Understanding how viruses protect their genome can now be accomplished using physics-based techniques.

Understanding how viruses protect their genome can now be accomplished using physics-based techniques.
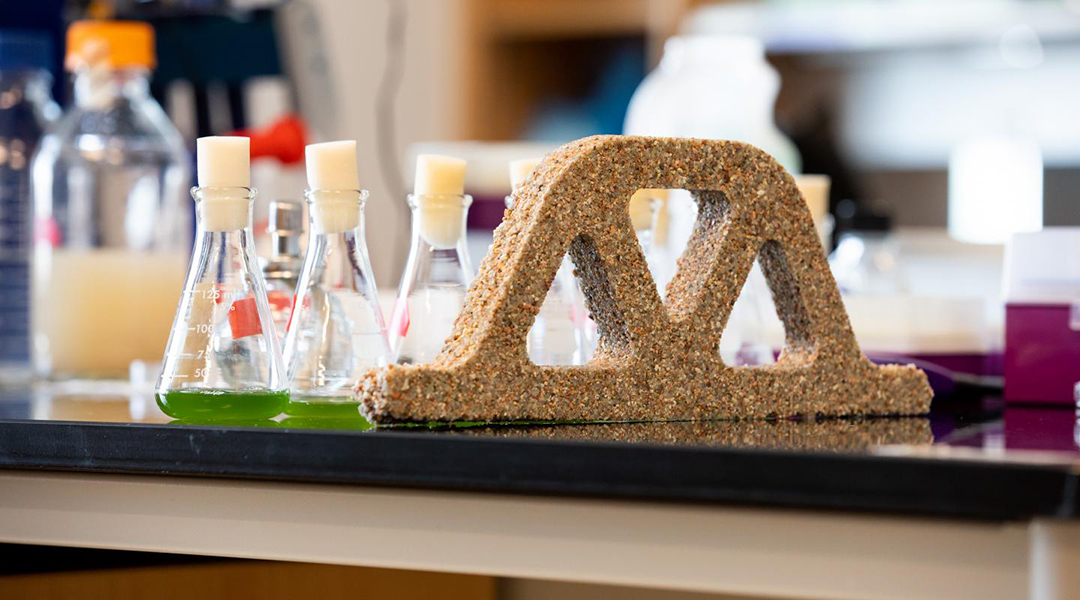

Regenerating bricks are created from sand, gelatin, and bacteria.
Researchers have successful implanted artificial factories into living cells with the hope of producing molecules for therapeutics.
A molecular probe maps misfolded proteome state in live cells.
![An Artificial Cell-On-A-Chip [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/bacteria-359956_1920.jpg)
An artificial cell, which uses a microfluidics-based approach to engineer a modular and programable artificial‐cell‐on‐chip.
Protein-protected metal nanoclusters have excellent biocompatibility and have received considerable attention as a luminescent probe in a number of fields such as biosensing, bioimaging, and imaging-guided therapy.
Decades of research in skeletal muscle physiology have provided multi-scale insights into its structural and functional complexity.
Whilst tissue engineering has benefited modern surgery, thousands of patents fail to see real-world applications.

The potential of spider venom for environmentally friendly insecticides

A team of Brazilean researchers explored photobiomodulation to find evidence of stimulation in the development of newborn rats – and possibly in humans.