Scientists pioneer mixed-valence molecules in quantum-dot automata for faster, room-temperature operation, overcoming transistor limits.

Scientists pioneer mixed-valence molecules in quantum-dot automata for faster, room-temperature operation, overcoming transistor limits.
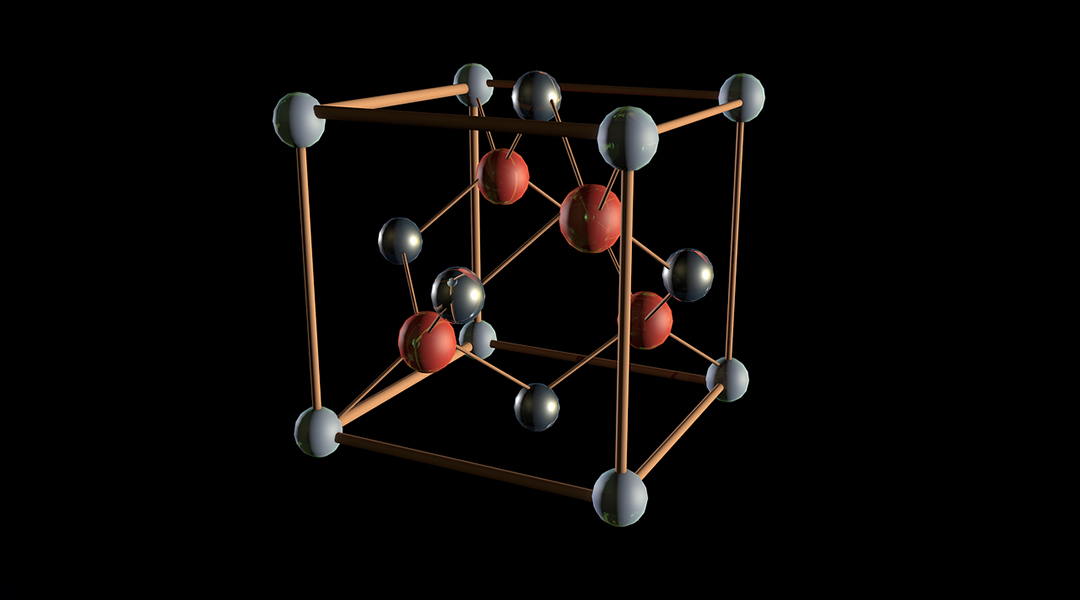
A newly discovered material and its intriguing properties could pave the way for more efficient computing.
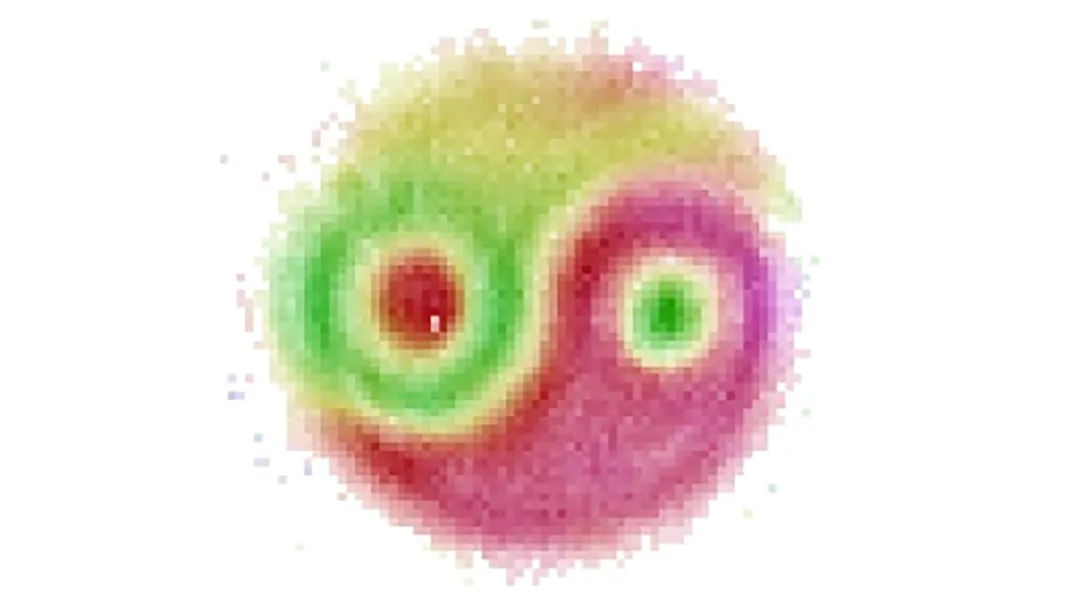

