A charged microneedle patch for pain-free delivery of anesthetics could replace anxiety-inducing needles in dental work.
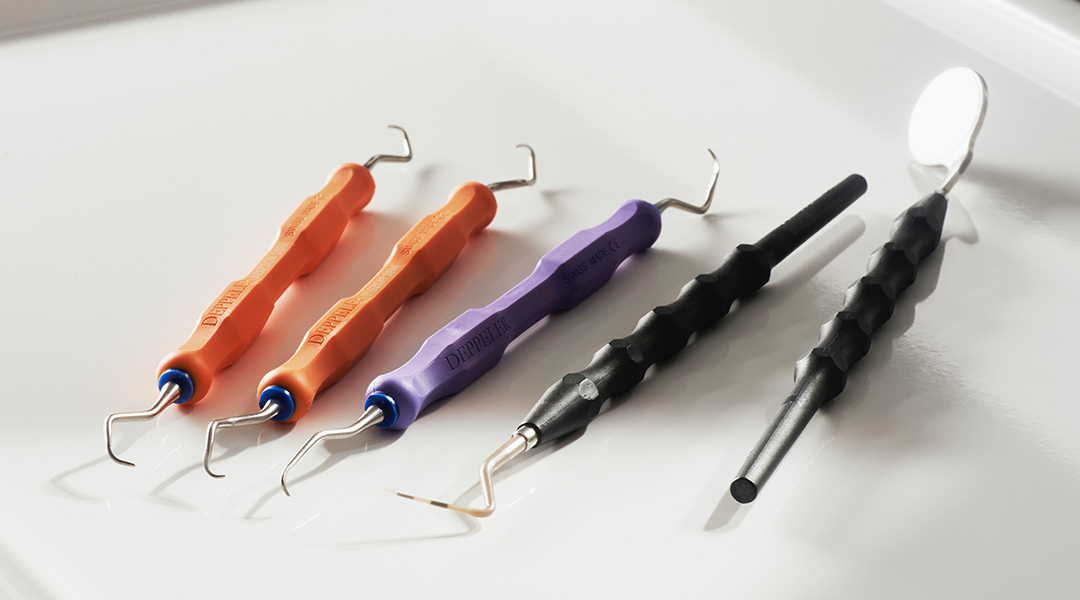


A charged microneedle patch for pain-free delivery of anesthetics could replace anxiety-inducing needles in dental work.
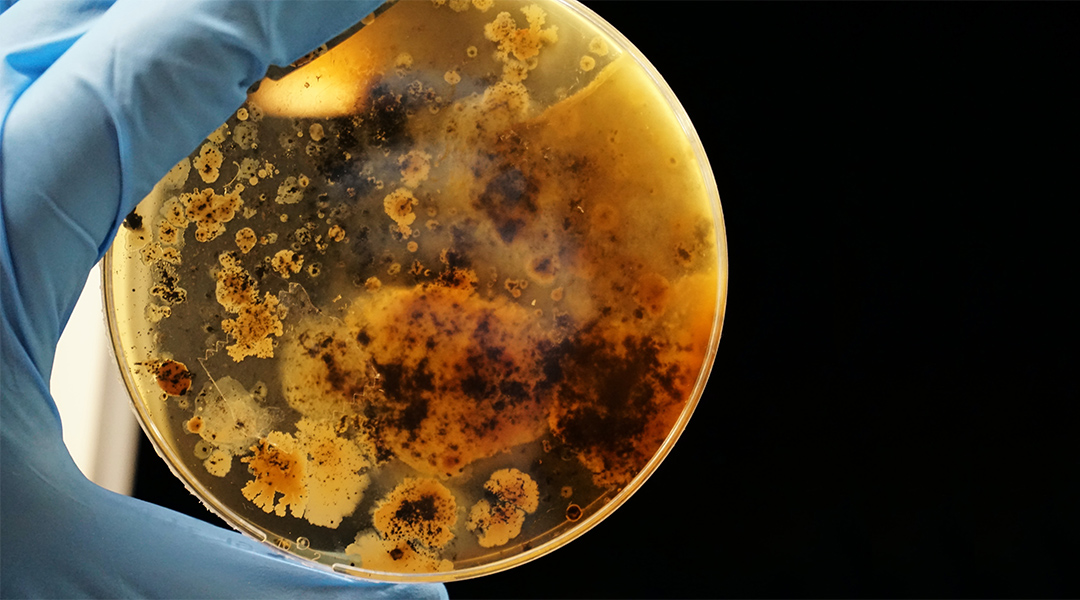
A team of scientists have created a cost-effective way to destroy bacterial biofilms, paving the way for advancements in everything from healthcare to utilities.
