Tsetse flies, which miraculously birth young bigger than the mother, show us what science is about.
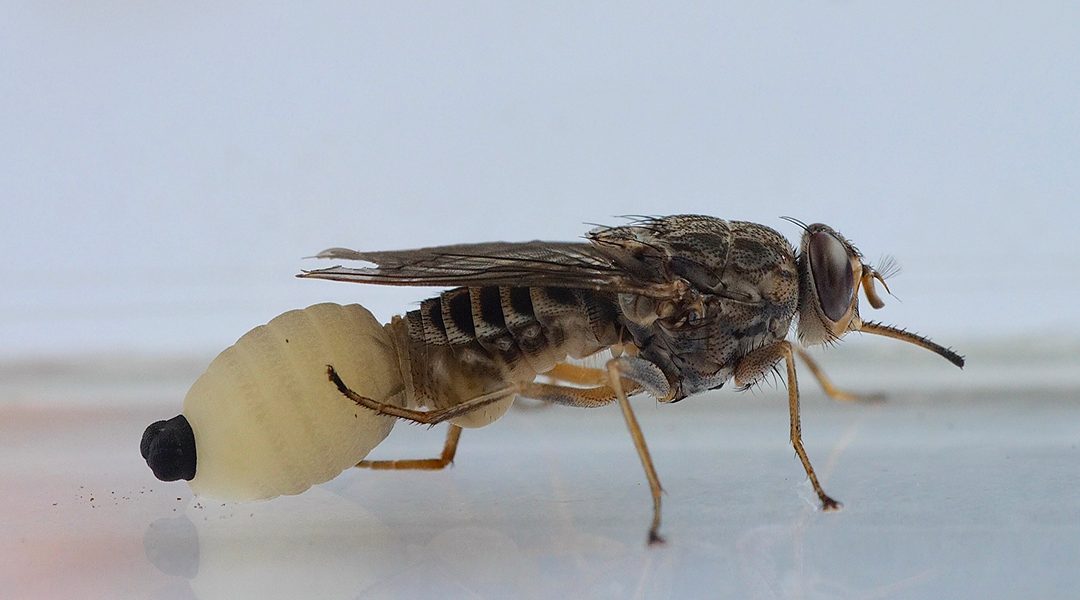


Tsetse flies, which miraculously birth young bigger than the mother, show us what science is about.
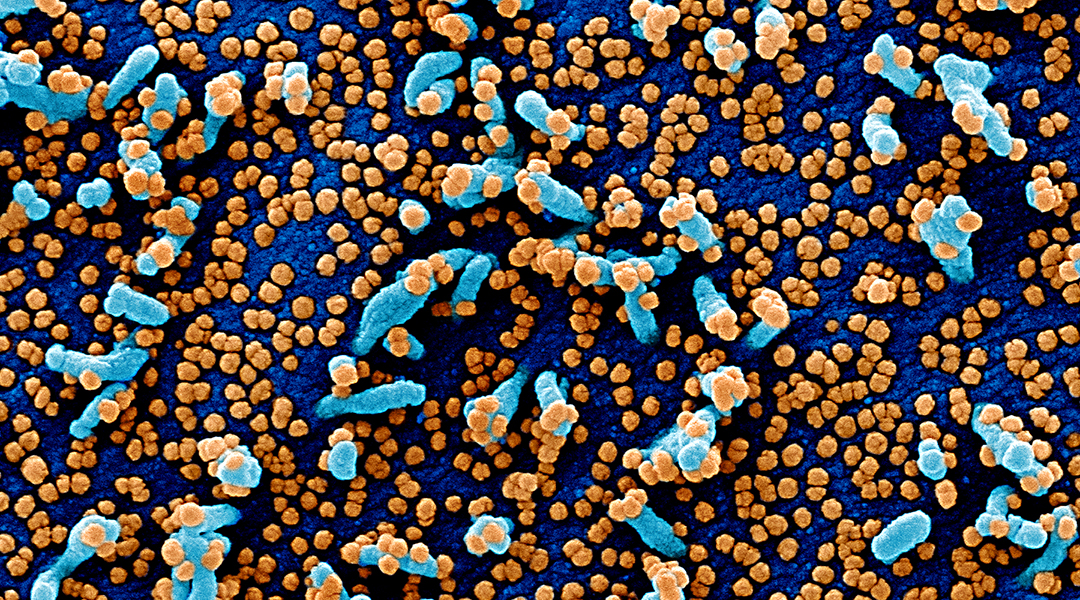
New study finds coronaviruses are masters of mimicry, reproducing their host’s immune proteins to remain invisible and help promote infection.

