Using the motion of sound waves through a superfluid liquid, scientists can model the Universe’s evolution on a reasonable time scale.
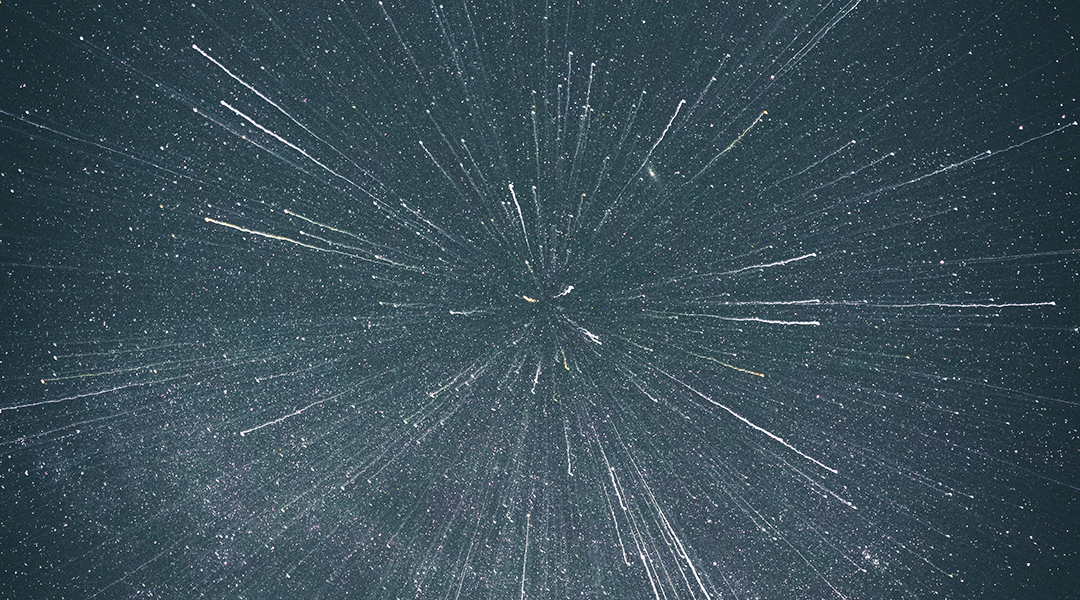


Using the motion of sound waves through a superfluid liquid, scientists can model the Universe’s evolution on a reasonable time scale.
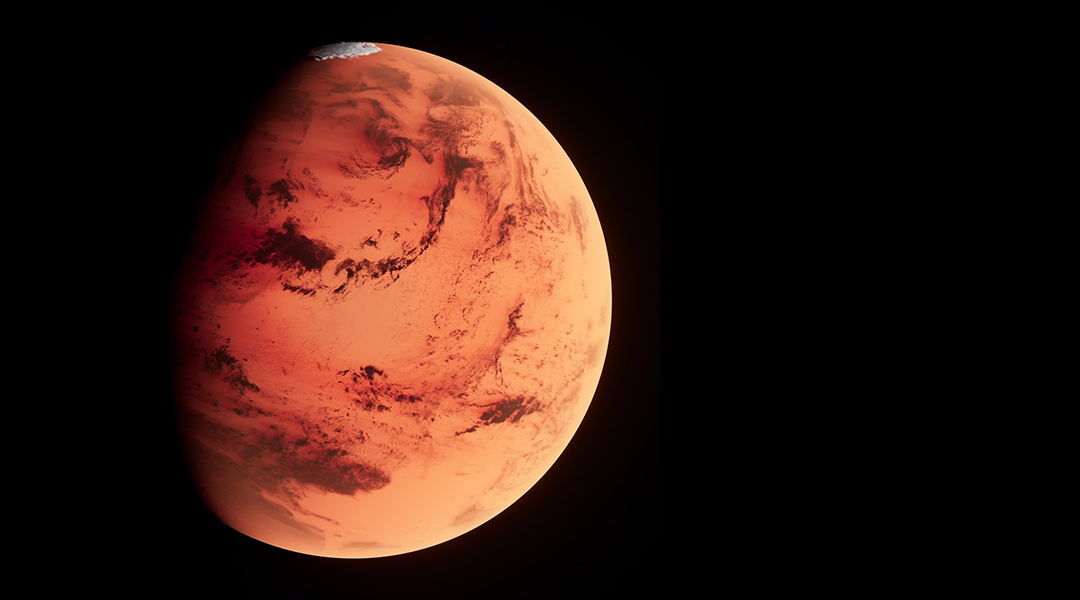

