Scientists pioneer mixed-valence molecules in quantum-dot automata for faster, room-temperature operation, overcoming transistor limits.
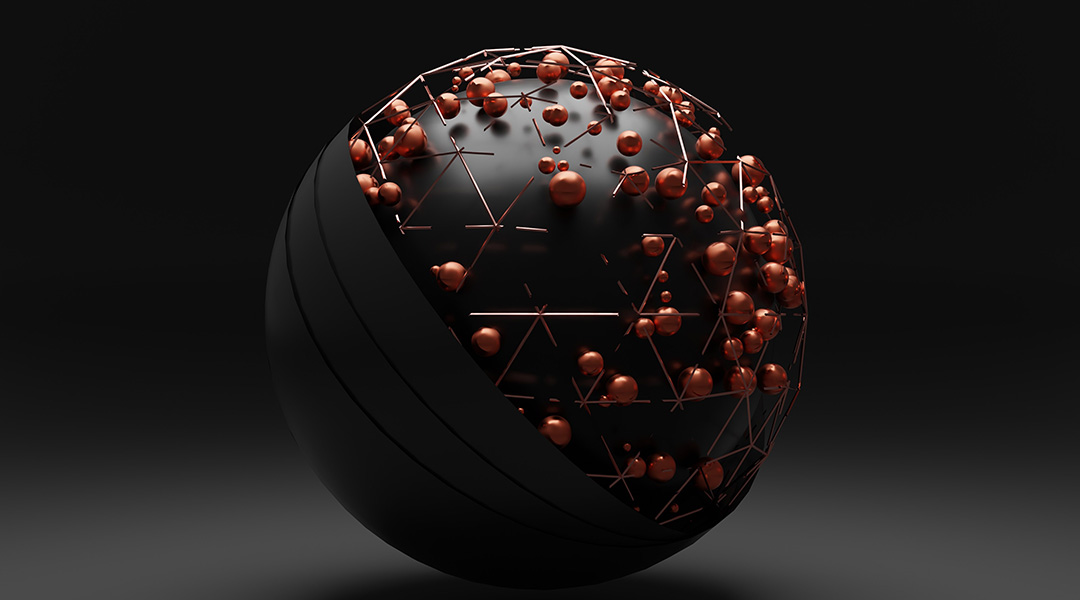

Scientists pioneer mixed-valence molecules in quantum-dot automata for faster, room-temperature operation, overcoming transistor limits.
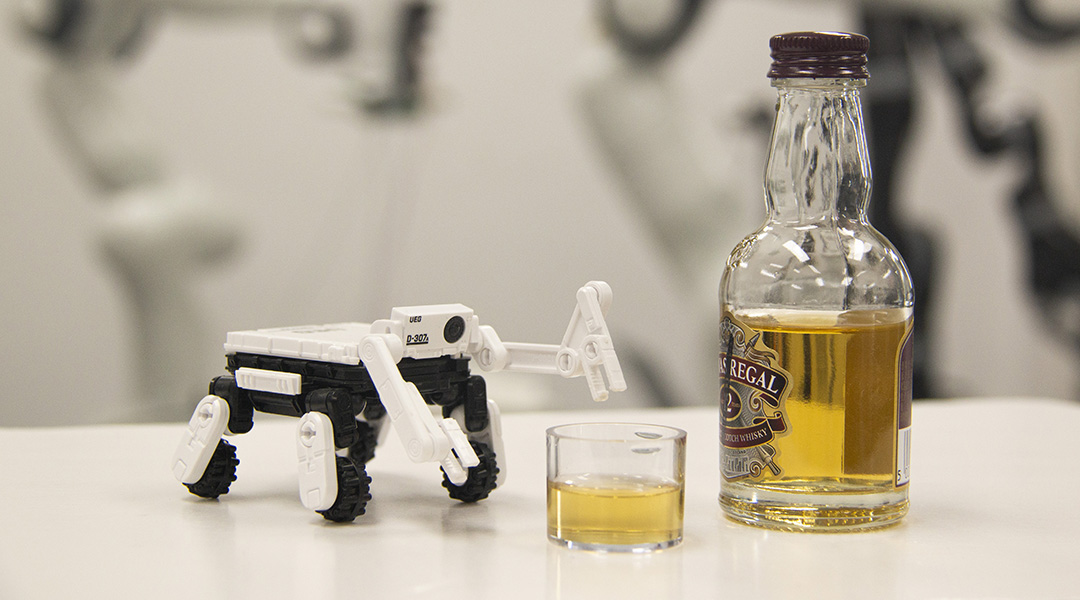

Precisely copying the capabilities of a biological nose with an artificial one is a lofty but potentially world-changing goal.
