A team of scientists have created a cost-effective way to destroy bacterial biofilms, paving the way for advancements in everything from healthcare to utilities.
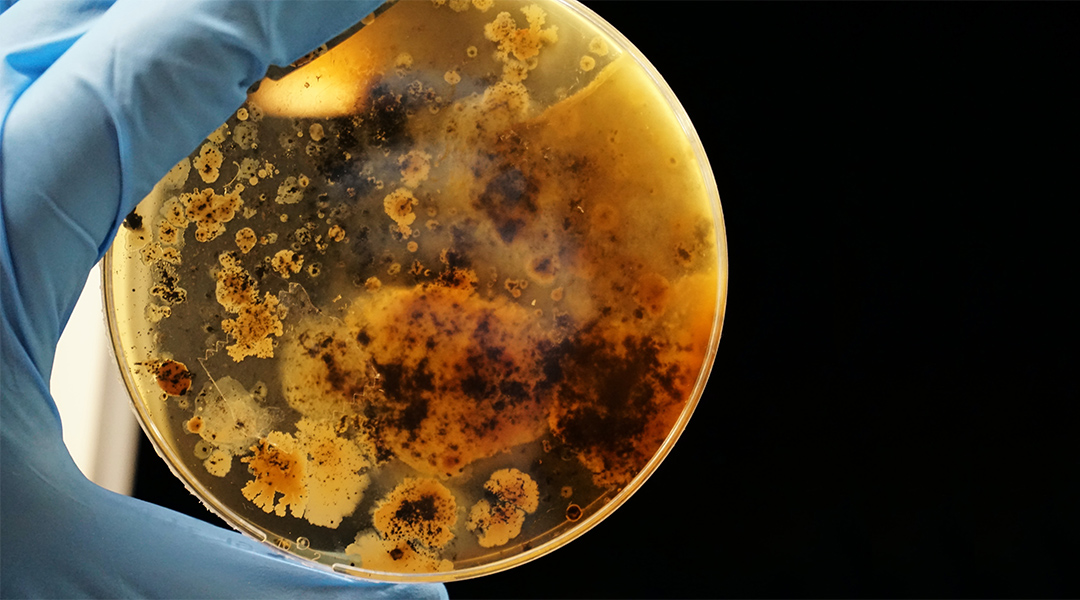

A team of scientists have created a cost-effective way to destroy bacterial biofilms, paving the way for advancements in everything from healthcare to utilities.
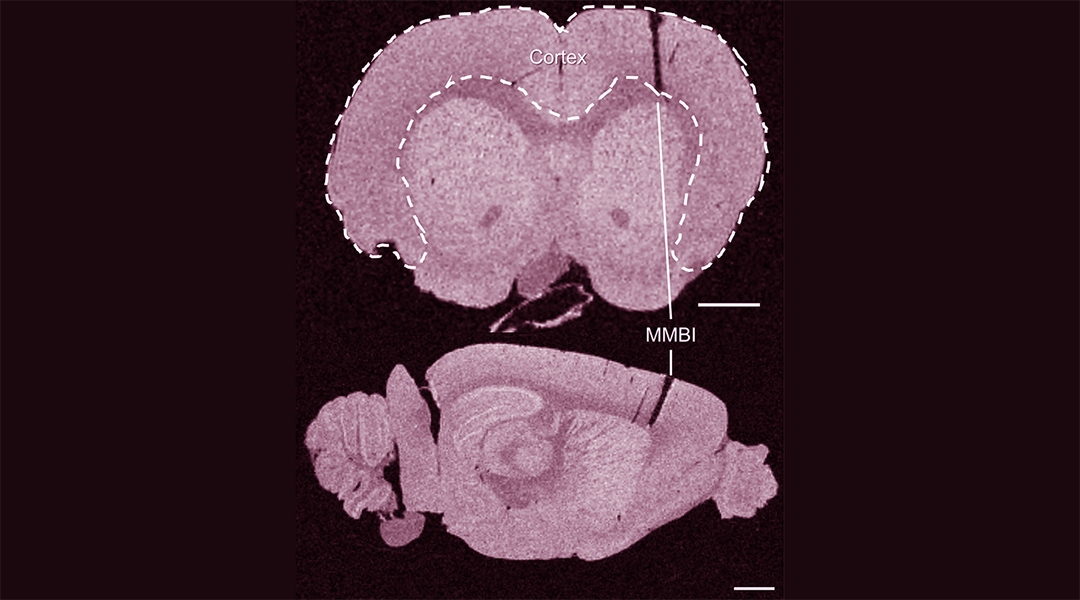
Pudding-like implants with a sugar-based delivery system show promise in reducing the foreign body response against brain implants.