The 3.5-billion-year-old shoreline provides evidence of an ancient ocean in Mars’ northern hemisphere as well as sea-level rise.
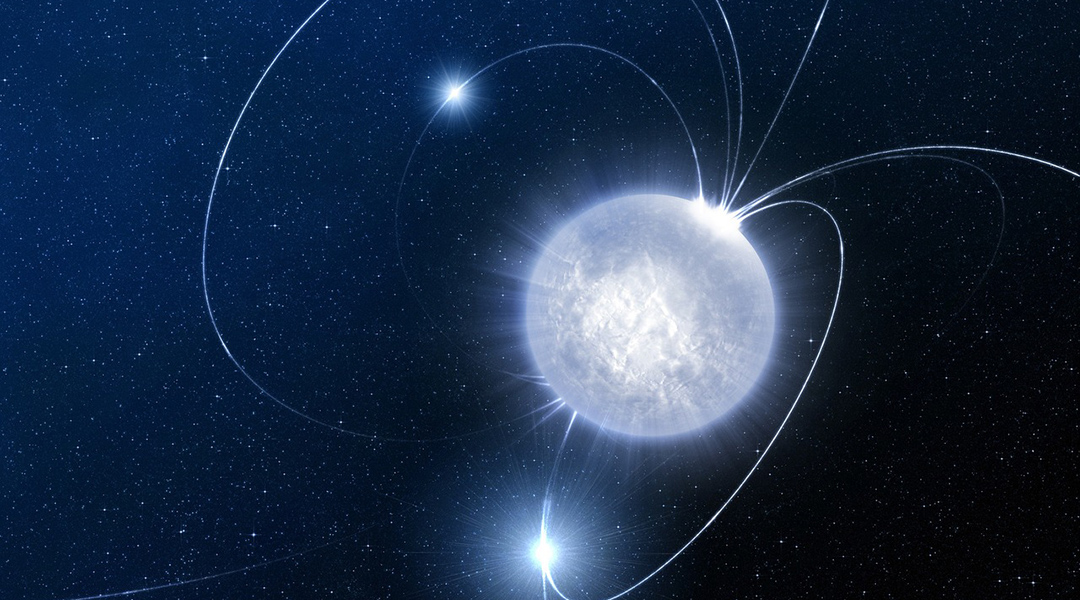

More confirmation needed to see if recently discovered object is a quark star.
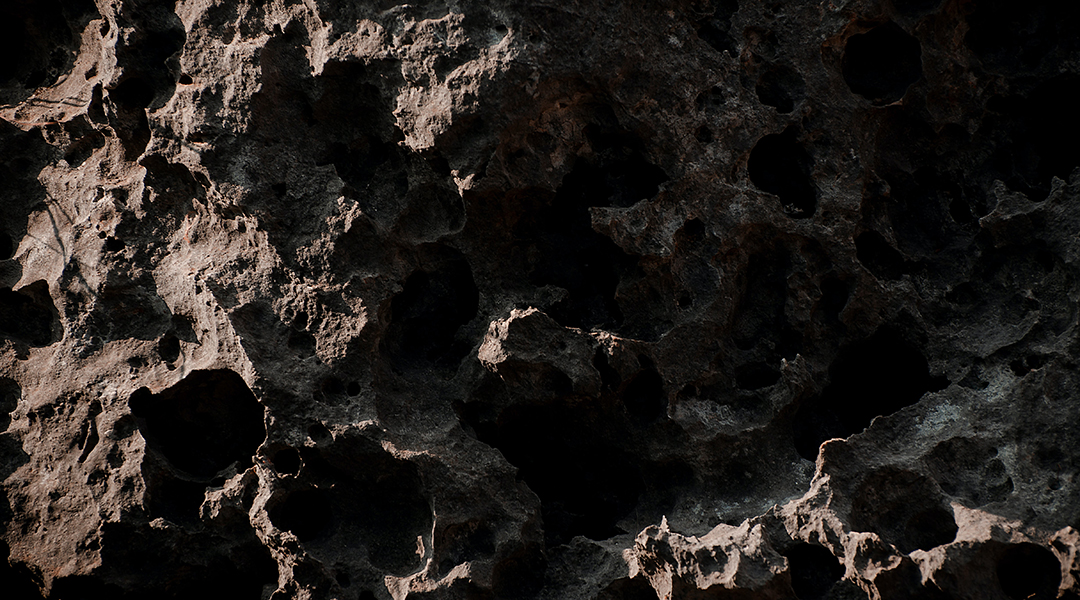