Computational chemistry is key to understanding the unusual properties of eumelanin.
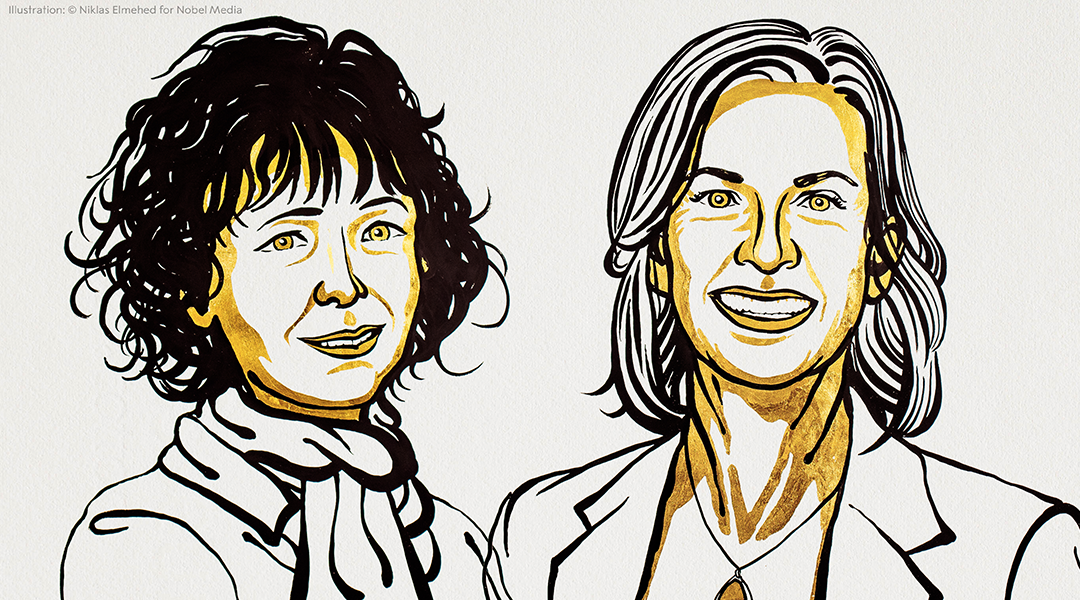

For the first time, two women share the Nobel prize for chemistry. Their work with CRISPR helped usher in a new generation of precision genome editing.
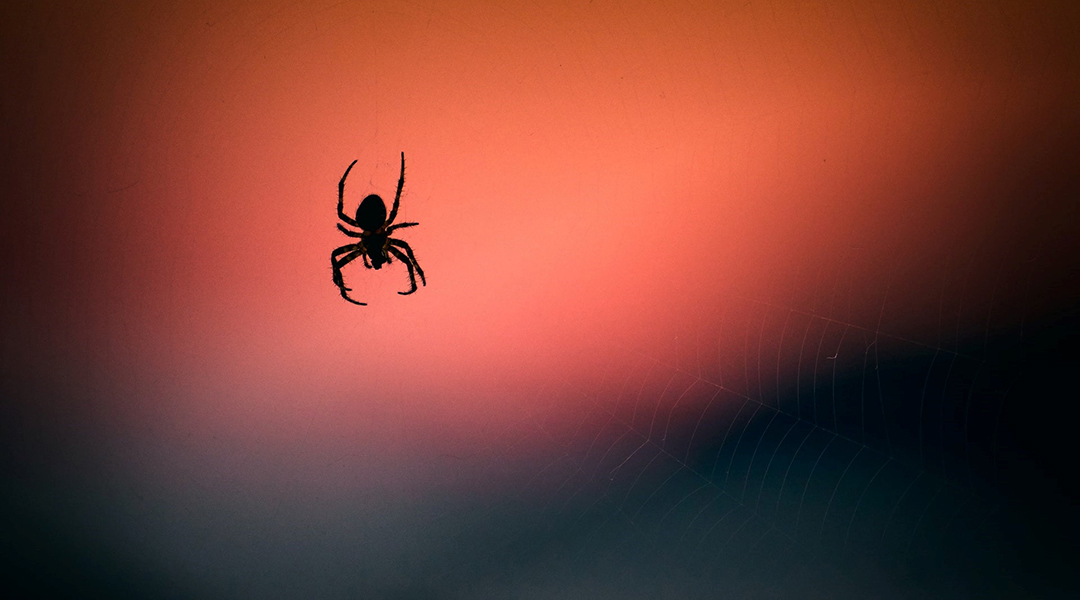

New research is uncovering the importance of small predatory species in shaping ecosystems and managing threatened populations.
