New research inspired by “viral factories” shows the potential of encapsulating target molecules in membrane-free compartments.
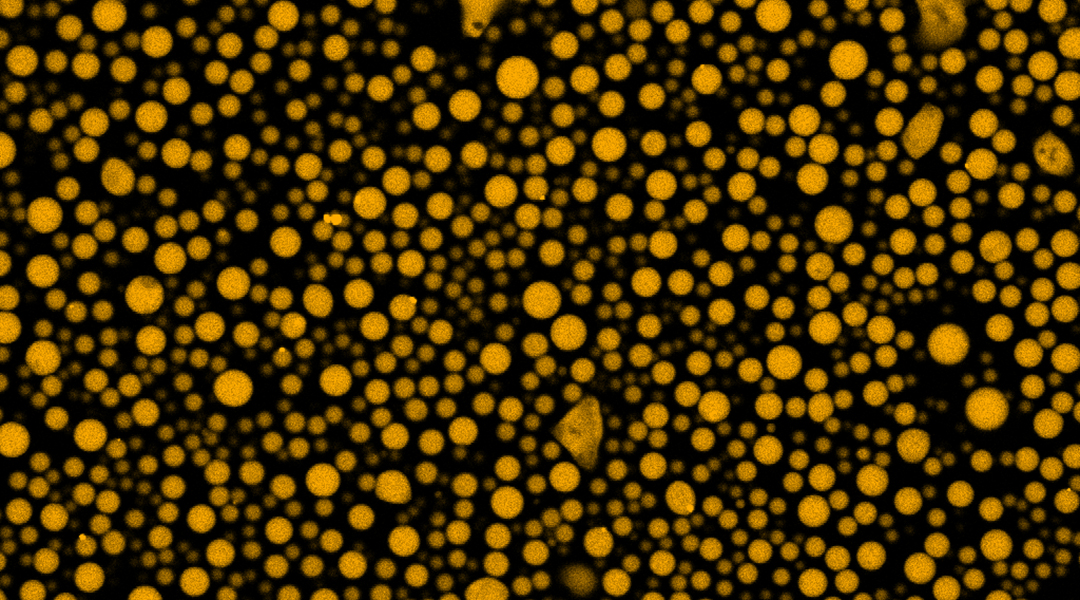

New research inspired by “viral factories” shows the potential of encapsulating target molecules in membrane-free compartments.

A new device setup enables an interface between biomolecules and electronic materials for biohybrid electronics.
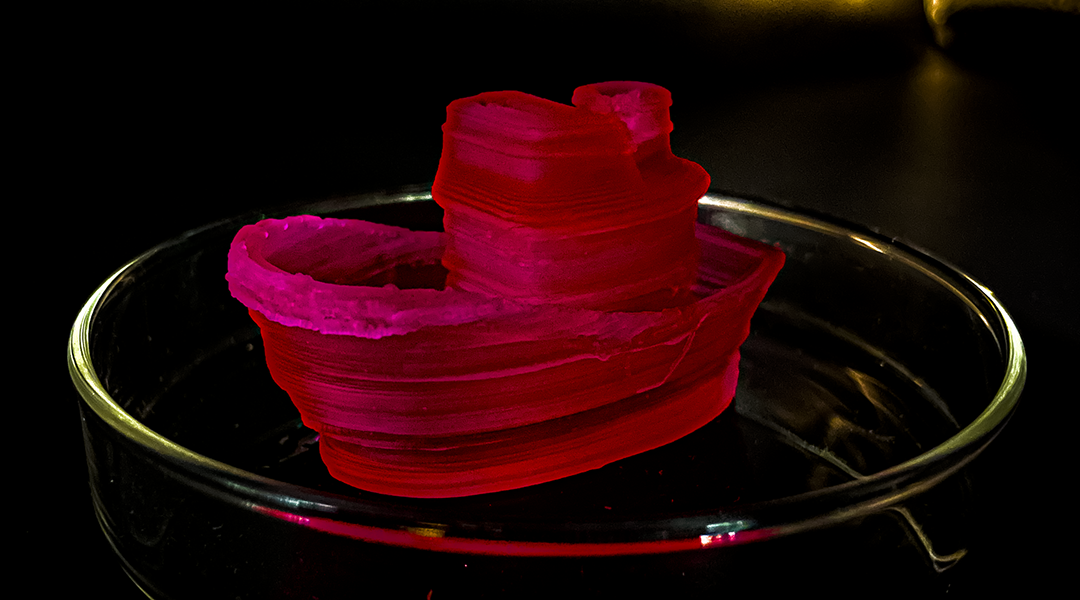
Researchers have created stiff, recyclable hydrogels that can be broken down into their base components and reshaped on demand.