The mysterious phenomenon that Einstein once described as “spooky action at a distance” was seen as a wavefunction between two entangled photons.

A new type of superconductor may just be what physicists have been searching for over the past 40 years.
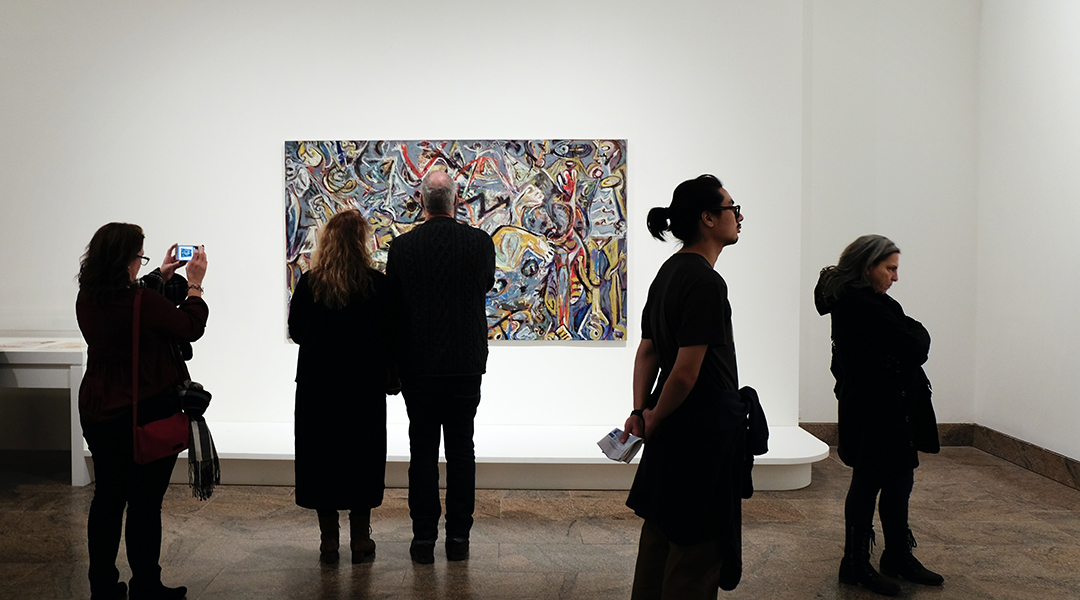

