Researchers have developed CellShape, a user-friendly image analysis tool for quantitative visualization of bacterial cell factories
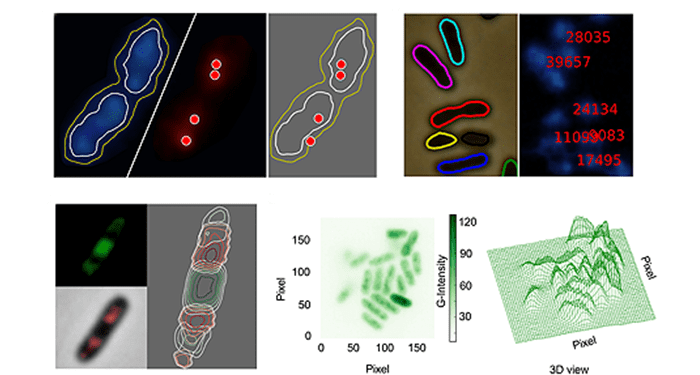

Researchers have developed CellShape, a user-friendly image analysis tool for quantitative visualization of bacterial cell factories
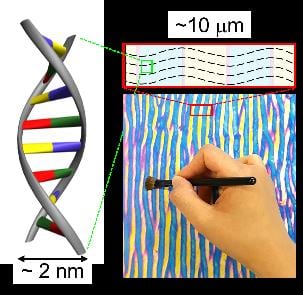
A research team from KAIST, Korea has successfully fabricated nanometer scaled DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) structures.
Surgical injury induces a system stress response which is associated with an over-activation of the innate immune response and a subsequent immunosuppression in the early post-operative period.
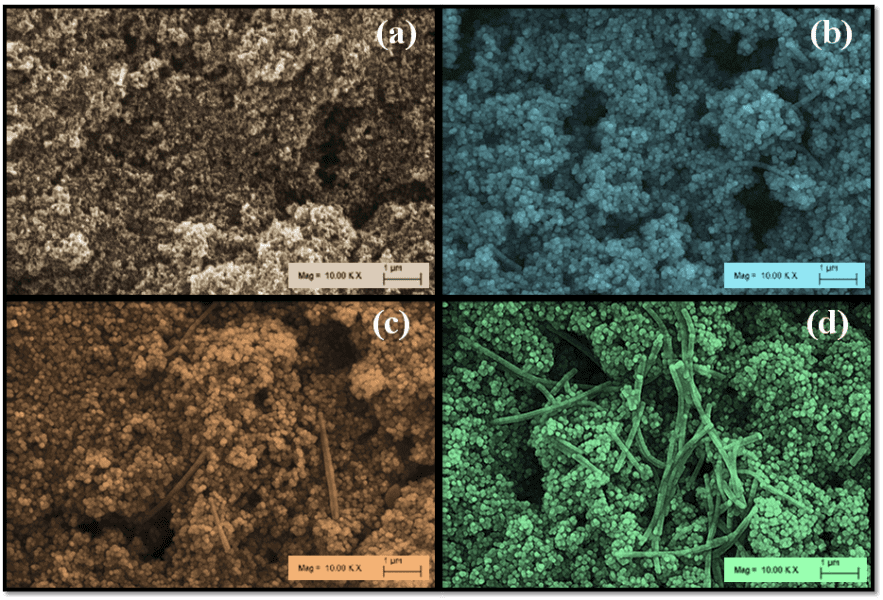
In a recent study, researchers succeeded in applying chickpea and wheat DNA as bridging unit and thin tunneling layer at the TiO2/dye interface.
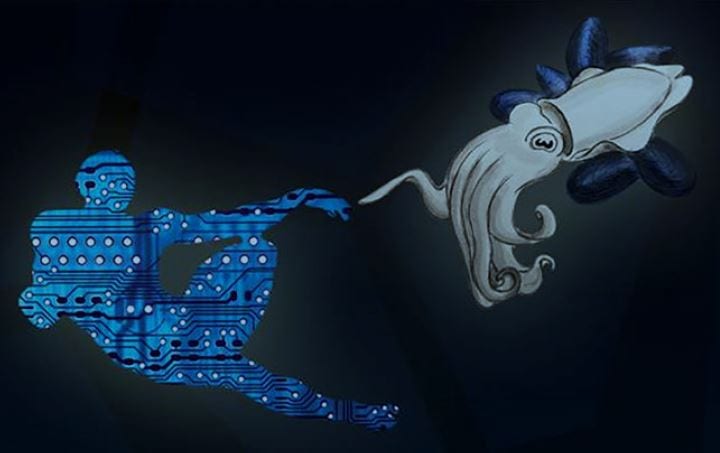
Over the past decade, melanin pigments and their subunits have attracted increasing interest as soft biocompatible functional materials with antioxidant properties for engineering high performance, low impact biocompatible optoelectronic devices, such as memory...
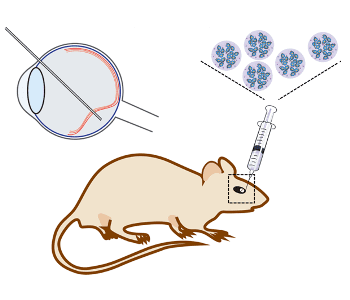
Researchers from Case Western Reserve University present an efficient non-viral gene delivery system for safe gene therapy to treat genetic eye disorders.
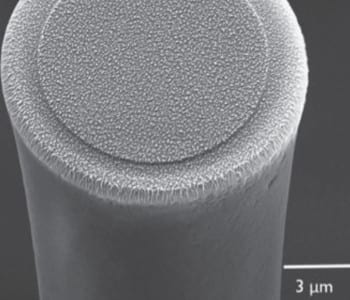
Nanowires can be produced by pulling DNA over micropillar arrays, leaving a simple overcoating step to improve conductivity.
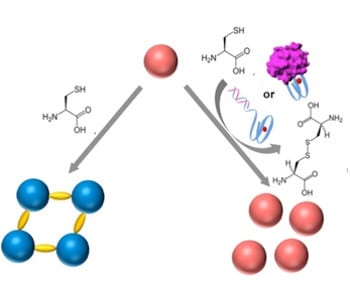
Researchers have developed a DNA biosensor system by controlling the aggregation of AuNPs using horseradish-peroxidase-mimicking DNAzyme.
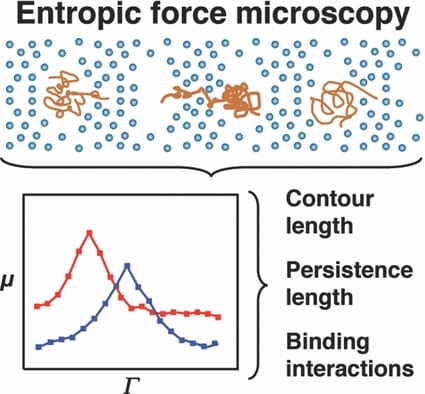
Researchers at Texas A&M have observed dynamics that could otherwise be discounted as noise in DNA/small molecule interactions.
Physicists have developed a “planet-satellite model” to precisely connect and arrange nanoparticles in three-dimensional structures.