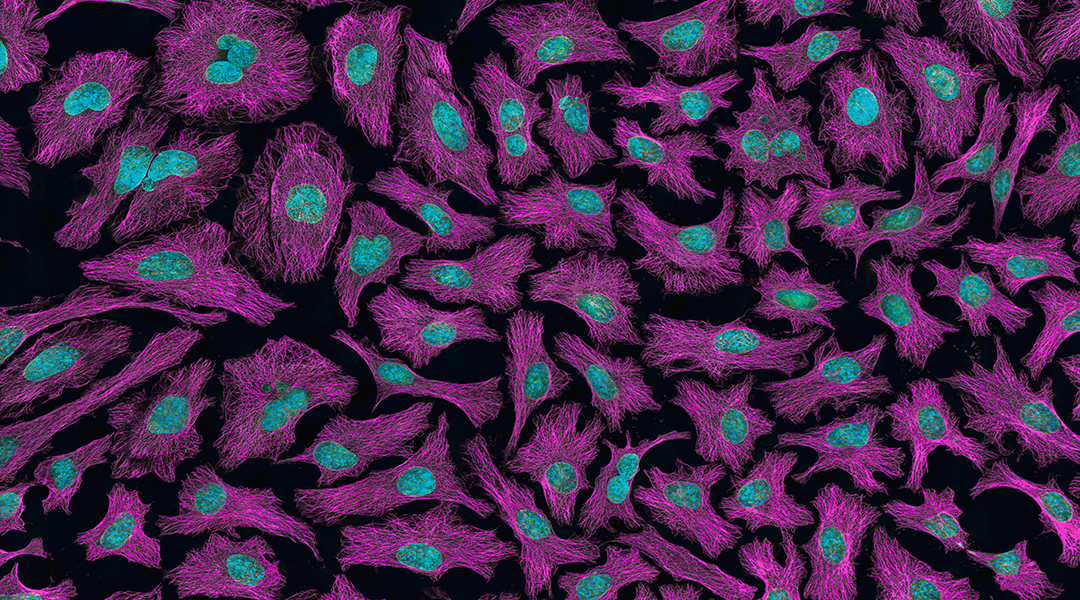
Nanoparticulate formula together with light augmentation could realize the potential for intranasal vaccines to protect against respiratory viruses.
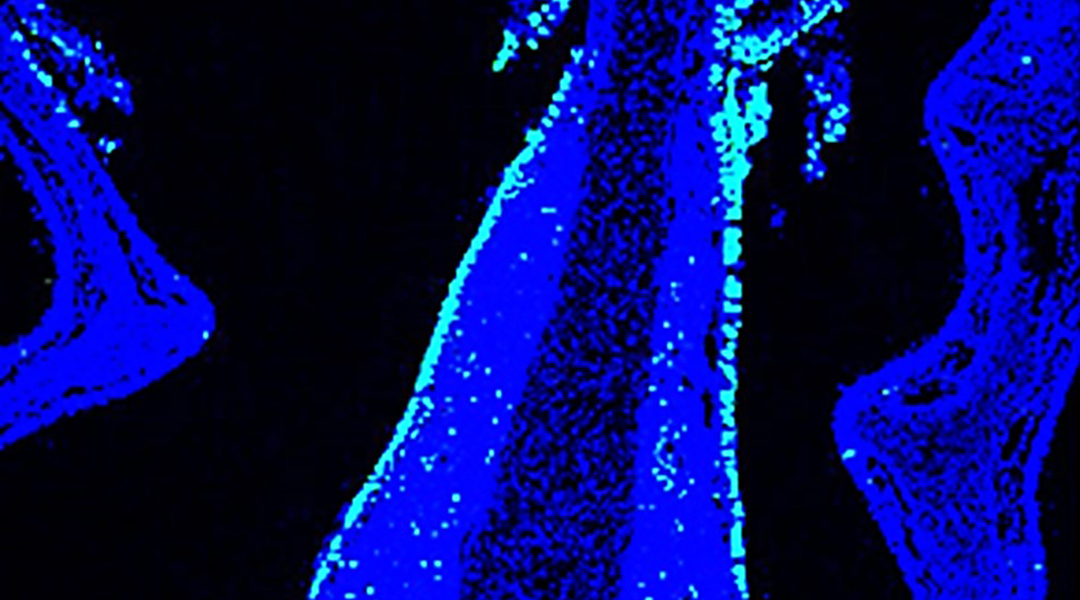
DNA robots built to transverse fluidic cell membranes and control cell function for future regenerative and cell-based therapies.
