A new biomimetic strategy provides a platform for the synthesis of ligand-targeted nanovesicles that can mediate selective drug delivery to specific tissues.

A new biomimetic strategy provides a platform for the synthesis of ligand-targeted nanovesicles that can mediate selective drug delivery to specific tissues.
Significant implications of and recent progress made in iCVD-based technologies in three fields: electronic devices, surface engineering, and biomedical applications are discussed.

Latest Advanced Healthcare Materials covers.
For nearly 35 years, CD4 T-cells and their immunephenotyping and enumeration were the focal points of HIV/AIDS research.

Advanced Healthcare Materials papers you have downloaded and read the most in the past two months.
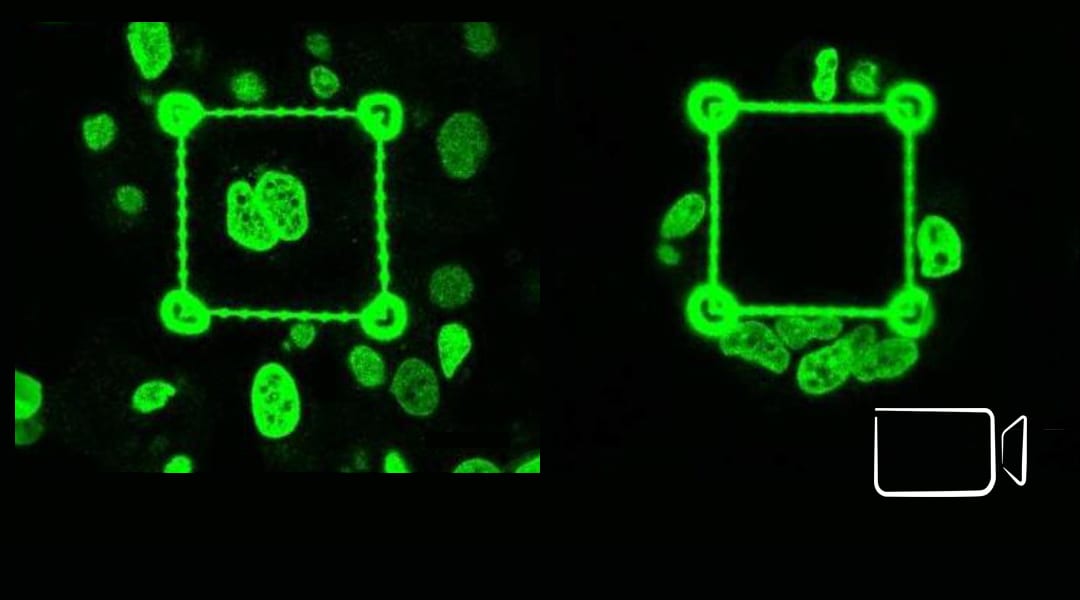
An approach to study tumor cell invasiveness by exploiting an innovative class of polymeric scaffolds based on two-photon lithography to control the stiffness of deterministic microenvironments in 3D is presented.
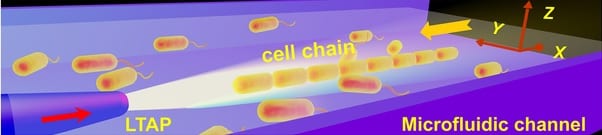
A team of Chinese researchers demonstrated an optofluidic strategy, by implanting the microfluidic technique with a large-tapered-angle fiber probe (LTAP), to organize and transport a cell chain in a noncontact and noninvasive manner.
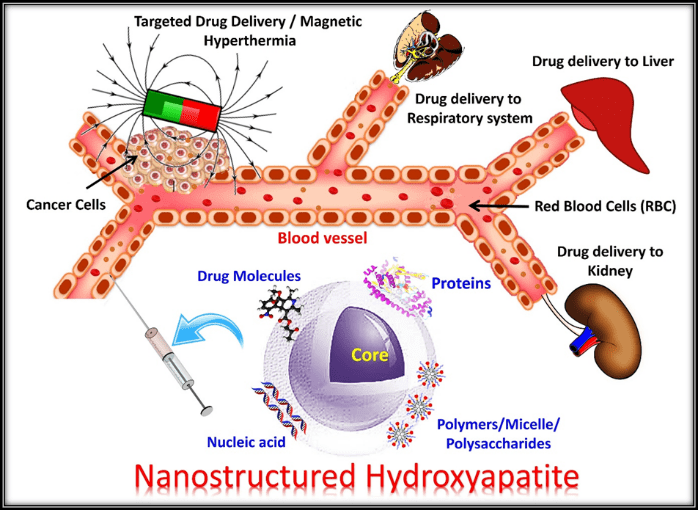
Nanostructured hydroxyapatite (nHAp) appears to have a great potential to revolutionize the hard tissue-engineering field, starting from bone repair and augmentation to controlled drug delivery systems.

A group of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) generate living materials and devices by 3D printing genetically programmed bacterial cells. The living bioink can be used to print novel materials including logic gates and a living tattoo for chemical detection on human skin.
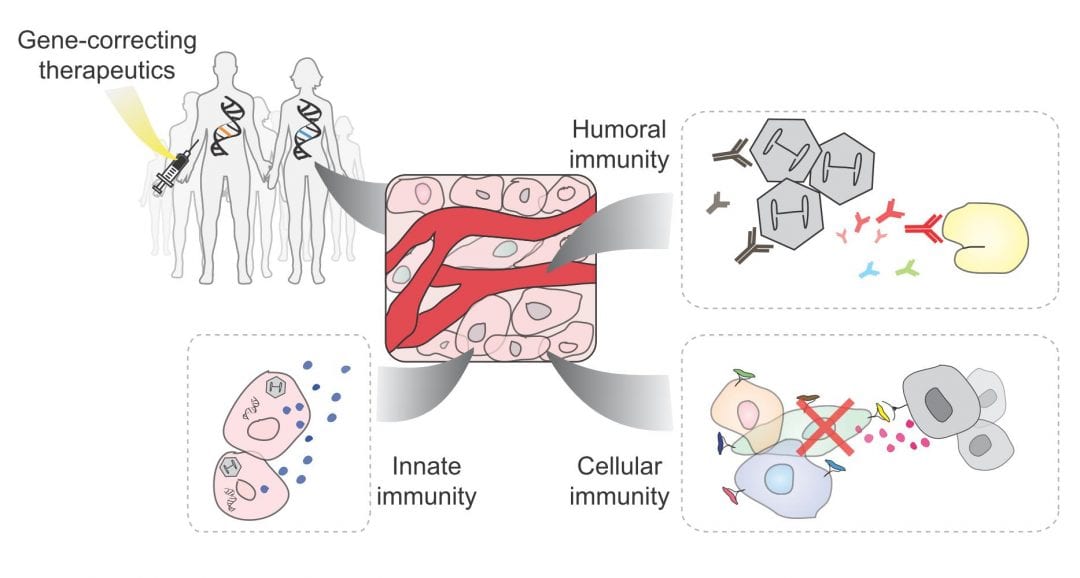
Genome-editing therapeutics introduce foreign nucleic acids and proteins into the circulation and cells, which can activate the innate, cellular, and humoral immunity in human patients. The key obstacle in translating CRISPR therapeutics to the clinic is hence to identify, diminish, and monitor these immunological risks before adverse immune reactions.