Curcumin produces the intense golden-yellow of curries. It’s also being explored as an antioxidant. A reliable source can now be generated from glucose.
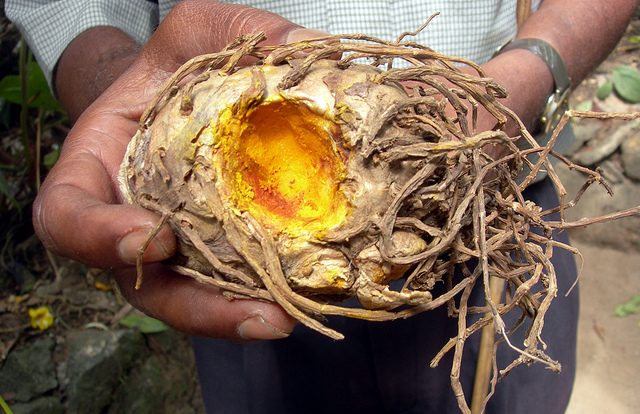


Curcumin produces the intense golden-yellow of curries. It’s also being explored as an antioxidant. A reliable source can now be generated from glucose.
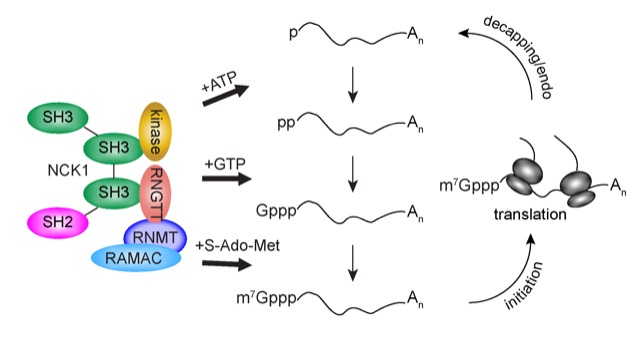
Mammalian cells are capable of recapping mRNAs that have lost their caps.

Researchers studied the possibilities of using cold atmospheric plasmas in wound healing and cancer treatment.
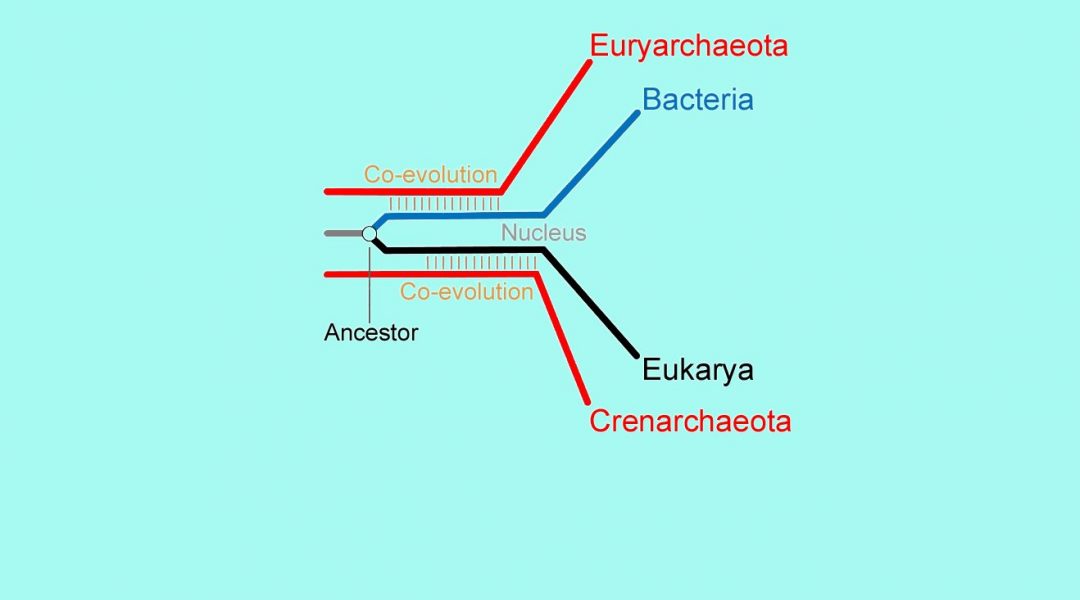
In their article published in BioEssays, James Staley and Gustavo Caetano-Anollés provide a novel perspective on the evolutionary origin of the three domains of life (Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya).

