A team of German scientist developed a new laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy approach that can differentiate between hard and soft tissue in the mouth region and could help improve surgical dental treatment.
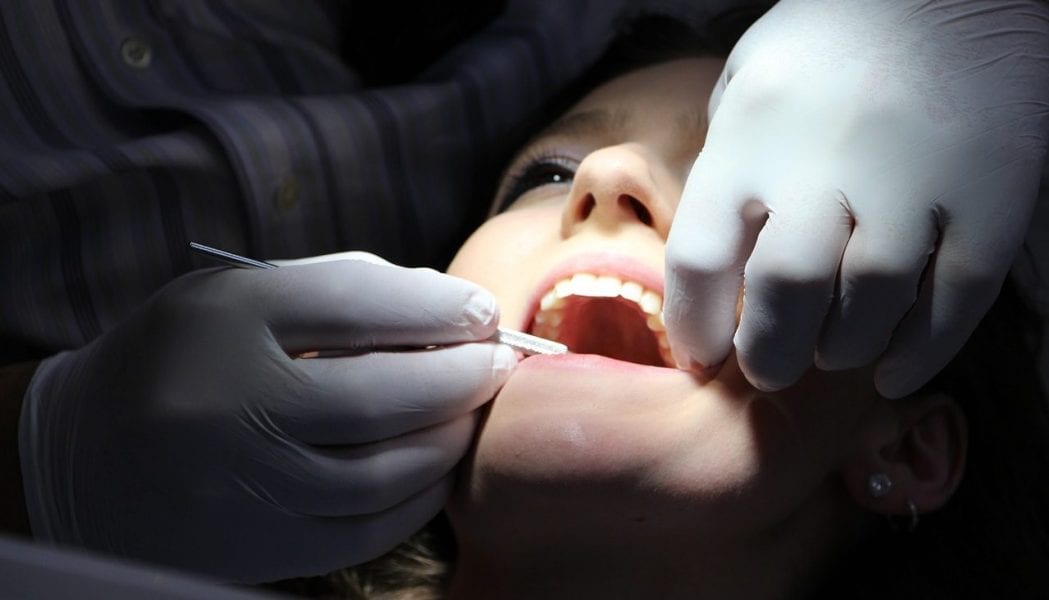

A team of German scientist developed a new laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy approach that can differentiate between hard and soft tissue in the mouth region and could help improve surgical dental treatment.
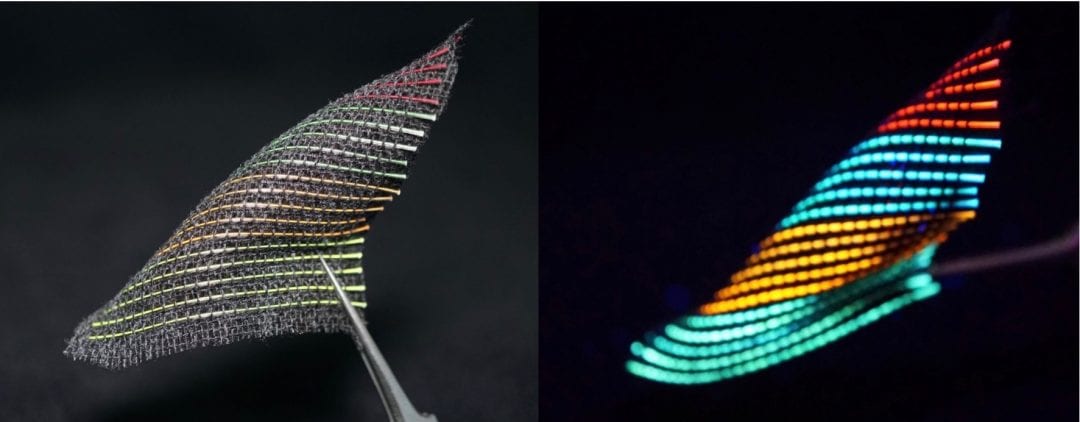
A novel family of colorful fluorescent supercapacitor fibers allows for continuous energy storage in flexible systems used in the dark.