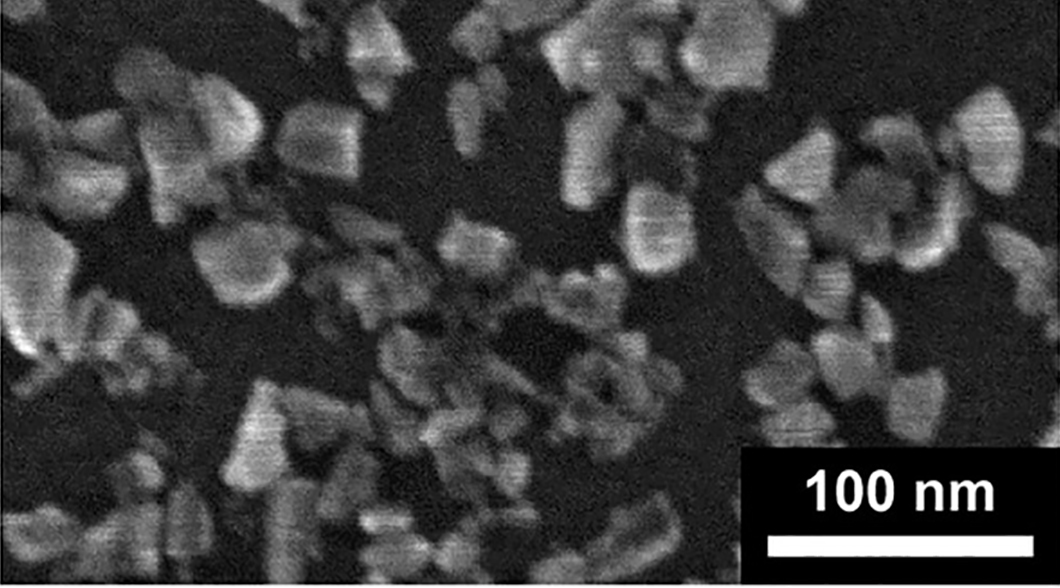
Fluorescent nano-sized diamonds give a better glimpse inside cells.
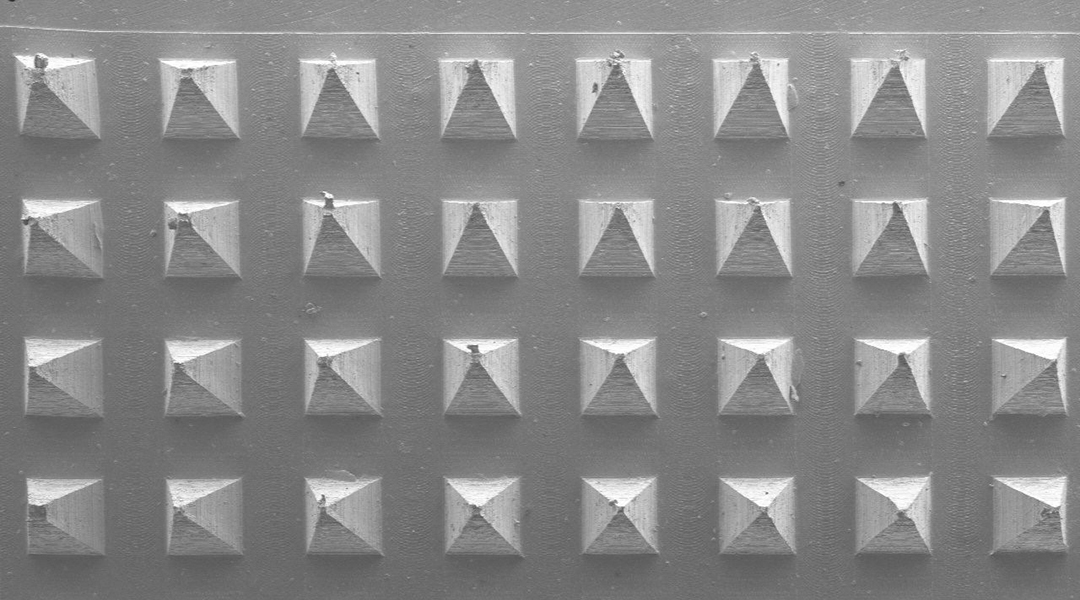
Minimally invasive delivery of capsaicin into adipose tissues under the skin shows promise for countering obesity.