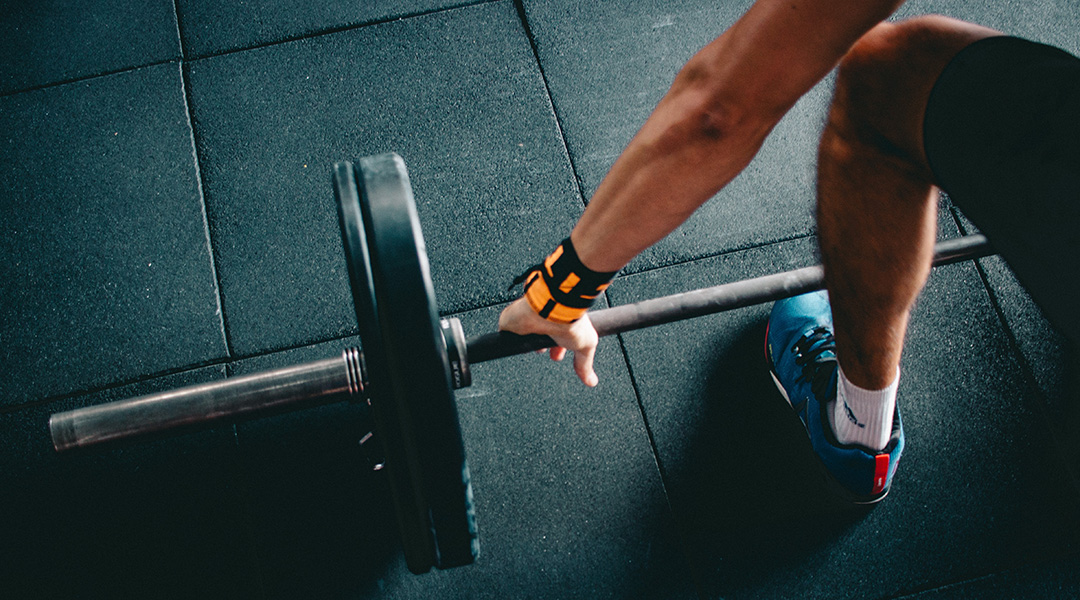

The generator harnesses energy from water and is built with a fiberform material derived from the straps of disposable medical masks.
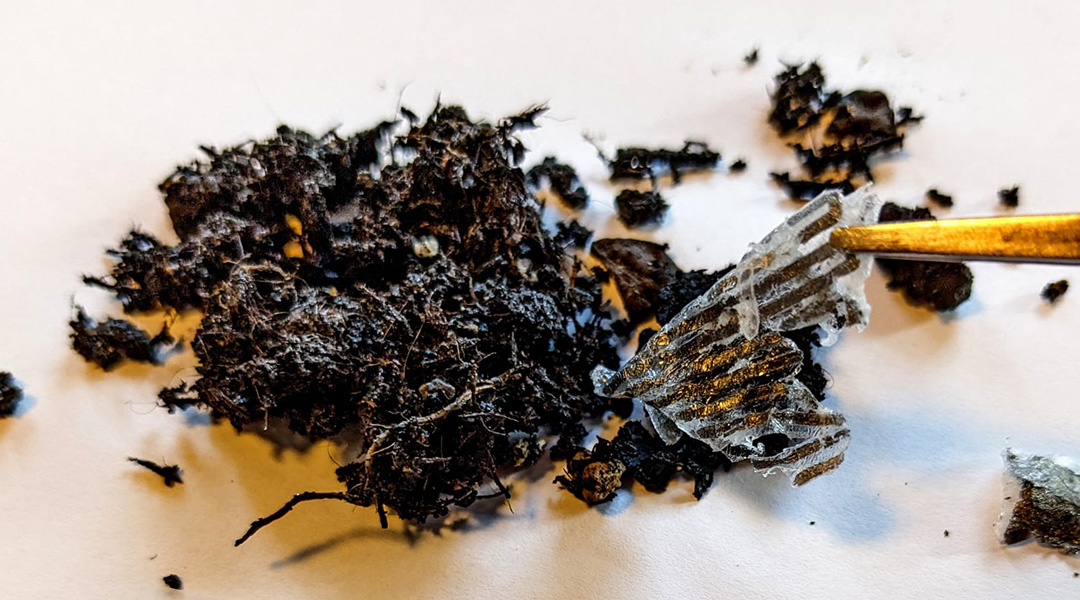

Discover how cellulose may revolutionize flexible electronics, replacing plastics in eco-friendly, sustainable substrates for innovative devices.