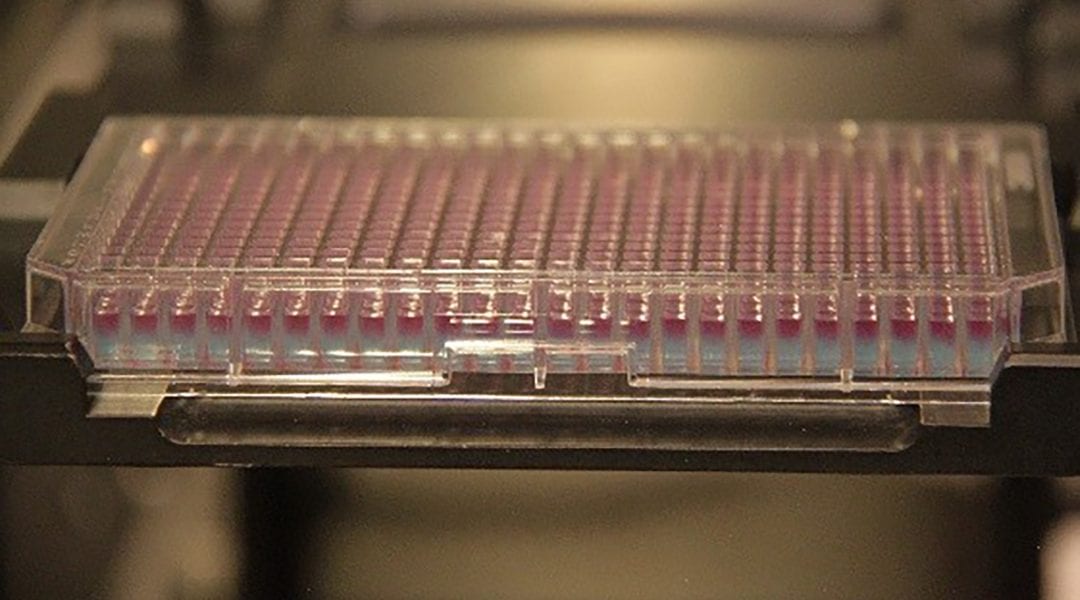

A temperature-responsive, porous hydrogel enables more efficient and sustained protein synthesis.
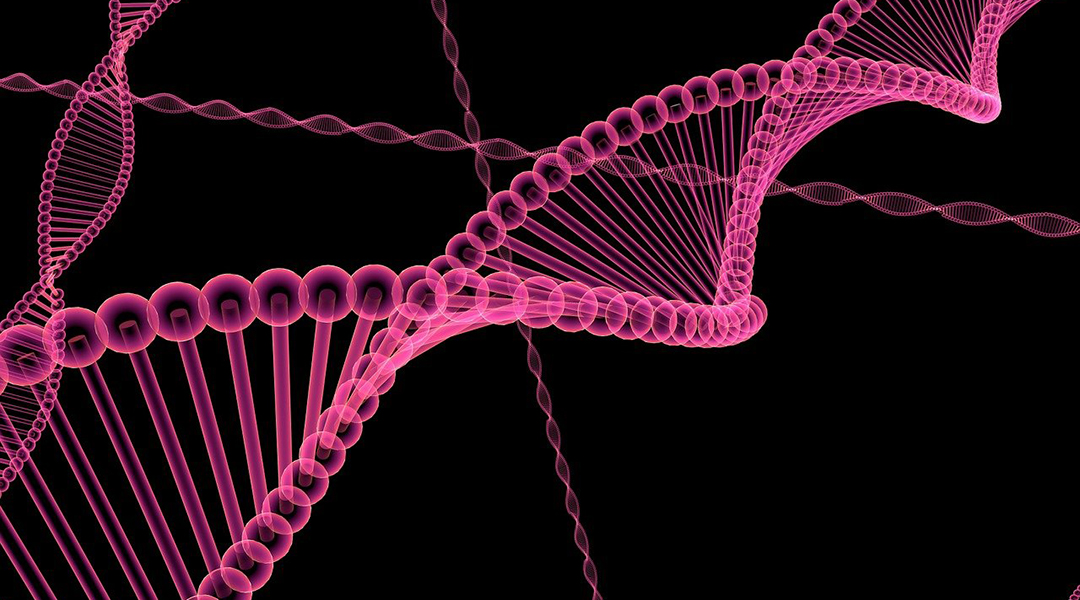
Complex 3D nanoscale architectures based on DNA self-assembly can conduct electricity without resistance and may provide a platform for fabricating quantum computing and sensing devices.
