Complex, aqueous-stable, hydrogel ionic circuits towards transparent, flexible, biocompatible bioelectronic devices.
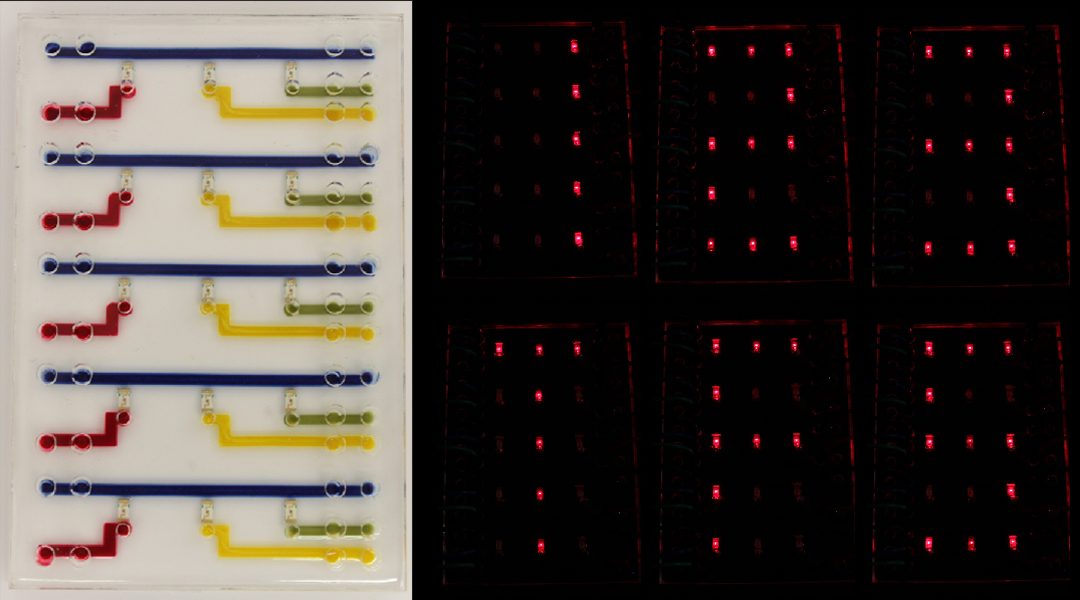

Complex, aqueous-stable, hydrogel ionic circuits towards transparent, flexible, biocompatible bioelectronic devices.
![Bioinspired Synthesis of Monolithic and Layered Aerogels [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/adma201706294_ASN_image.png)
A new ambient drying method for aerogel fabrication is reported.
![Bioinspired Hydrogel Interferometer for Adaptive Coloration and Chemical Sensing [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/adma201800468_ASN_image.png)
A hydrogel interferometer is revealed as a simple and universal adaptive color platform.
Protein immobilization directly from cell lysates is demonstrated in a new process that avoids expensive purification steps but expertly maintains target protein selectivity.
In situ vaccination therapy has immense potential in cancer treatment for clinical use. To date, in situ vaccination is already used to treat bladder cancer and melanoma, and with further study could become an important approach to expand immune-based cancer treatment.
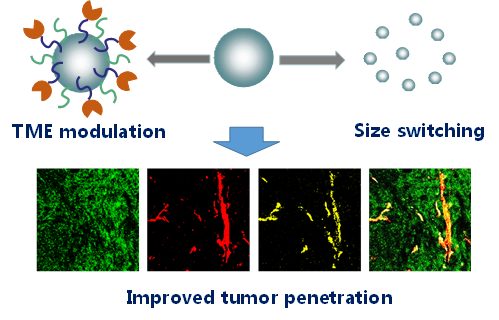
Rational design of nanoparticles with state-of-the-art strategies can effectively improve the penetration as well as therapeutic efficacy of cancer nanomedicines
![Separating Chiral Molecules with Thermoresponsive Nanotubes [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/smll201800030_ASN_image.jpg)
Dr. Naohiro Kameta from the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) and colleagues design thermoresponsive poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-coated nanotubes for simple and efficient separation of chiral molecules.