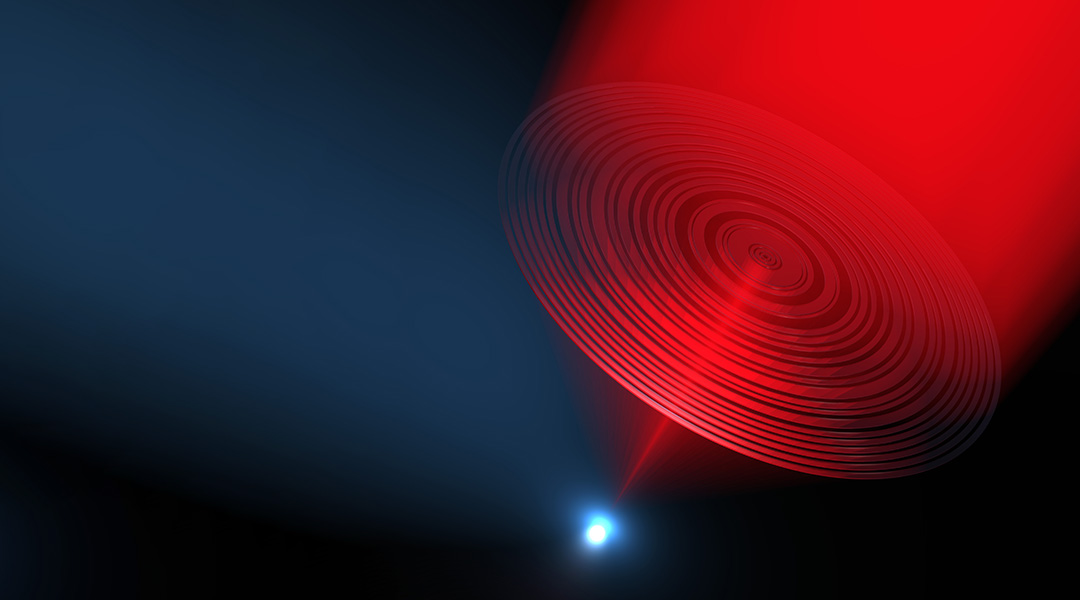
New research lays out the future of a pioneering form of electromagnetic imaging.
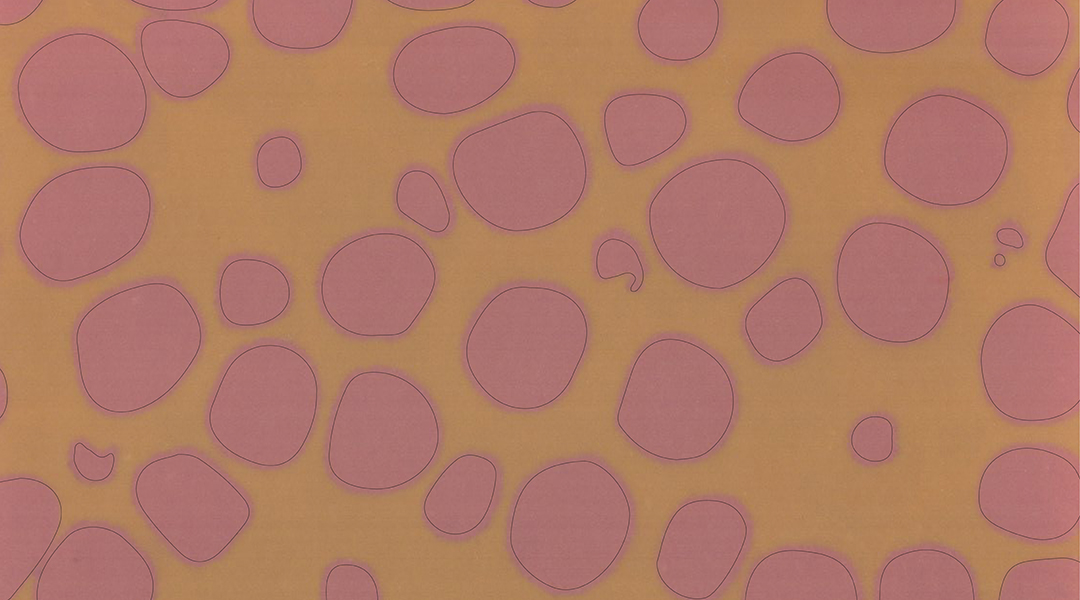
Scientists have designed a new paint formulation based on a natural pigment that changes color in response to sunlight.