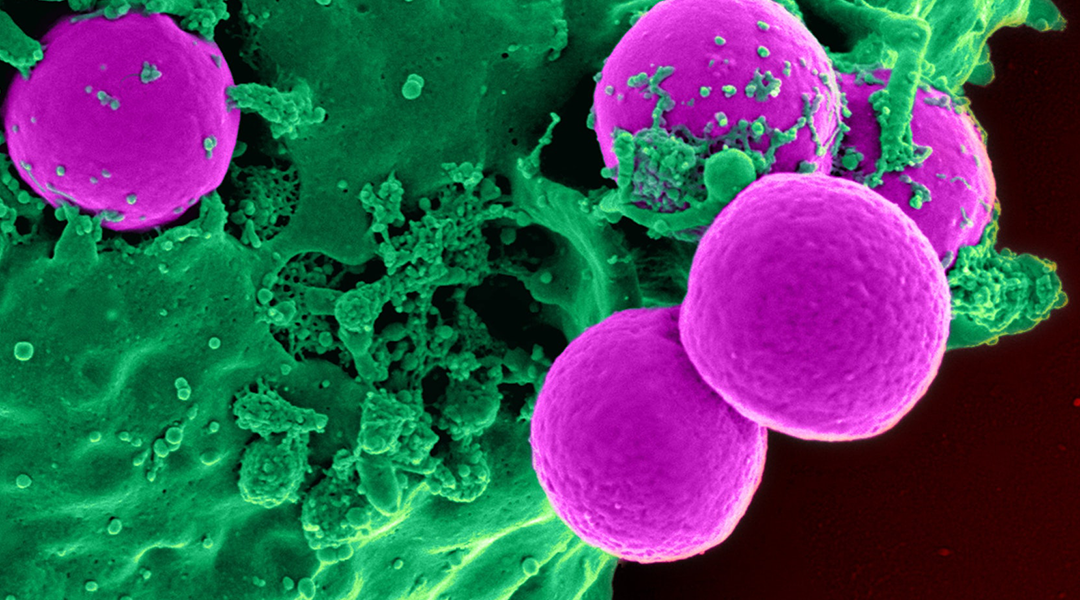
Nanoparticles are not new; bacteria have been making them long before we had a language to name them.