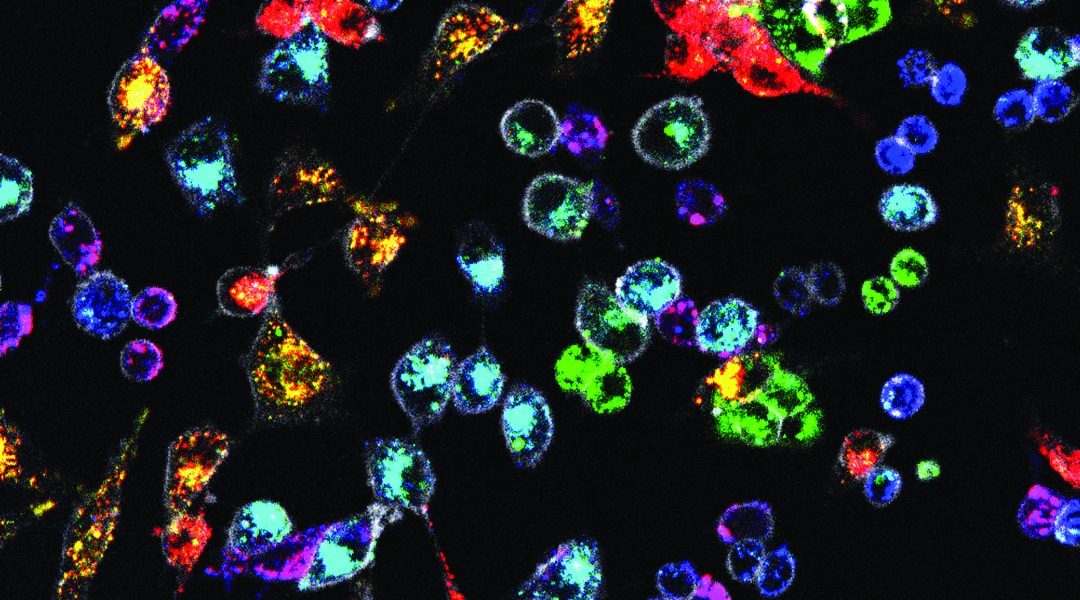
A method that allows the long-term labeling of different cell populations in tens of different colors using fluorescent nanoparticles.
Two new, Special Sections dedicated to imaging technologies.
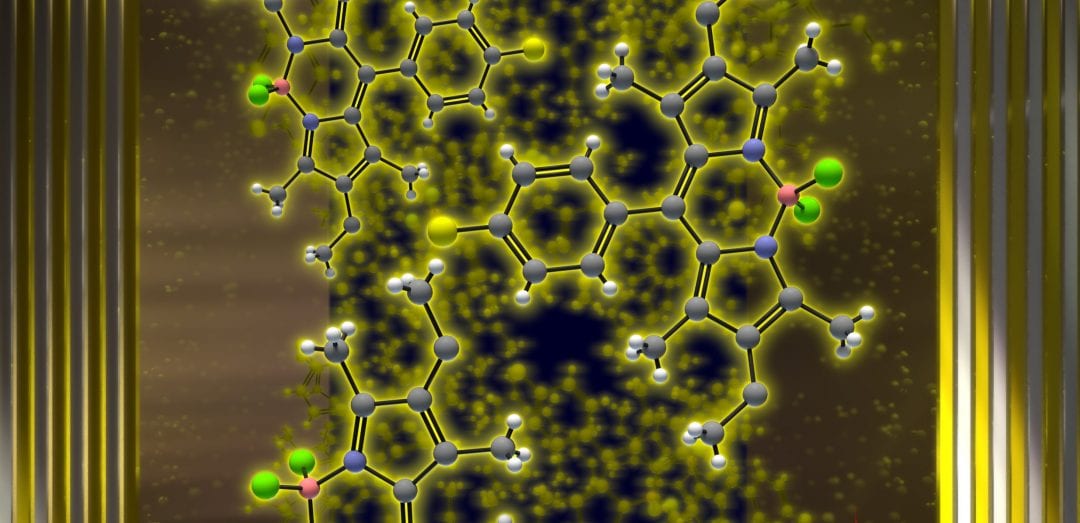
Pavlos G. Lagoudakis, David G. Lidzey and co-workers observed polariton condensation in the yellow part of the visible spectrum from a planar organic semiconductor microcavity containing the molecular dye bromine-substituted boron-dipyrromethene.

A team of German scientists used fast spontaneous Raman and Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) combined imaging to study the distribution and composition of lipids related to cardiovascular disease.
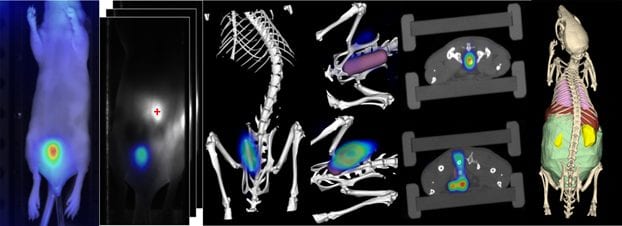
German scientists recently developed an improved FMT reconstruction for the imaging of deep tissue regions which could be beneficial in imaging colon cancer and inflammatory bowel disease.
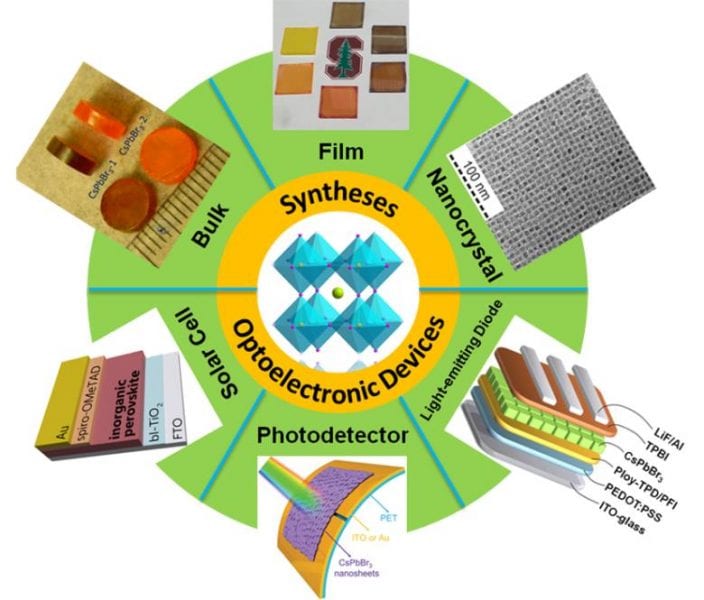
An outline of the recent progress in the syntheses of IMH perovskites is provided.
