Rice University scientists have developed a simple way to produce conductive, three-dimensional objects made of graphenefoam.


Rice University scientists have developed a simple way to produce conductive, three-dimensional objects made of graphenefoam.
Small solar systems seem to have a significant impact in terms of quality of life for their users and in helping them to keep connected to the global world.
![Polyphosphate-based Smart Material for Implants [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/smll201801170_ASN_image.jpg)
A team of researchers demonstrate Ca–polyphosphate (polyP) nanoparticles (NPs) as a smart biomaterial for regenerative medicine applications.
To fight antibiotic-resistant pathogens, and to ensure wide-spread application and high compliance, oral vaccinations are desirable, but pose drug delivery complications. An efficient nanoparticle system for vaccination against stomach ulcer causing Helicobacter pylori was recently reported.

Polymer therapeutics represent promising novel chemical entities under development for addressing CNS disorders, in which intravenous and intranasal administration are the most appealing strategies to achieve this paramount goal.
![A Dual-Modal Probe for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/smll201800901_ASN_image.jpg)
A novel probe for imaging amyloid-β (Aβ) in vivo is developed, enabling the early detection and diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease.
A vibrotactile actuator and robotic gripper that operate based on the Lorentz force principle are demonstrated.
![Glassomer: Glass That Can Be Processed Like Polymers [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/adma201707100_ASN_image.jpg)
A solid silica nanocomposite, ‘Glassomer’, can be processed using polymer fabrication techniques to obtain optical-grade fused silica glass.

A team of German researchers created a new multimodal system for rapid, noninvasive in vivo skin cancer screening is presented, combining optical coherence tomography (OCT) and optoacoustic (OA) modalities to provide precise tumor depth determination with a Raman spectroscopic modality capable of detecting the lesion type and, thus, providing diagnostic capability.
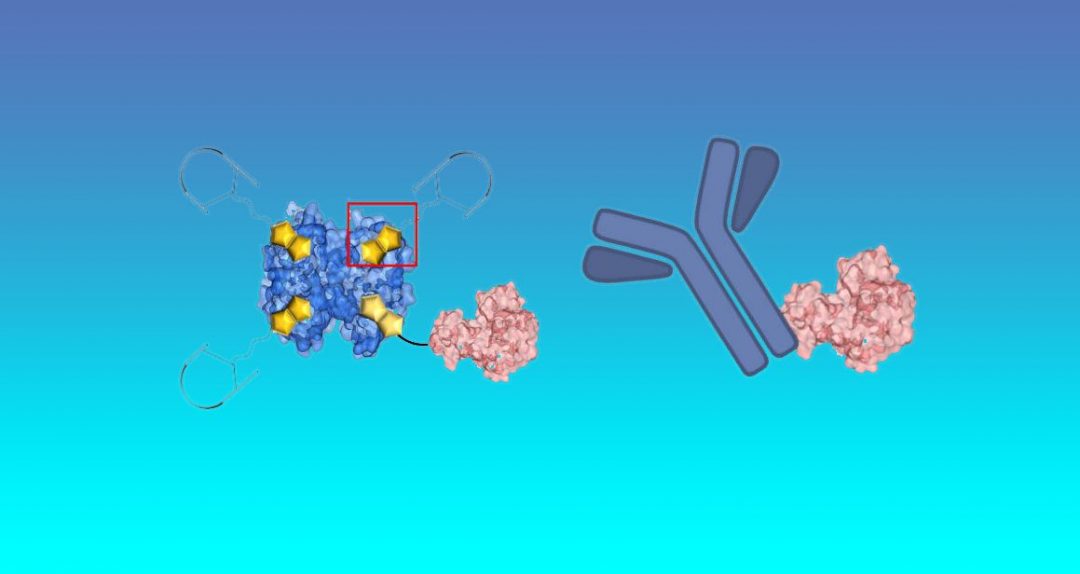
Bioactive entities are combined into structurally ordered multidomain protein complexes to mitigate selective targeting of a hallmark protein molecule in cancer diseases.