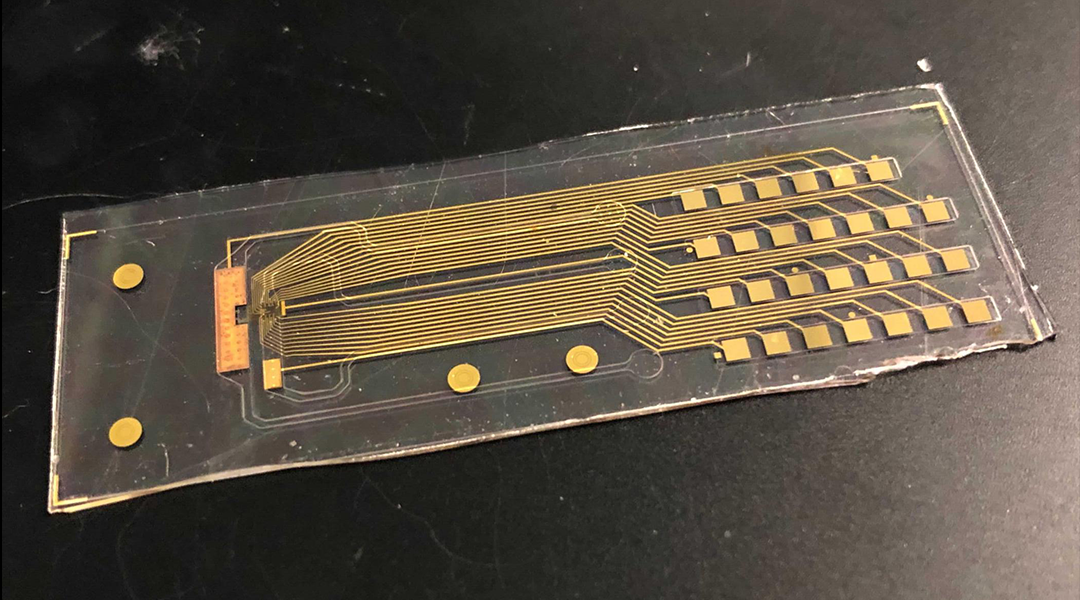
Driven by a machine learning algorithm, the closed-loop biohybrid device maintained a set membrane voltage in human stem cells for 10 hours.

Microalgal biorefinery has emerged as one of the sustainable solutions for the production of biofuels and biochemicals. However, there are still some difficulties to be solved.
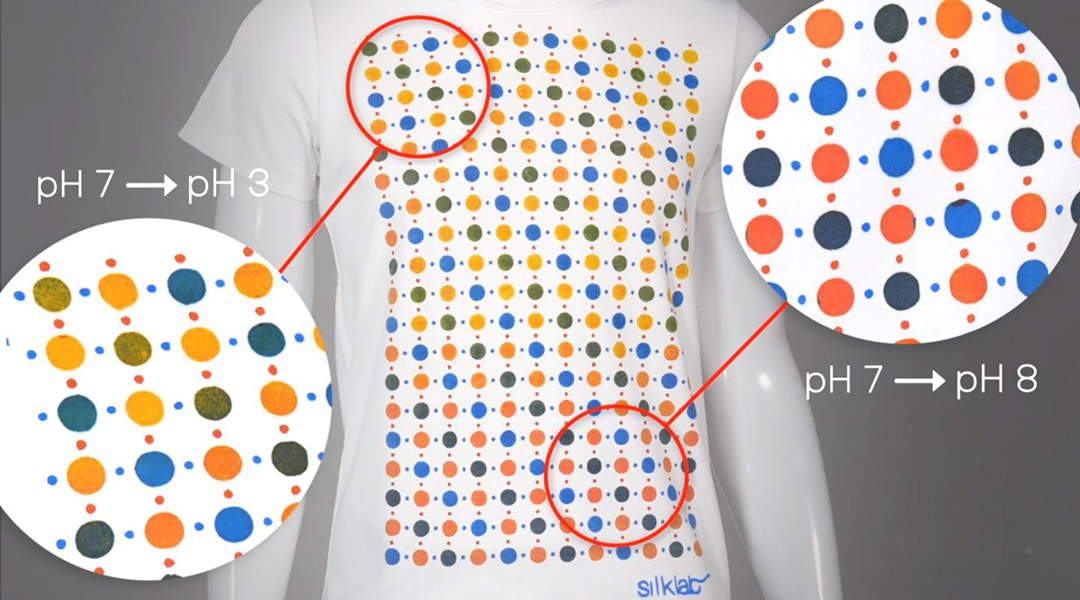
Bioactive inks printed on wearable textiles can map conditions over the entire surface of the body, including possible pathogens.
A new stretchable and conductive nanocomposite shows promise as a biocompatible material for correcting arrhythmia in patients.
A nanocarrier that can deliver siRNA into the lungs is investigated for the treatment of severe asthma and other lung diseases.