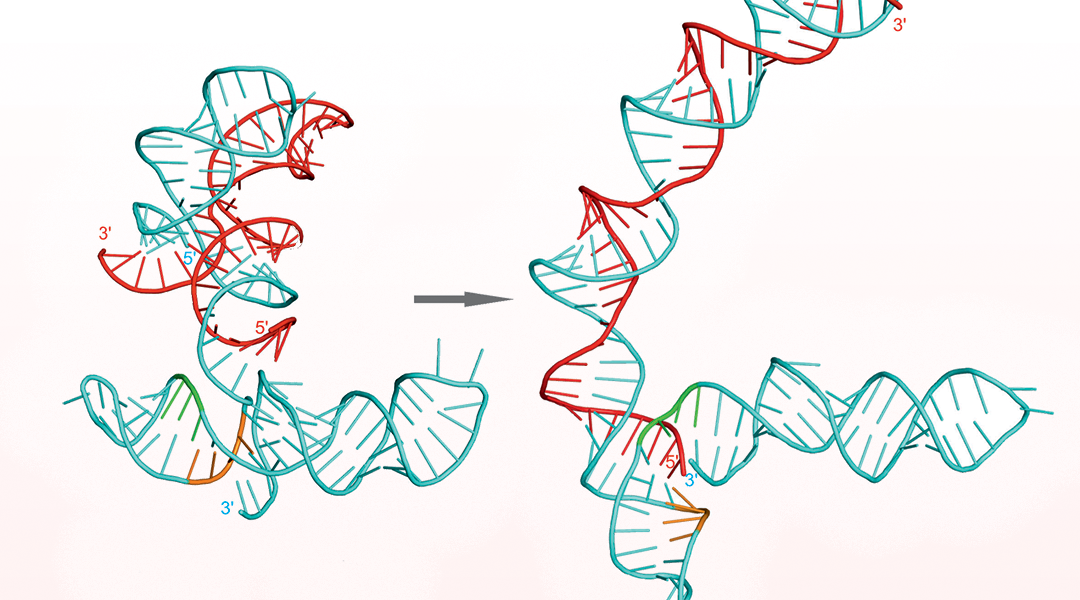
Sequencing of the human genome led to the surprising discovery that we do not have many more protein coding genes than presumably simpler organisms.

The key players within the pathways of RNA decay are well conserved with their mutation or disruption resulting in distinct phenotypes as well as human disease.
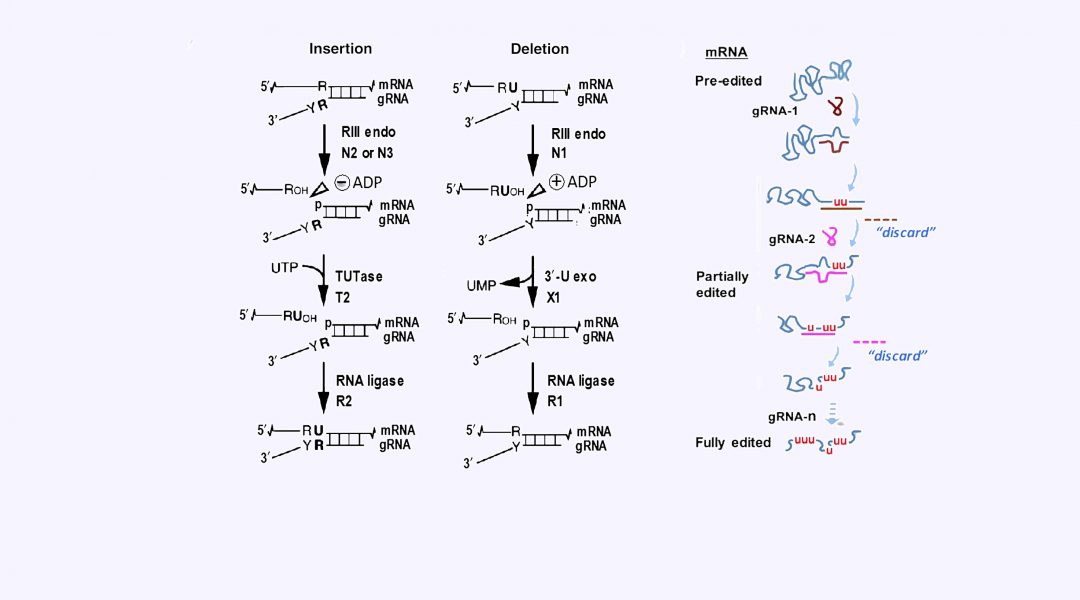
Specific examples of complex variants, differential effects of editing proteins on the mRNAs within and between T. brucei life stages, and possible control points in the holo-editosomes are examined.

A collection articles that highlight the outstanding work in the areas of Health, Medical and Life Sciences published in Advanced Science.
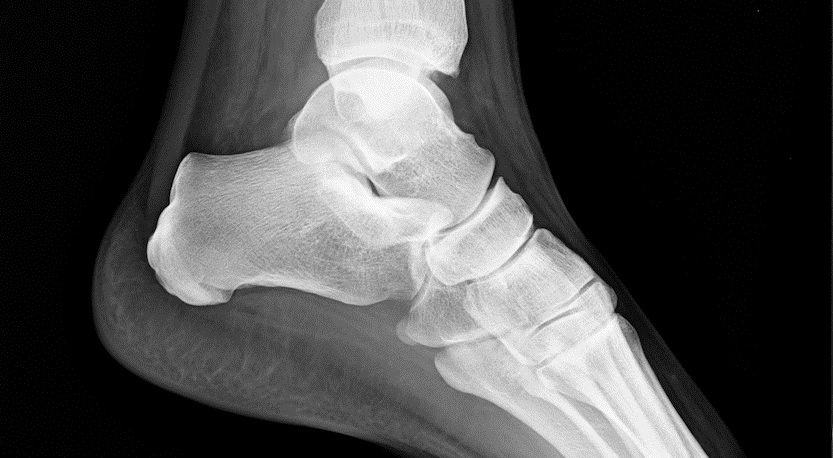
A team of American researchers tested the possibilites of using Raman spectroscopy to assess collagen structure or collagen integrity in bone.
Bacterial plasmids constitute a wealth of shared DNA amounting to about 20% of the total prokaryotic pangenome. Plasmids replicate autonomously and control their replication by maintaining a fairly constant number of copies within a given host. Plasmids should acquire a good fitness to their hosts so that they do not constitute a genetic load.