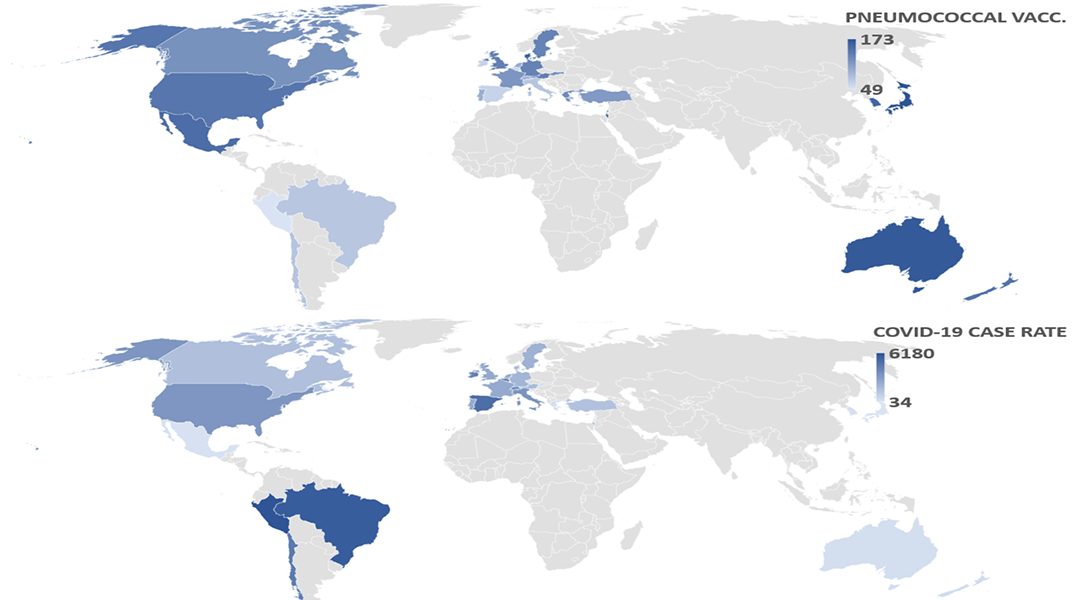
Where pneumococcal vaccination rates are high, COVID-19 cases are low and vice-versa.
Who were the vikings and where did they come from? Sequencing of skeletons allows researchers to understand Vikings through their genetic legacy.