A team of Korean researchers established an energy efficient dry reforming process using a rotating arc plasma to produce synthesis gas.
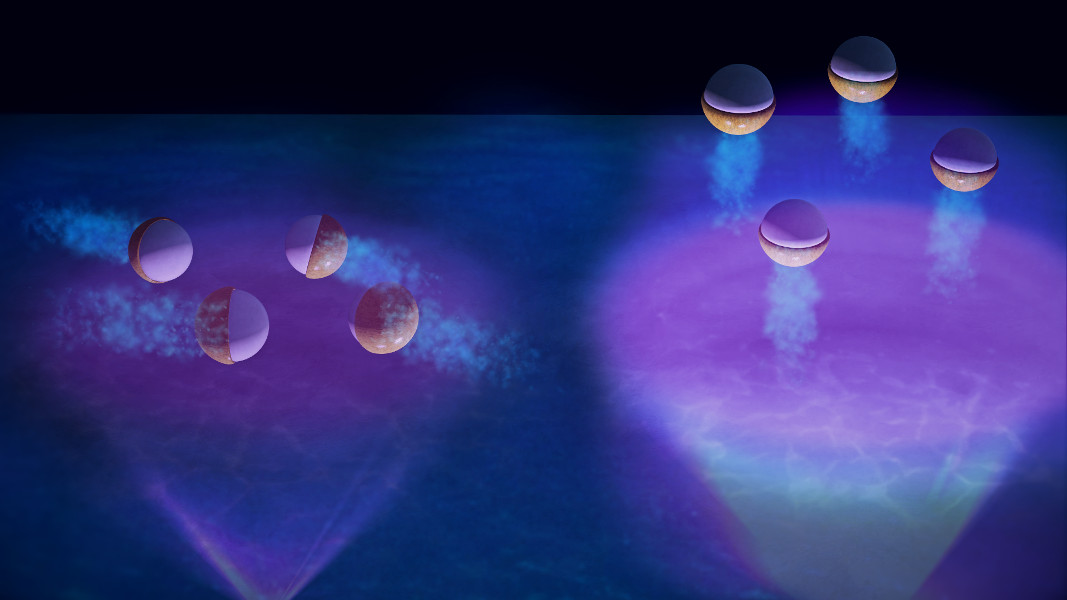
Artificial photochemically-active microswimmers, with 2D or 3D swimming behavior, can also swim against gravity.
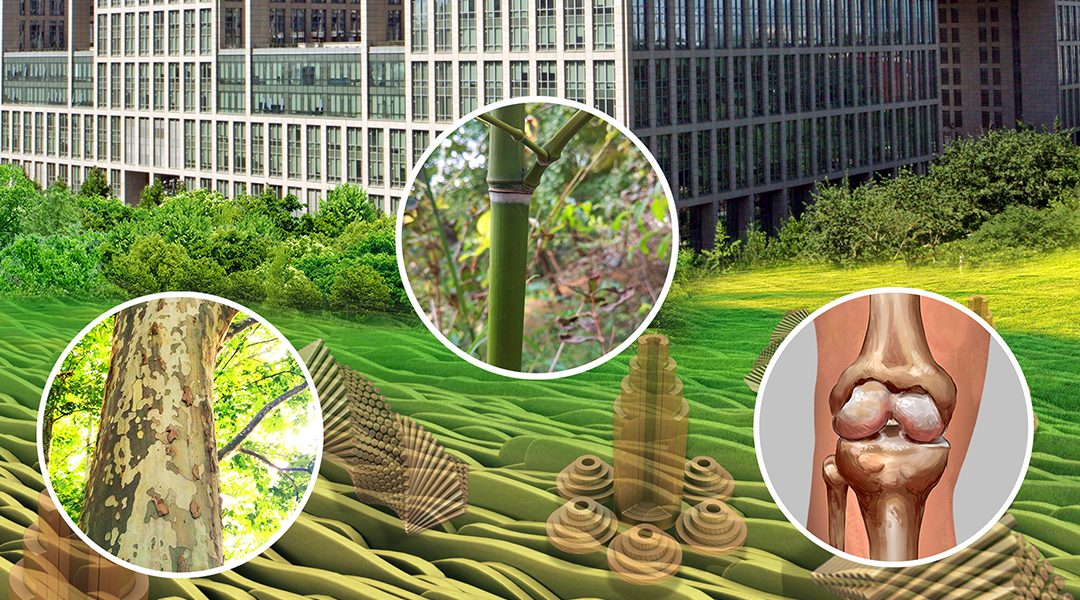

A recent special issue of Advanced Materials, issue 45 in 2017, was dedicated to highlighting nature-inspired surface and materials research at Beihang University in Beijing, China.