A novel reactive oxygen species (ROS)-promoted nanomedicine platform can effectively inhibit tumor growth, reduce side effects experienced in common anticancer drugs, while promote on-target uptake.
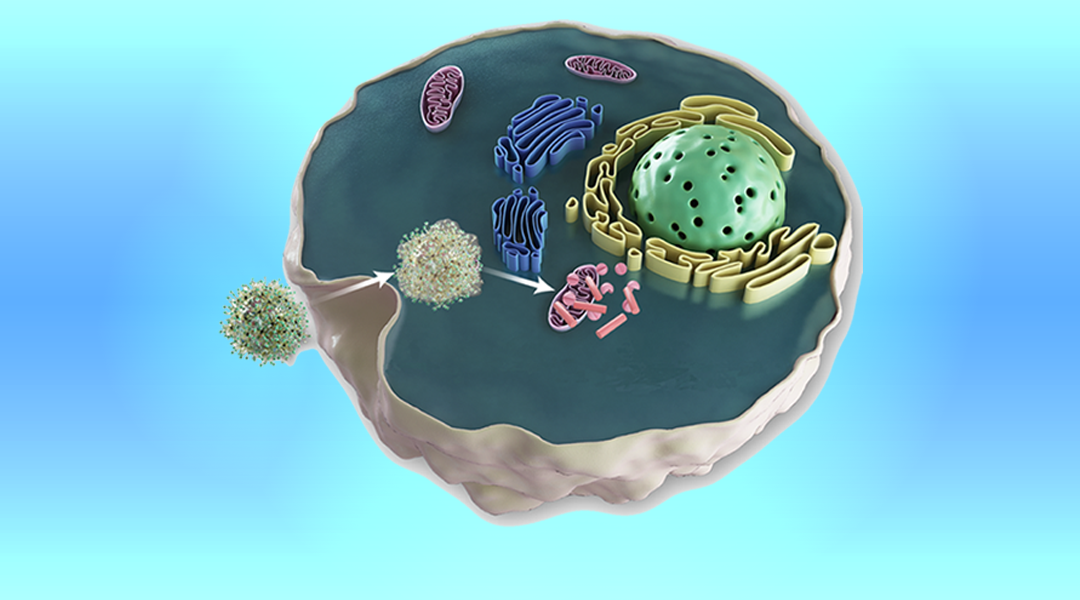

A novel reactive oxygen species (ROS)-promoted nanomedicine platform can effectively inhibit tumor growth, reduce side effects experienced in common anticancer drugs, while promote on-target uptake.
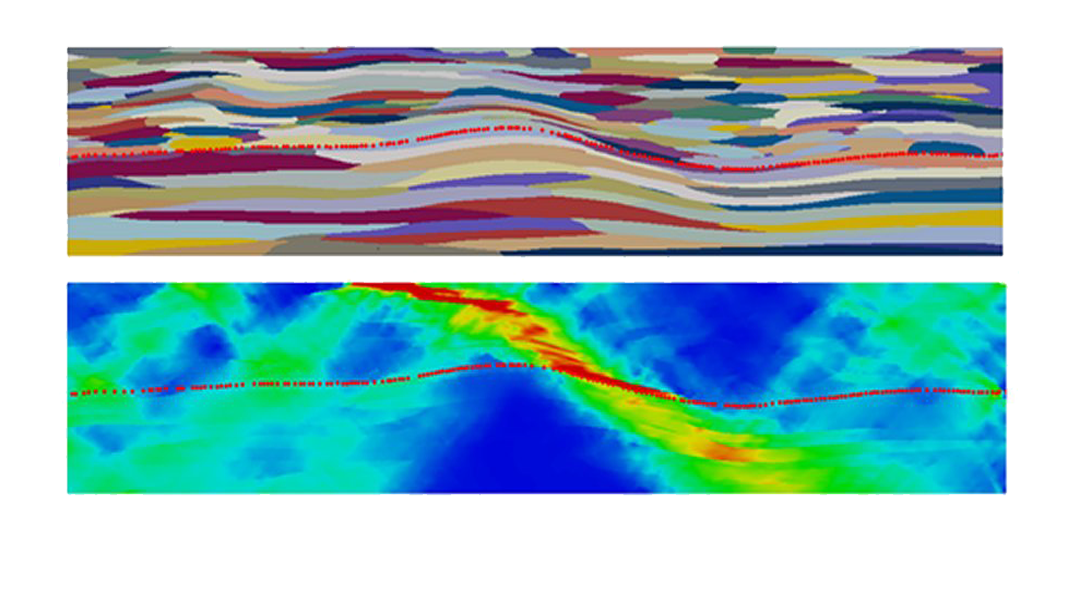
This review emphasizes the importance of the physics-based plasticity theory in constitutive material descriptions for more accurate simulations of deformation in the development of metal forming processes, for controlling mechanical behavior via tailoring microstructural features, and for subsequent component performance testing.

A team of researchers design broadband field-effect phototransistors based on molybdenum disulfide. The photodetector has the ability to detect very weak optical signals and is promising for applications in thermal imaging and sensing.