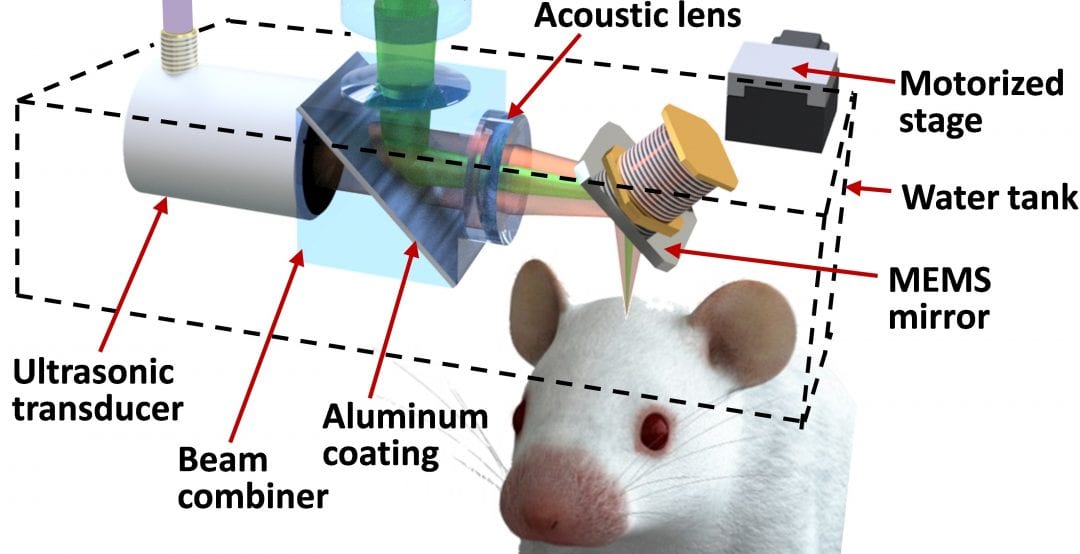
American neuro-scientists recently demonstrated getting a small step closer to creating a better understanding of so-called mini-strokes, which are related to cognitive decline and dementia, using high-speed optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy.
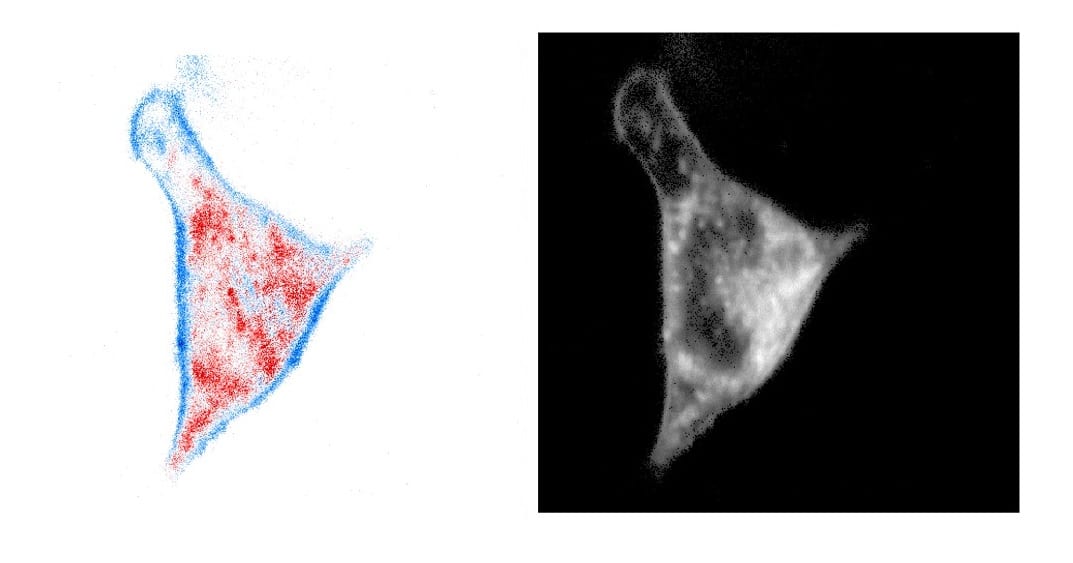
German and British researchers tested a novel Noise-Corrected Principal Component Analysis (NC-PCA) method for time-domain FLIM data and showed how useful and robust this new technique can be.