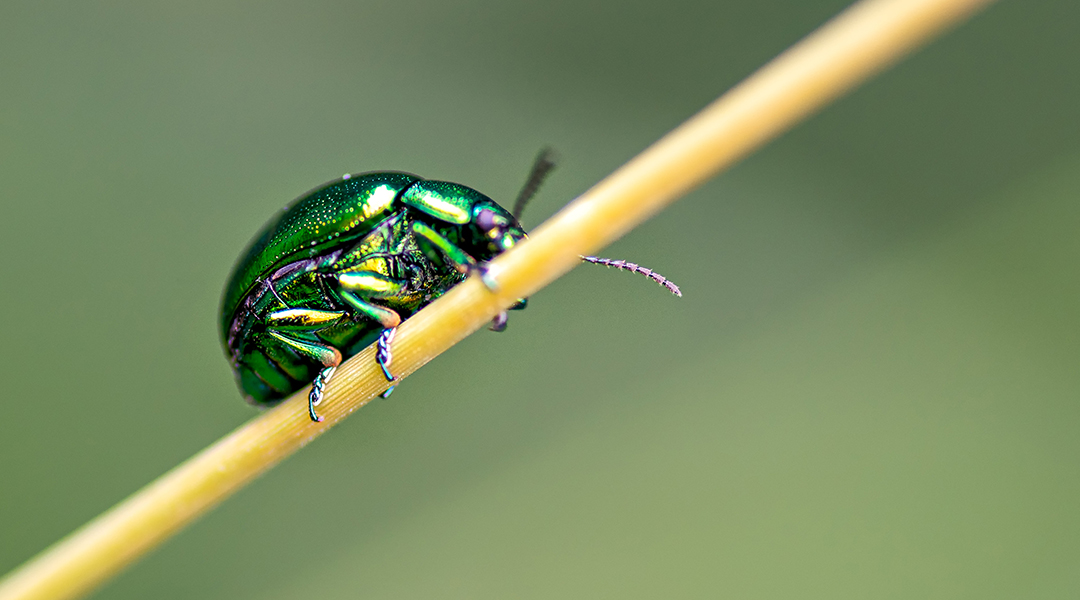

Exoskeletons of tree-dwelling and terrestrial beetles differ in their structural-mechanical properties and have inspired the design of new composite materials used for bioengineering.

Genomic editing tools can reverse disease causing mutations to provide cures — once we can conquer the remaining barriers.
