Through veiled mirrors: Fish fins help researchers understand relative growth and proportion in developmental biology.
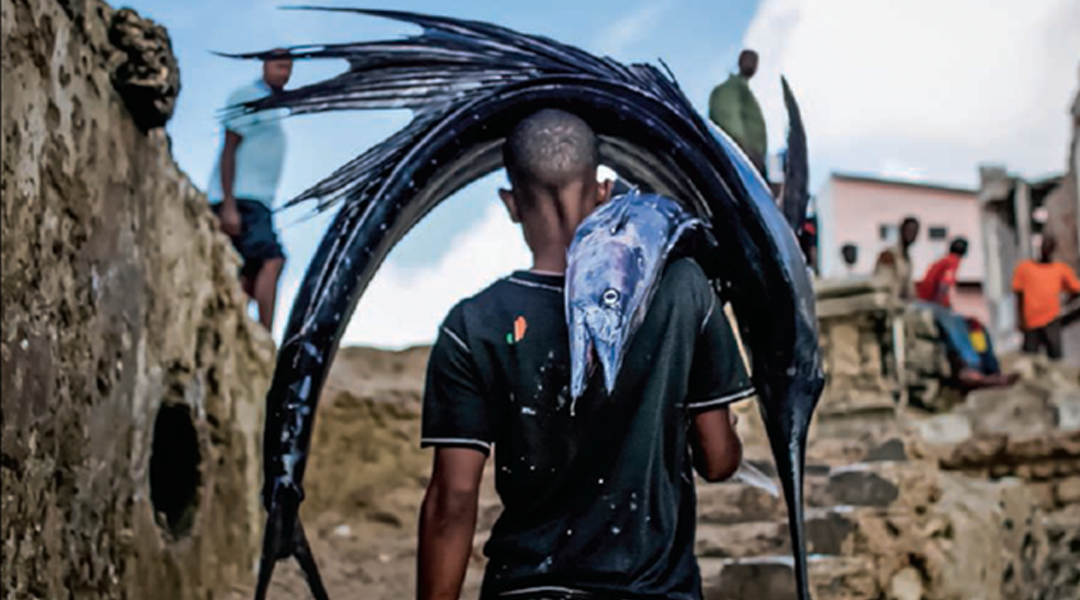


Through veiled mirrors: Fish fins help researchers understand relative growth and proportion in developmental biology.
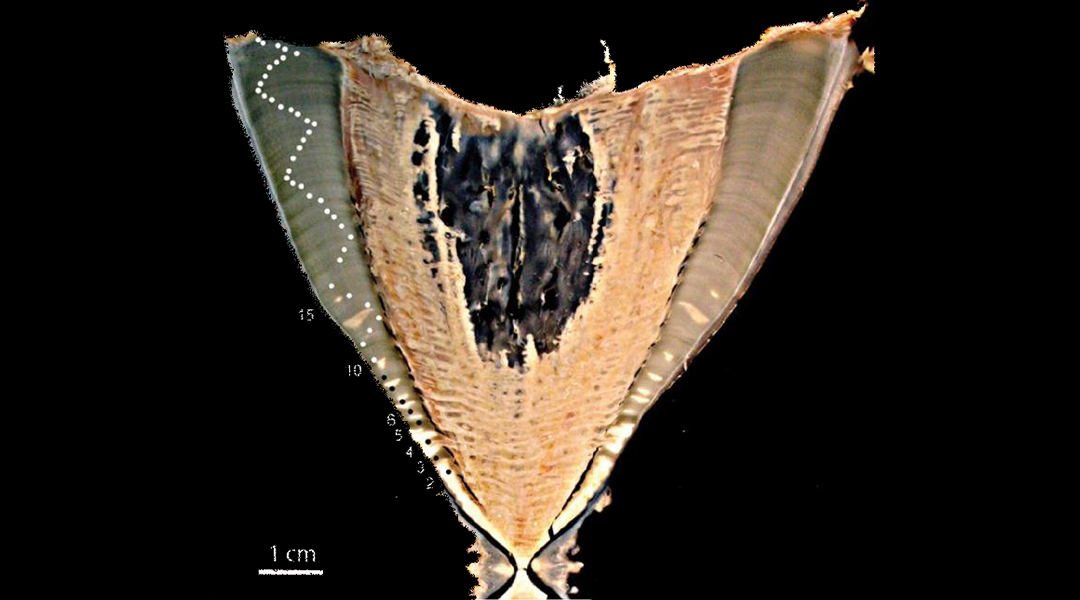
The radioactive legacy of the arms race solves a mystery about the world’s largest fish.
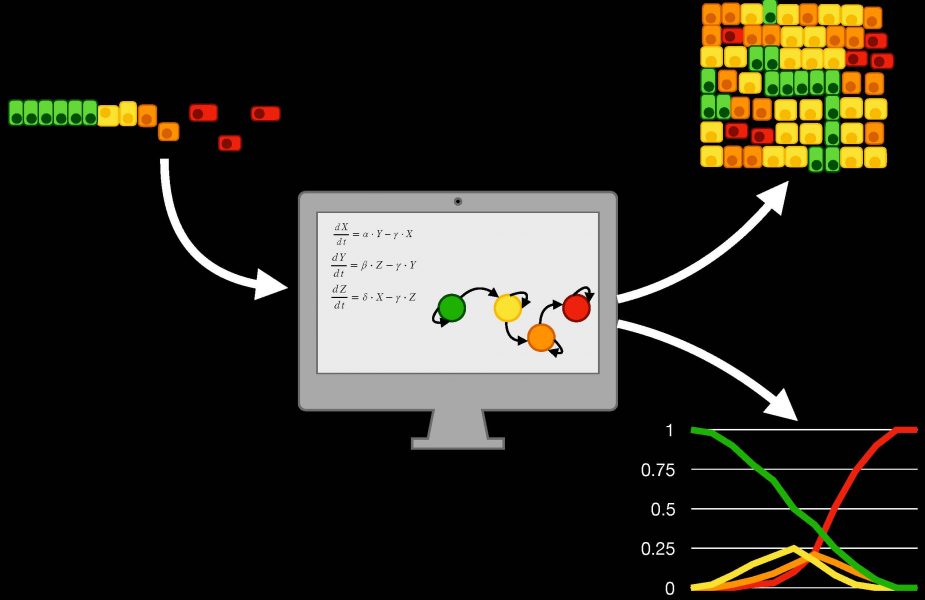
Computational modelling enhances the multidisciplinary approach to understanding the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis.

Computer modeling decodes the chemistry carried out by complex DNA repair enzymes to remove DNA damage caused by environmental exposure.
Exploring advances in extracellular vesicles research made in the last ten-years and how its leading to better clinical applications.
Understanding how mRNA localization changes during healthy brain functions and pathological conditions.

Every gene found in our DNA exerts its action via the activity of its encoded protein product. However, the synthesis of the protein cannot take place directly from the gene. An intermediate messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule is first produced from the gene via a process...

Researchers studied two important protein mutations that are known to cause cataracts, and hope that their improved understanding will help in future treatment plans.
Artificial enzymes promise to not only help us understand the complex functioning of enzymes, but will create a new generation of biosystems for sustainable chemistry practices.

The lifespan of C. elegans, an organism that responds to cellular stress in a similar way to humans, can be extended by activating a mechanism initiated by glial cells in the brain.