Structure-predicting AlphaFold could help revolutionize soybean crop breeding through AI-guided precision gene editing.
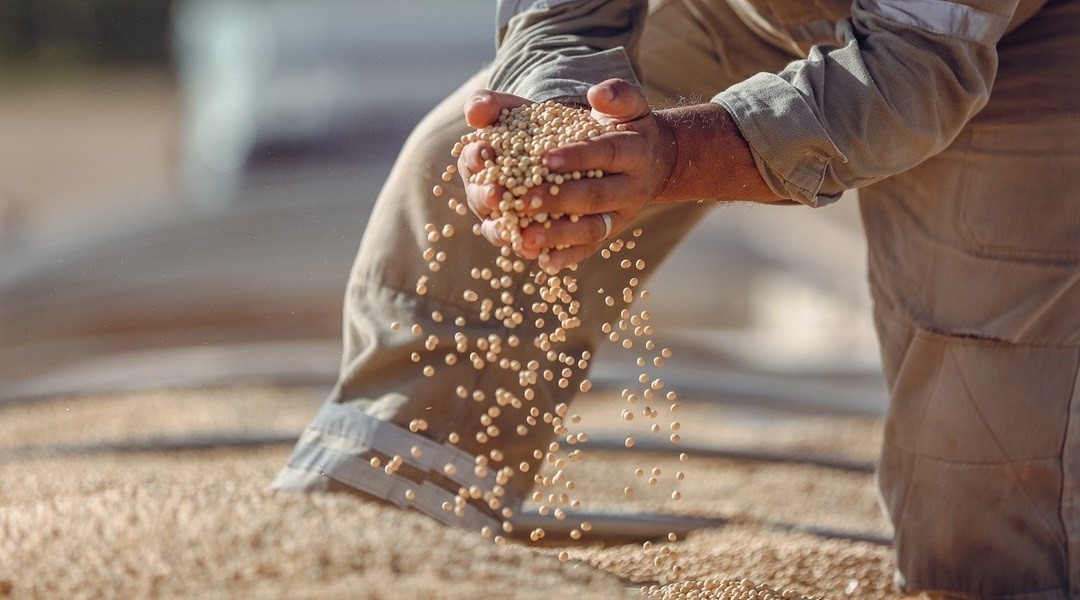


Structure-predicting AlphaFold could help revolutionize soybean crop breeding through AI-guided precision gene editing.
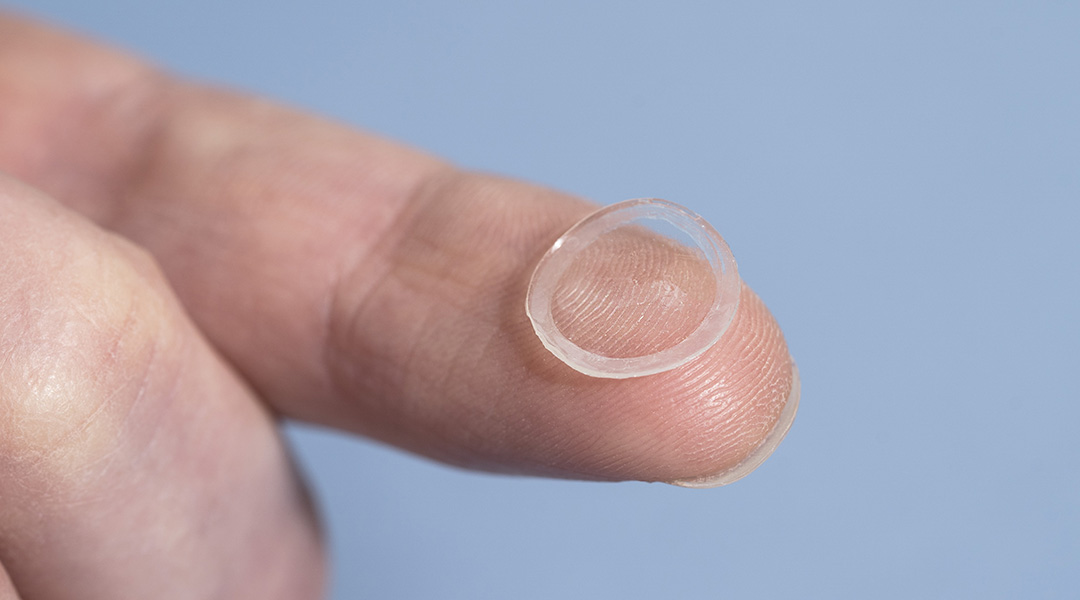
Bacterial biofactories embedded in the rim of the lens continually produce hyaluronic acid, a natural lubricant, to keep the contacts moist.

