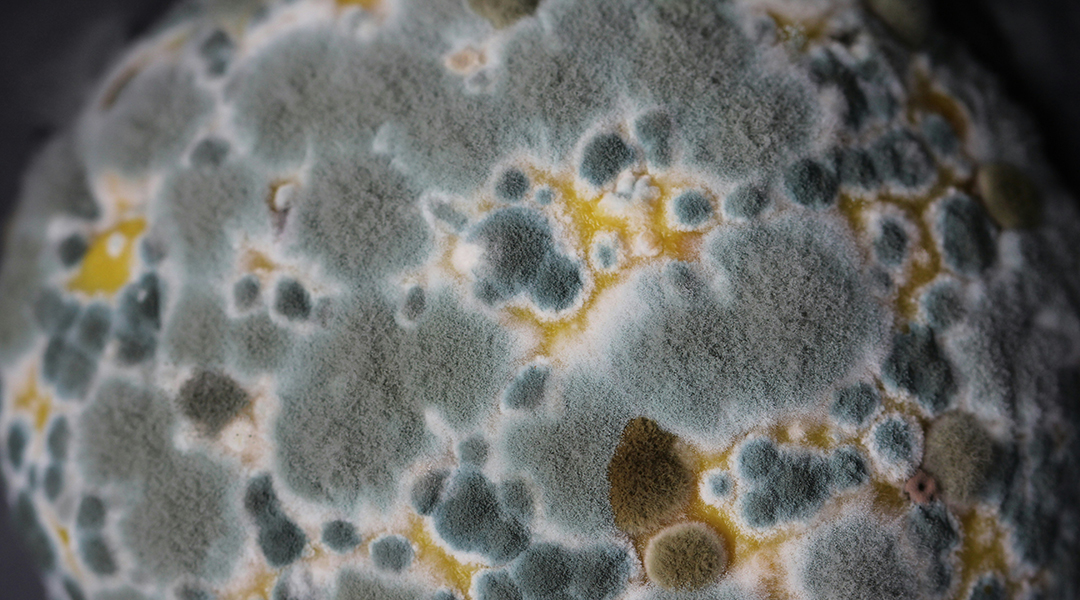
A vaccine to prevent melioidosis, a tropical bacterial disease and possible bioterrorism threat, succeeded in initial trials.
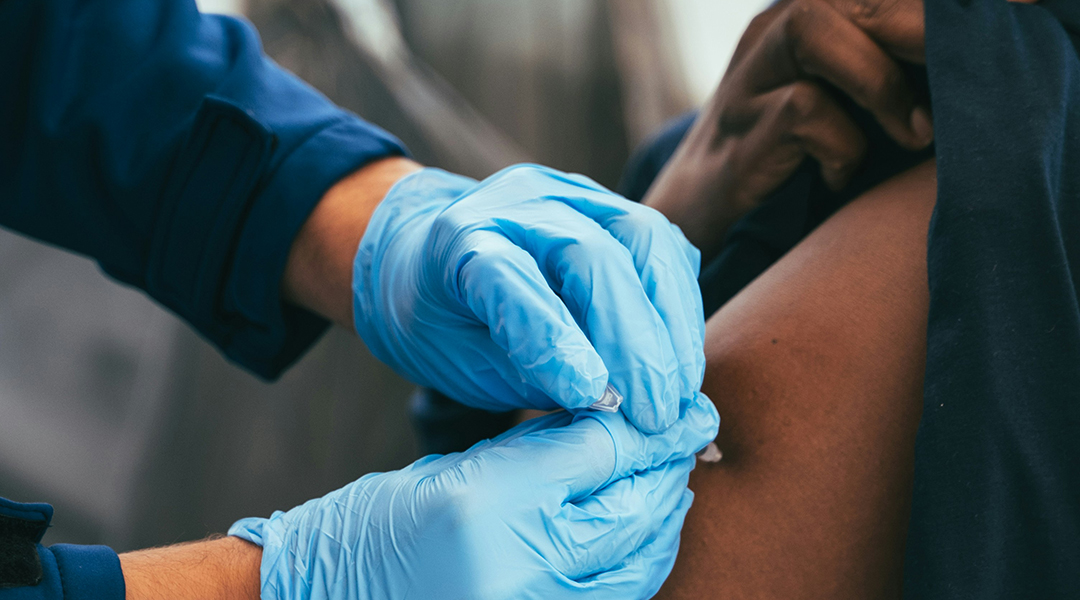
An RNA-based vaccine approach that is effective against all virus strains and safe for infants and immunocompromised individuals.

A modification to conventional microscopes pushes the limits of their resolution and enables high-precision observation of difficult-to-observe pathogens.
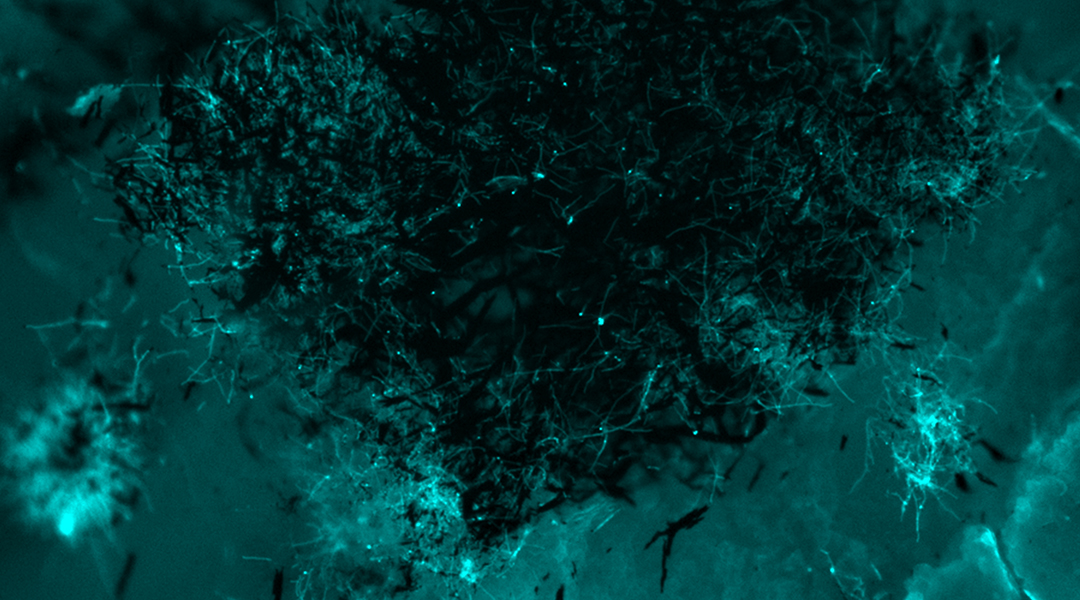
To curb the rising threat of fungal infections, researchers crafted iron oxide nanoparticles as speedy, effective, and inexpensive antifungal agents.
Revolutionizing respiratory disease detection with a portable E-Nose for non-invasive breath analysis.

Researchers turn to nanotechnology to boost the detection of pathogens, including SARS-CoV-2.
To create a flu vaccine that doesn’t require annual tweaking, researchers develop a nanovaccine that uses an inverted hemagglutinin protein.