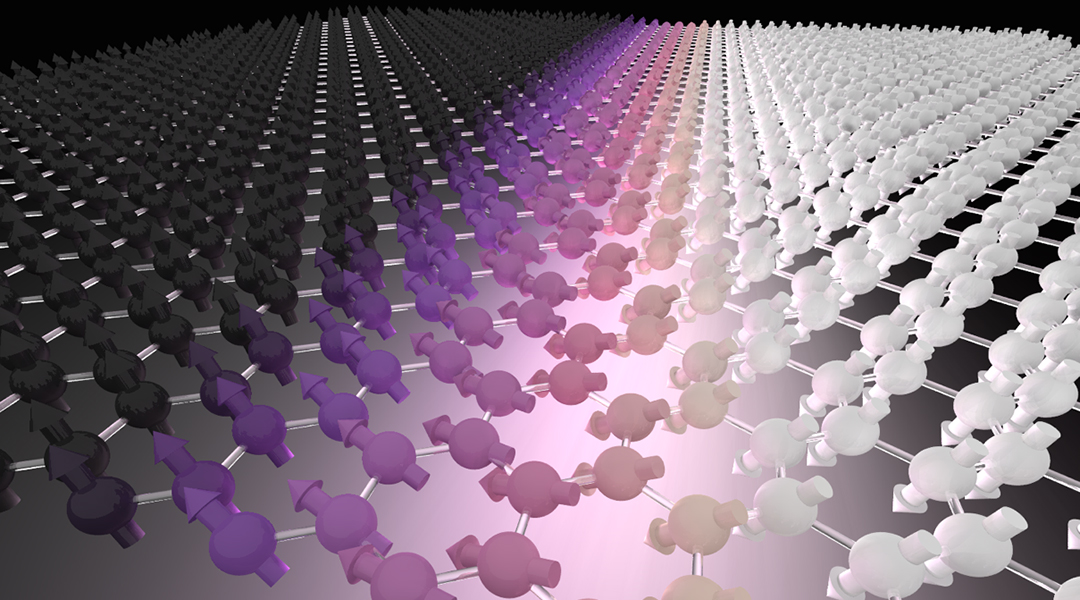
Using theoretical and experimental analysis, researchers aim to better understand the novel and intriguing magnetic properties of 2D materials for the next generation of information technologies.
Bacteria controlled by magnets could one day deliver medicine directly to the cells that need it.