Chaotic pools of DNA could be the future of encryption, proving authenticity of artwork or securing passwords against quantum computers.
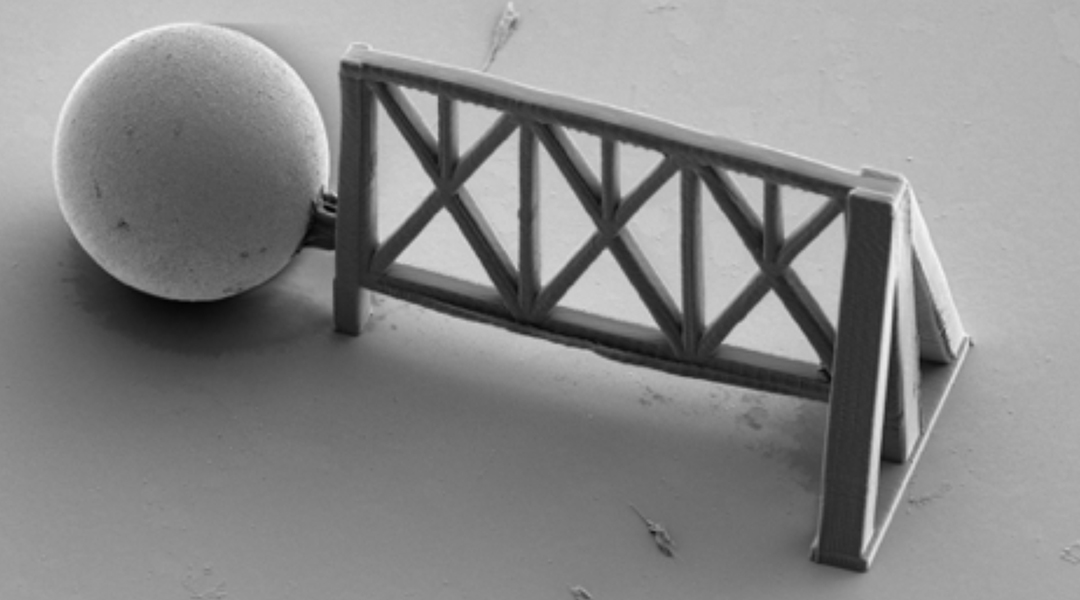
Scientists employ cutting-edge 3D printing to recreate human-like tissue, promising a breakthrough in cellular research and potential insights into aging and disease.
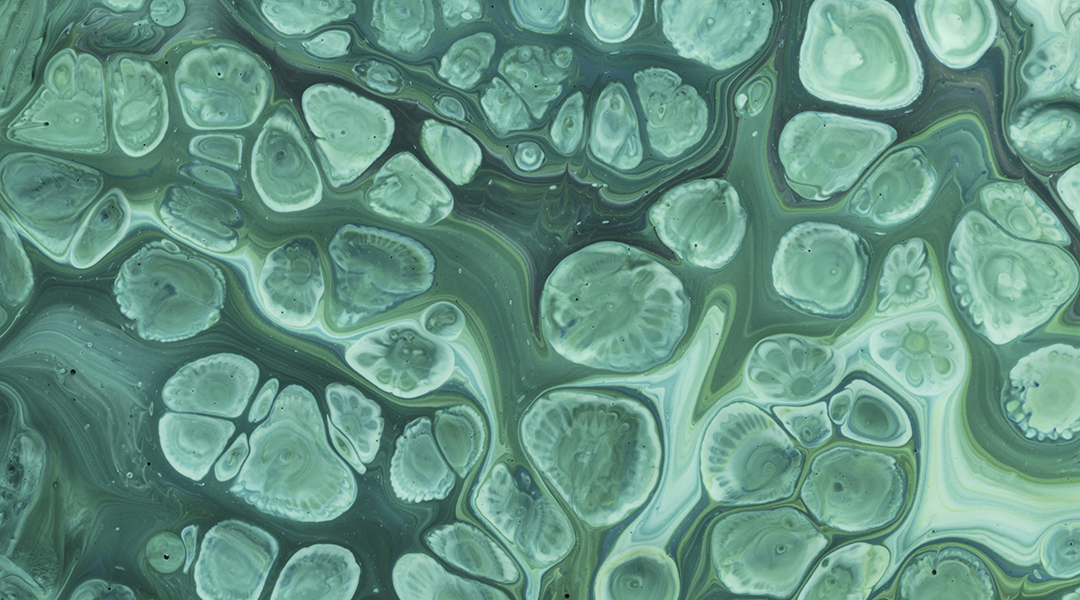
A textured film maximizes sunlight by generating an increased amount of red light, reducing the costs of algae production on a significant scale.