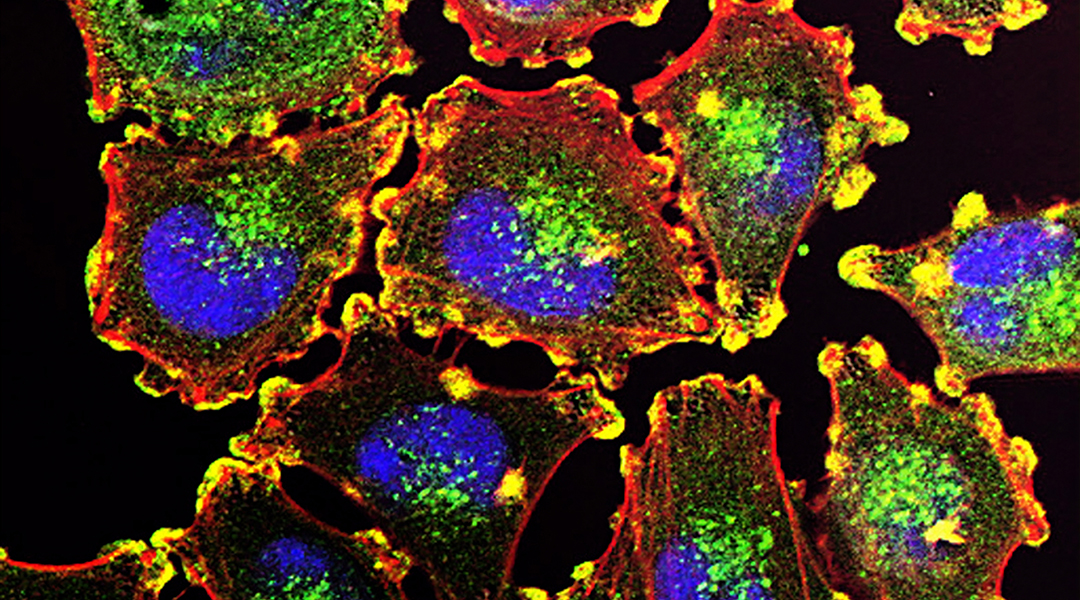
Light-activated proteins enable scientists to study and engineer subcellular structures for research and biotechnological applications.
Similar to eukaryotes, prokaryotic cells can spatiotemporally regulate localization of RNAs, which is crucial for the survival and proper function of these tiny organisms.
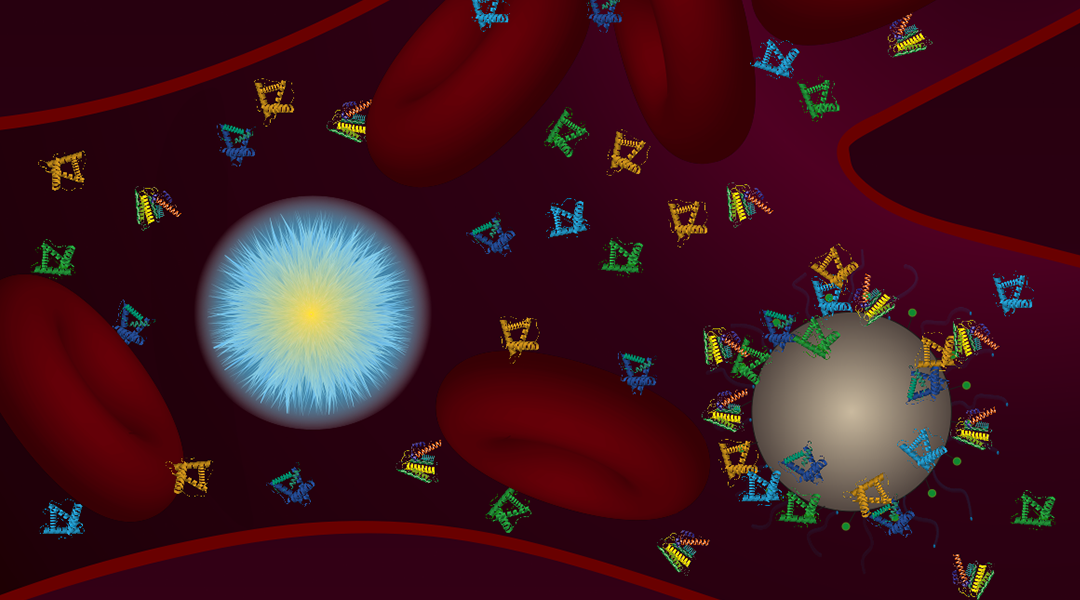
It seems that not all nanoparticles attract a protein corona.