Years’ worth of radar data from the now-destroyed Arecibo Observatory has helped detail almost 200 near-Earth asteroids.
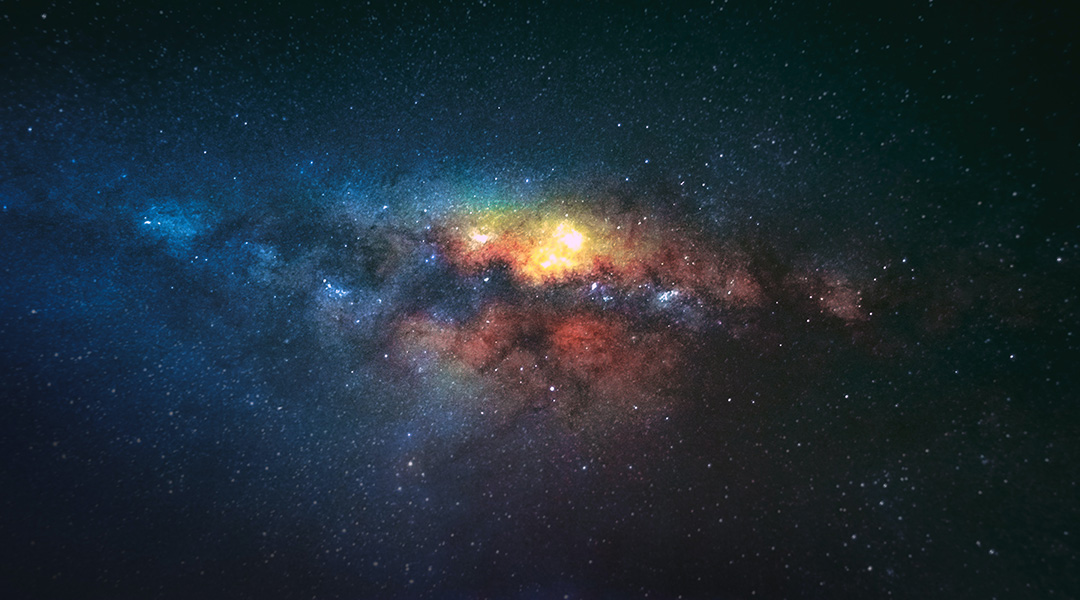

Using a new definition of galaxy size, astronomers have uncovered new, exciting findings about how they formed and evolved.
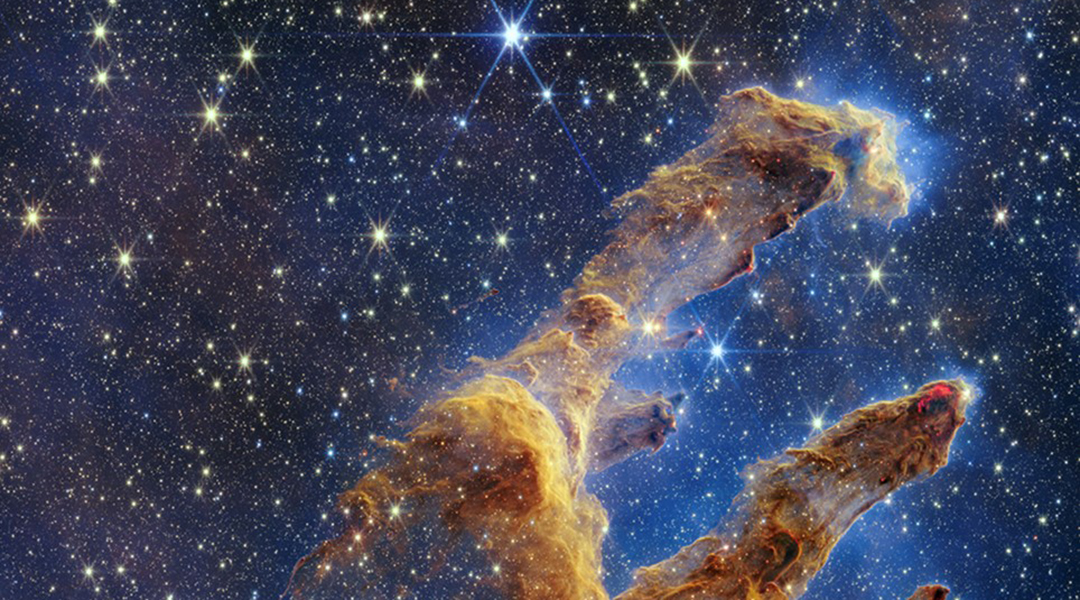

This month, NASA’s James Webb Telescope captured images of the Pillars of Creation in breathtaking detail.