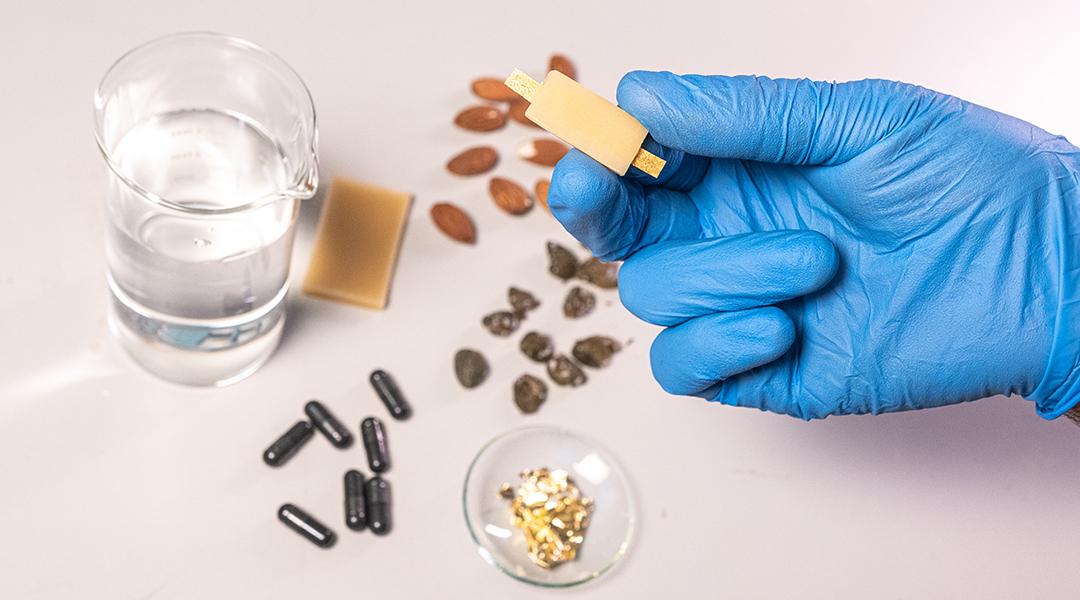

An edible and rechargeable battery to power devices used for GI tract monitoring, therapeutics, and analyzing food quality.
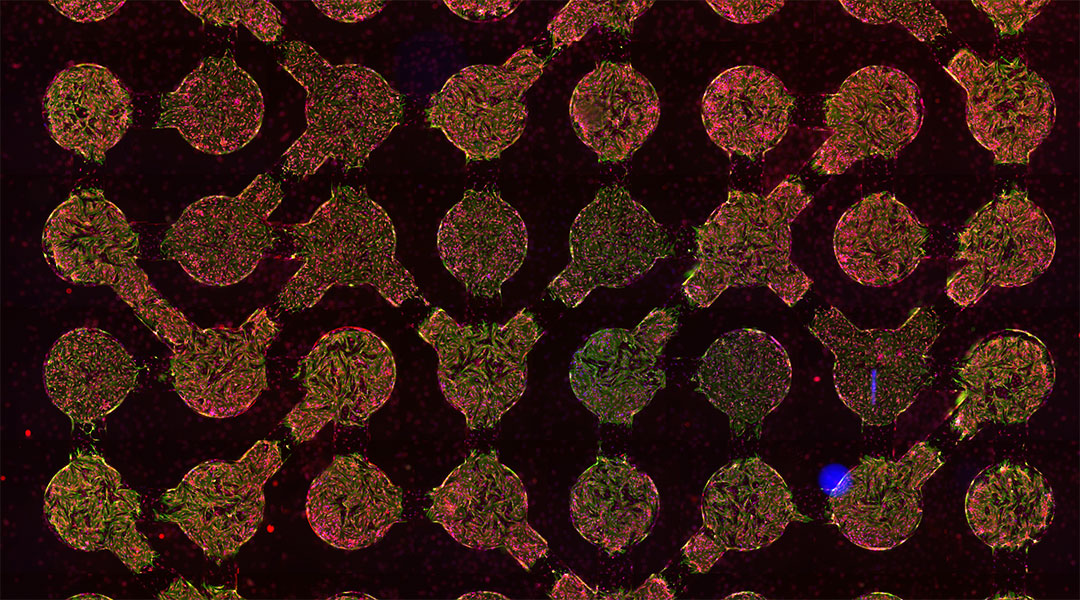
A biocomputer built from connected heart cells solves computational problems with high accuracy and at a low computational cost.