Is AI that predicts which paintings are memorable and famous, regardless of content, style, or context, a threat to creativity or tool for positive change?
Quantum key distribution is the only way to ensure an absolutely secured connection protected by the laws of quantum physics.
An optical device uses light-based signals for computation and communication and is a vital step toward advanced neuromorphic computers.
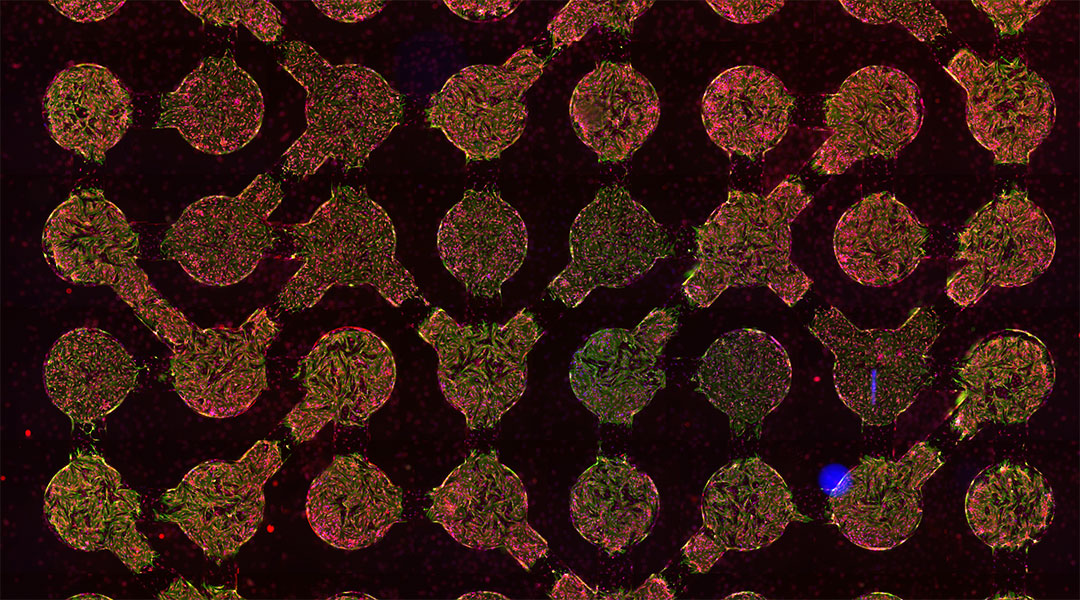
A biocomputer built from connected heart cells solves computational problems with high accuracy and at a low computational cost.

Crediting ChatGPT as an author on scientific papers has sparked debate around the role it should play in the scientific literature.
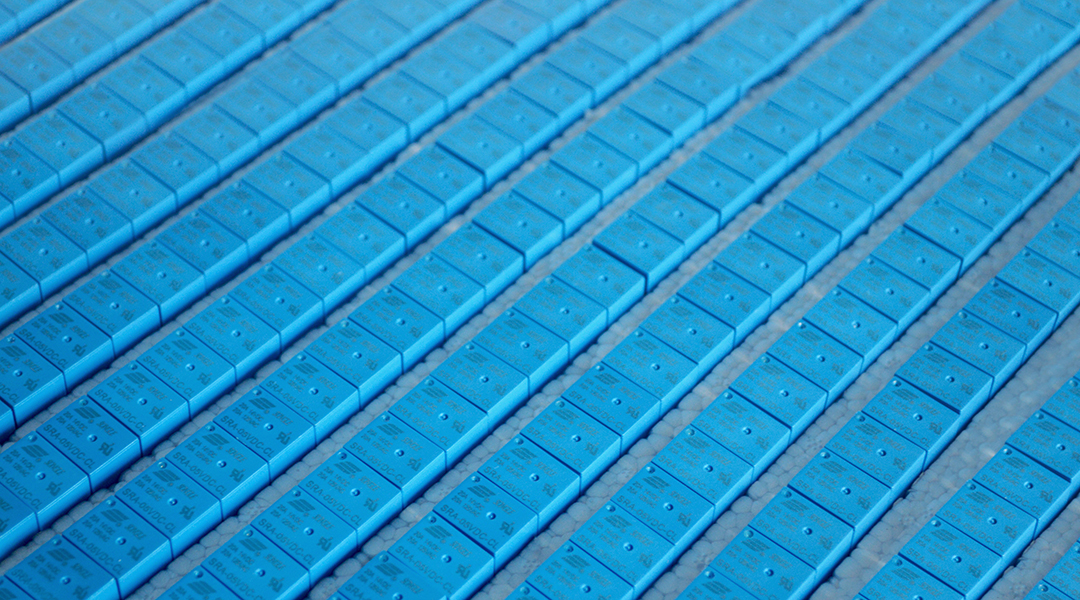

A device brings memory and processing together, helping minimizing errors and avoiding increasing energy demands due to huge amounts of data.