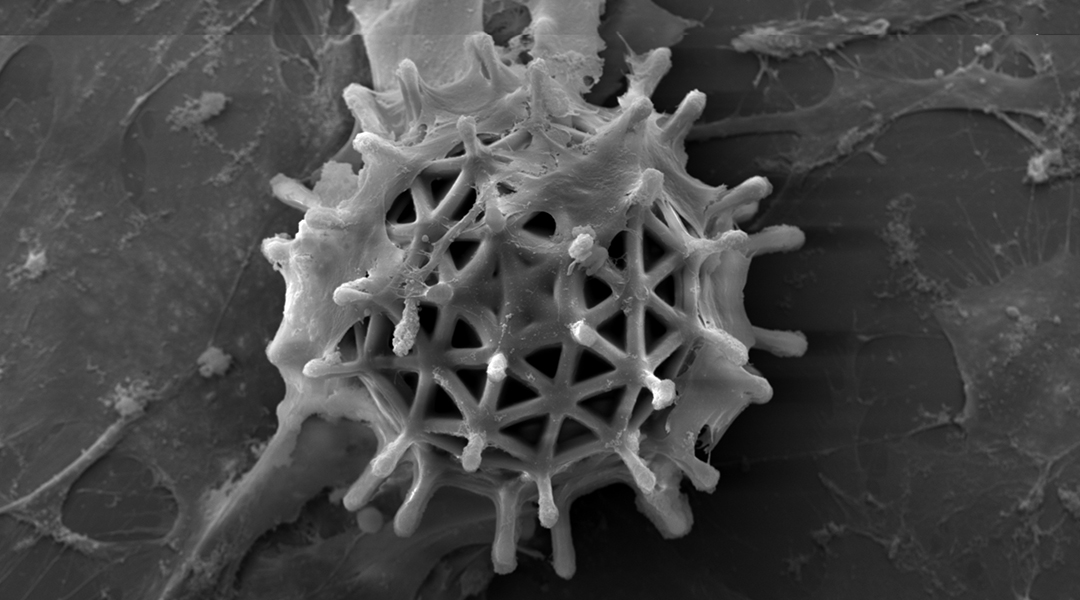
Researchers find the sweet spot between strength and biocompatibility in these tiny cell-carrying microrobots.
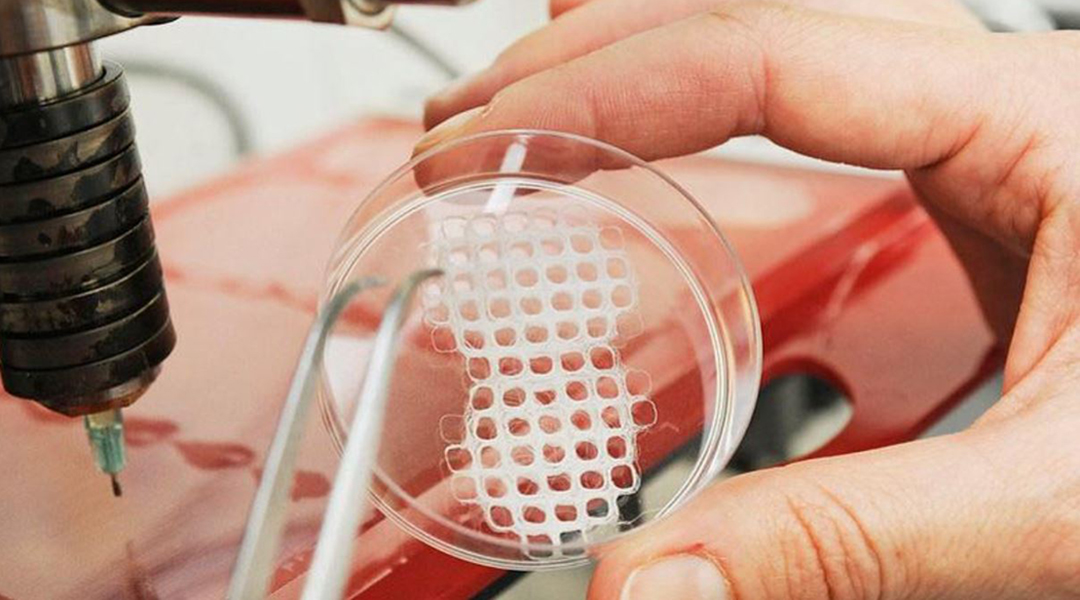
Machine vision and artificial intelligence can fine tune medical 3D printers to enable custom made tissue implants to suit the individual patient.

Scientists use 3D printing to combine fundamental biology research methods with high-throughput screening of cell culture surface topographies.