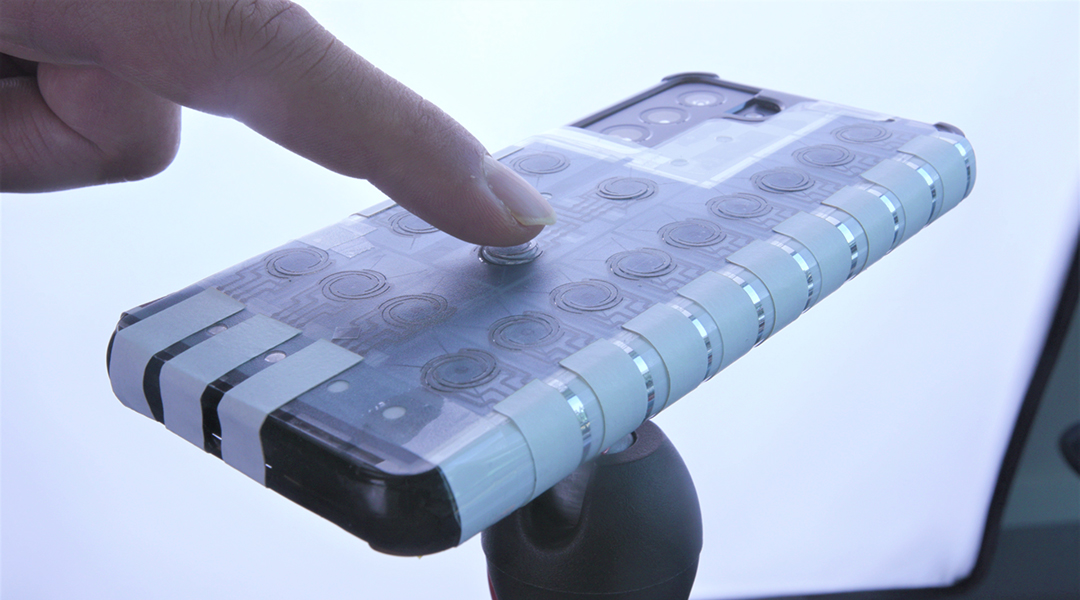

PopTouch blends transparency and touch, bringing traditional tactile buttons to a world of flat screens and smooth surfaces.
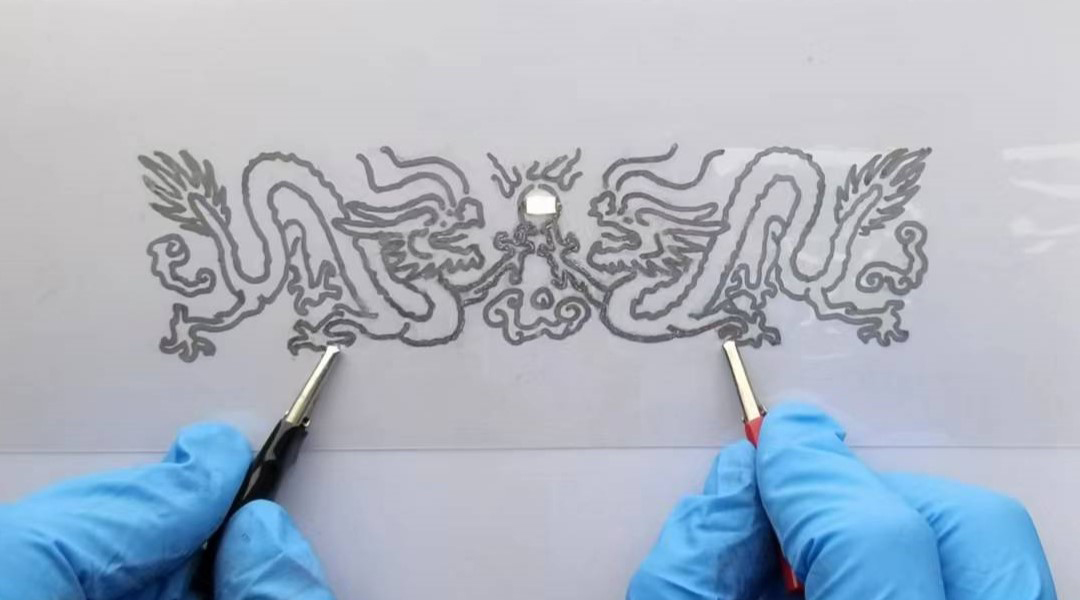
A liquid metal encapsulated within bio-based shells allows researchers to “draw” functioning electronic circuits with ease.