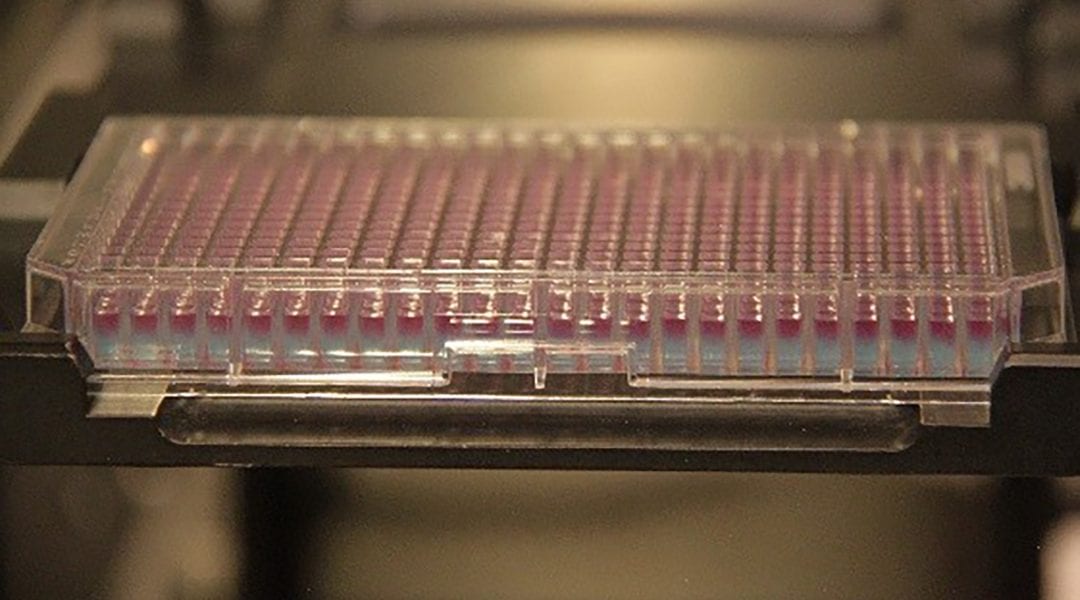

A temperature-responsive, porous hydrogel enables more efficient and sustained protein synthesis.
Researchers enhance the immune response against the receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 by presenting it on liposomes, providing a promising strategy for vaccine development targeting this domain.
Nanoparticles are not new; bacteria have been making them long before we had a language to name them.
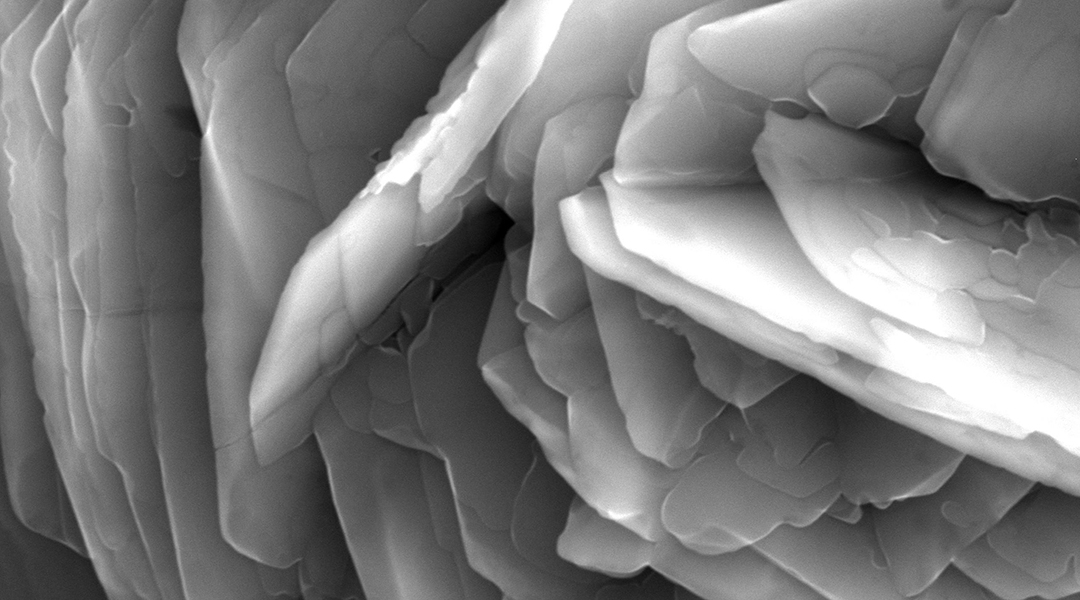

Novel rosette-like formations may open new opportunities in corrosion science, manufacturing of titanium-based implants, and fluid-surface interactions.