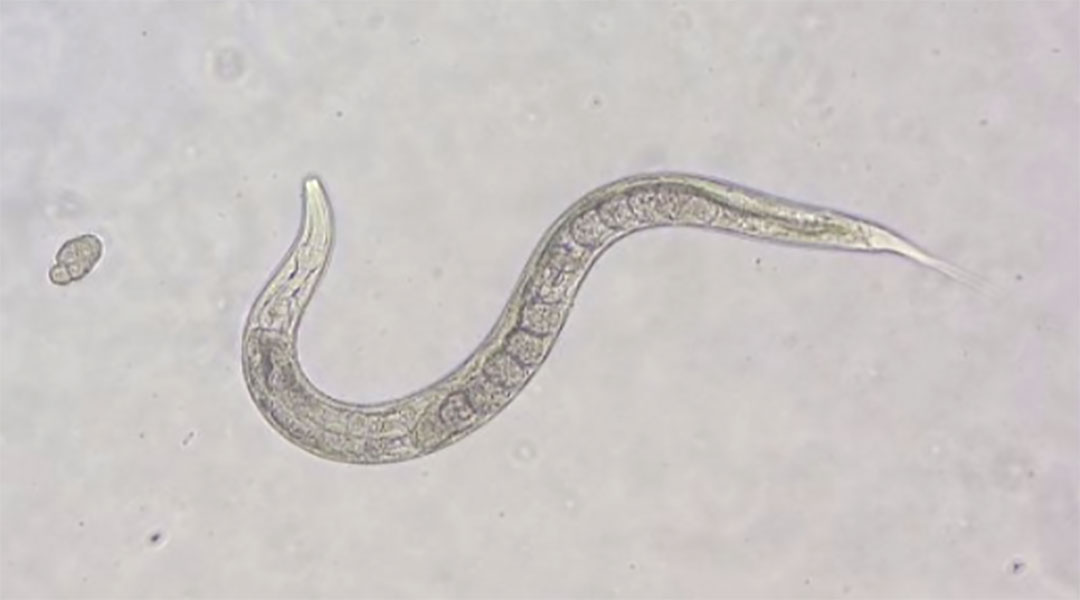
Scientists are turning to C. elegans for biobot designs, guiding their movement through reconfigurable microtopographies.
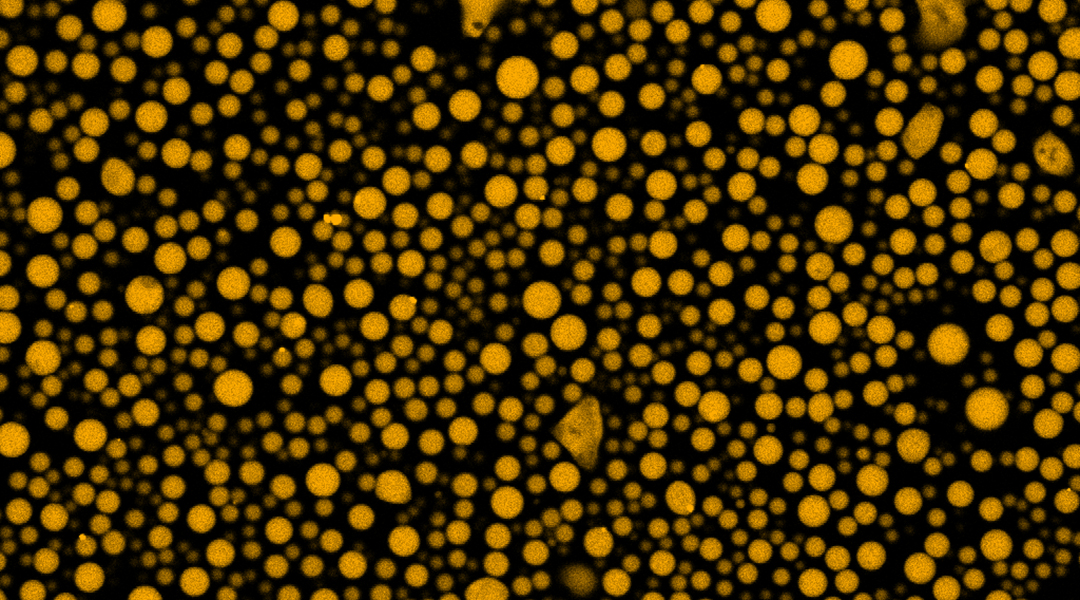
New research inspired by “viral factories” shows the potential of encapsulating target molecules in membrane-free compartments.

A new device setup enables an interface between biomolecules and electronic materials for biohybrid electronics.