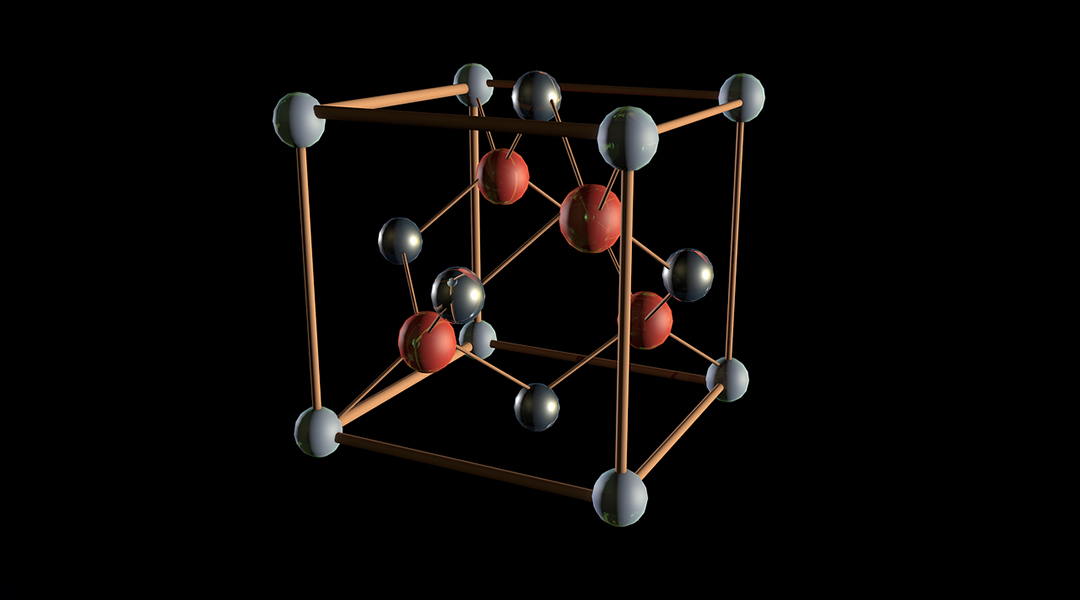
A newly discovered material and its intriguing properties could pave the way for more efficient computing.
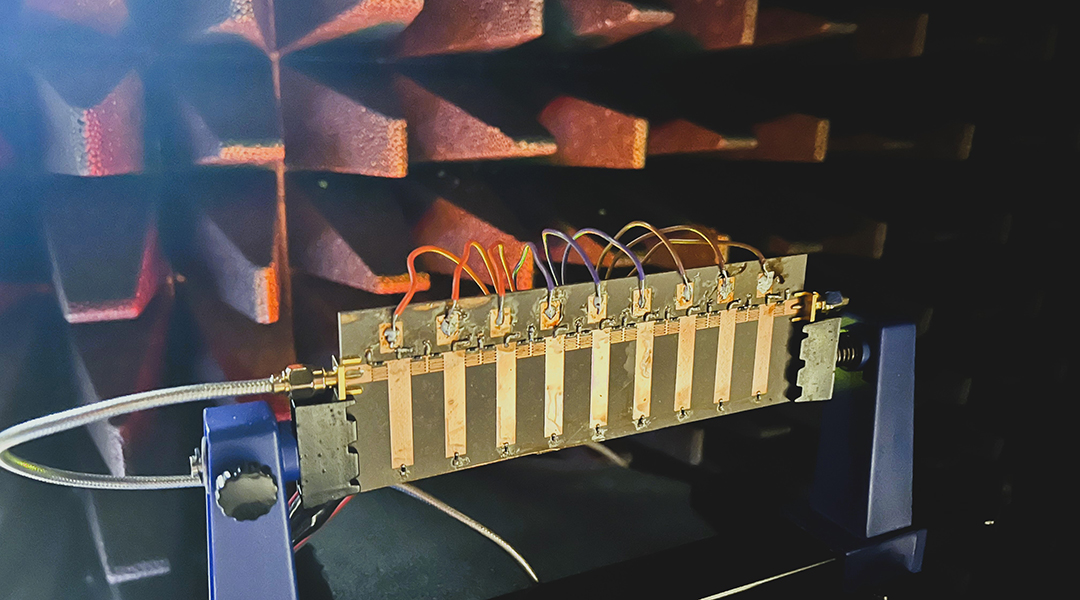
A cutting-edge security system for IoT devices uses physical layer security to make personal data significantly more difficult to hack.