Oscillations measured in the orbits of a pair of black holes have once again helped confirm predictions made using general relativity.
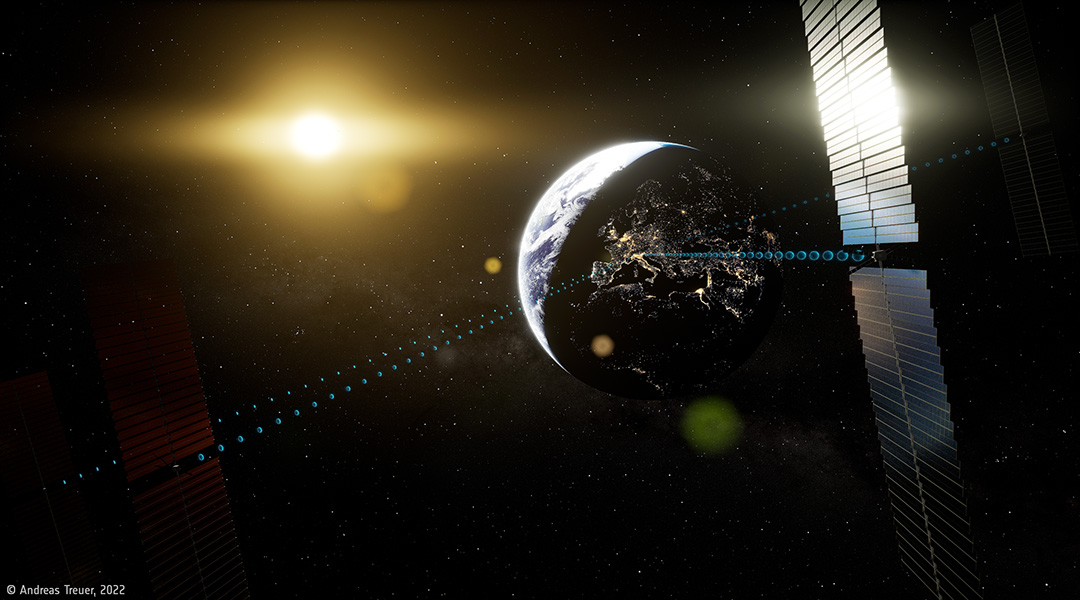

With climate change, the weaponization of energy, lower satellite launch costs, incentives to harness space-based solar power are on the horizon.
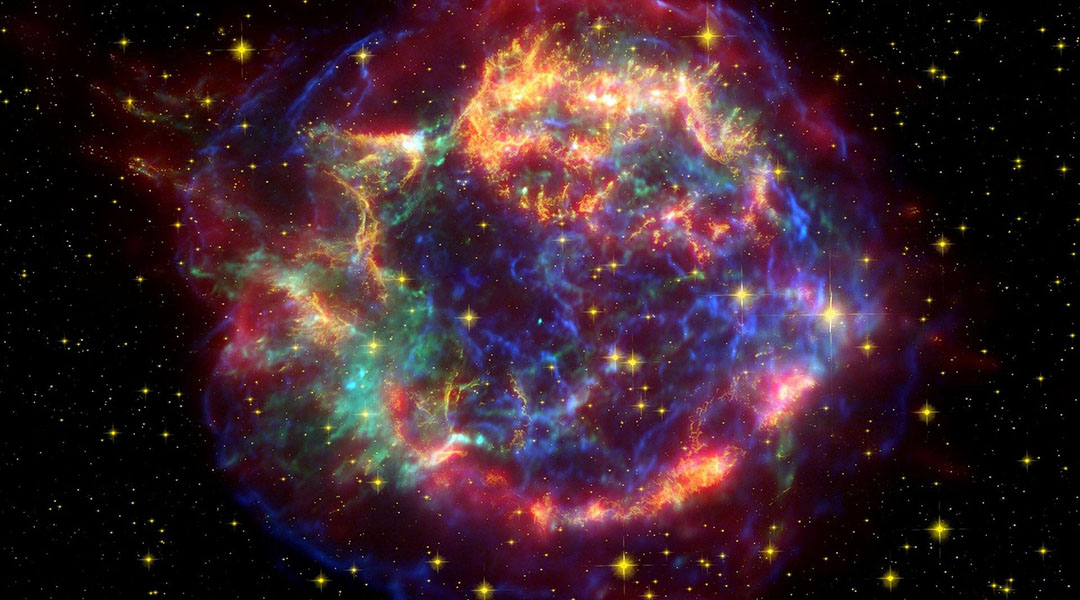
Researchers have found that supernovae explosions are preceded by observable radiation whose features should make it possible to distinguish the radiation of a future supernova from other light sources in space.

Researchers at the Southern University of Science and Technology in China ask if gravitons can be promising candidates for dark matter components.