Topical reviews from the Advanced Materials Interfaces Hall of Fame series are among the most popular articles on offer to our readership – and they’re free to read for a limited time.


Topical reviews from the Advanced Materials Interfaces Hall of Fame series are among the most popular articles on offer to our readership – and they’re free to read for a limited time.
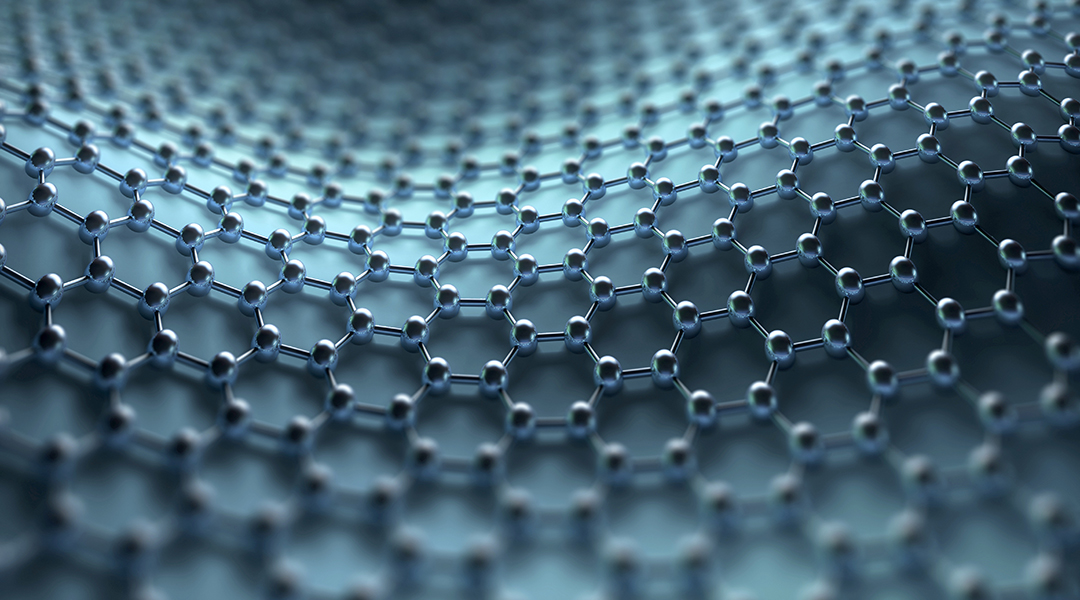
A new method to improve the mechanical durability of graphene films based on the introduction of chemically-attachable nanometer-thick organic patches onto a graphene surface is reported.
In situ vaccination therapy has immense potential in cancer treatment for clinical use. To date, in situ vaccination is already used to treat bladder cancer and melanoma, and with further study could become an important approach to expand immune-based cancer treatment.
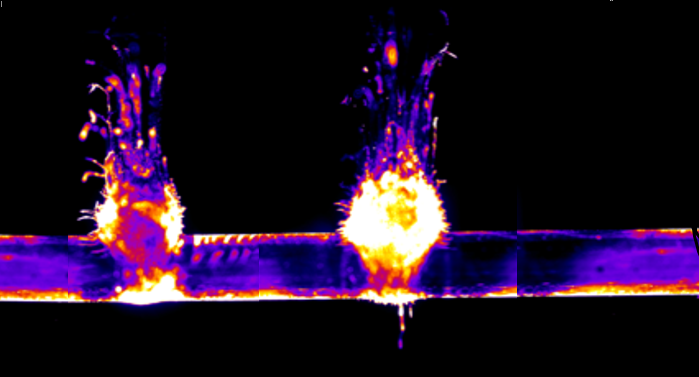
Cone-shaped gold nanoparticles are activated by ultrasonic waves, with applications in cost-effective targeted drug delivery.
![Microfluidic Devices for Affordable Personalized Healthcare [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/adma201705759_ASN_image.jpg)
Muhammad Mustafa Hussain and co-workers from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology address the potential of complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS)-based microfluidic devices for affordable personalized healthcare.
A colloidal nanocrystal layer enables 2D to 3D shape transformations of “hard” inorganic materials.

A team from the USA have developed a technique for making gold nanoparticles from old SIM cards .
![3D Microflower Cathode Promotes Oxygen Diffusion in Lithium–Oxygen Batteries [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/aenm201800089_ASN_image.png)
Dr. Mingsen Zheng, Prof. Quanfeng Dong, and co-workers from Xiamen University design a plant-inspired, high-performance cobalt sulfide–porous carbon foil (PCF) electrode for lithium–air (Li–O2) batteries.
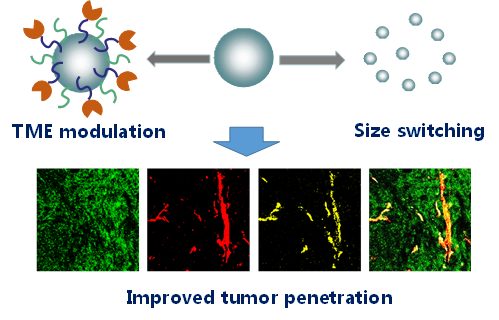
Rational design of nanoparticles with state-of-the-art strategies can effectively improve the penetration as well as therapeutic efficacy of cancer nanomedicines
![Separating Chiral Molecules with Thermoresponsive Nanotubes [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/smll201800030_ASN_image.jpg)
Dr. Naohiro Kameta from the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) and colleagues design thermoresponsive poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-coated nanotubes for simple and efficient separation of chiral molecules.