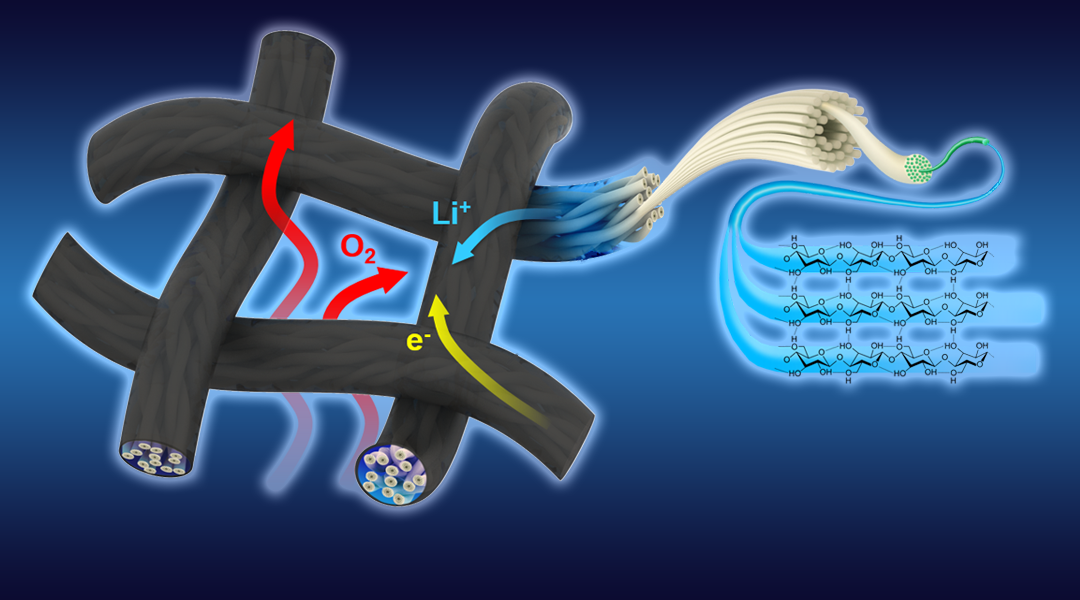
A novel flexible textile-based cathode with a unique triple-phased structure is presented, that shows improved non-competitive transport properties.
![Tumor-Targeting “Polywraplex” for siRNA Delivery [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/ASN_feature_adfm201703207.jpg)
Tuo Jin and colleagues from Shanghai Jiao Tong University synthesize a synthetic carrier system for small interfering RNA (siRNA) with customizable size, pH-responsive degradability, and optimized surface population of cell-targeting agent.
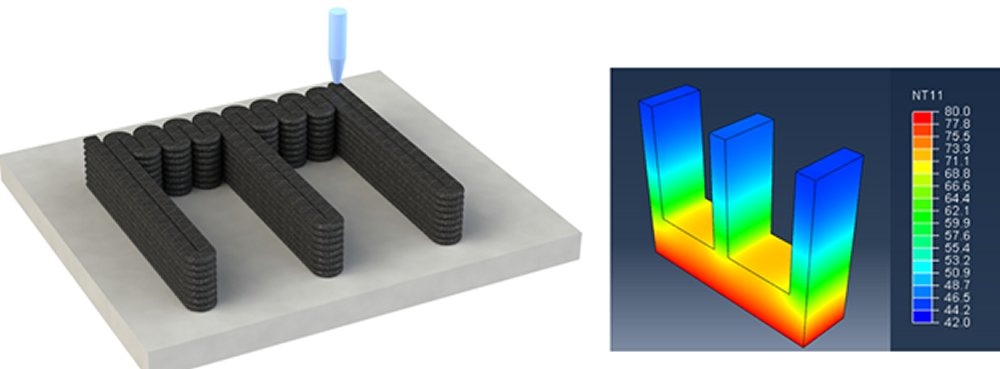
Recent research results in fabricating thermal management devices using 3D printing methods are reviewed.
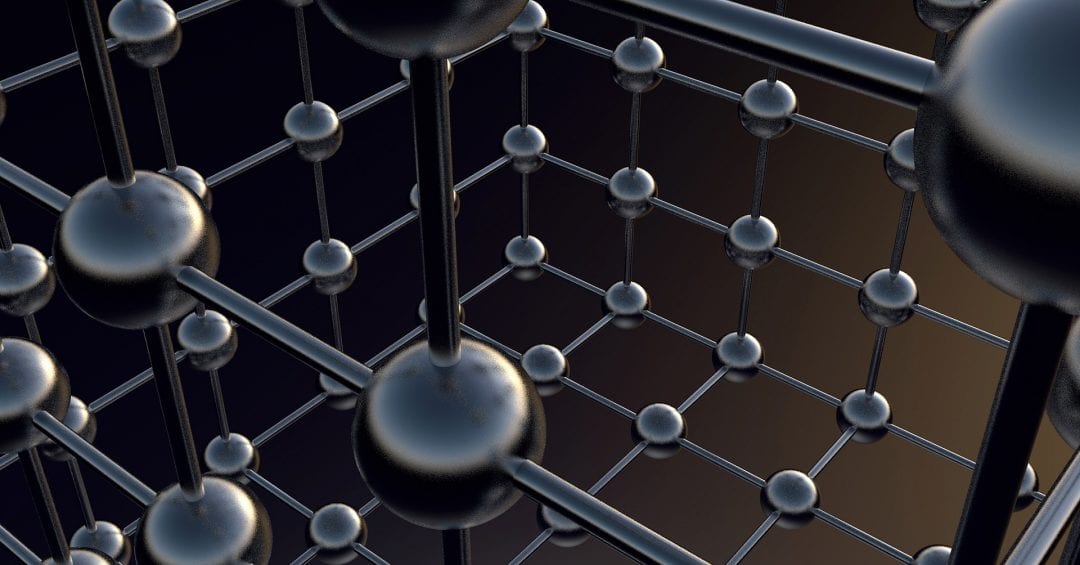
Researchers from the University of Tokyo shed light on the formation of the crystallographic structure of organometal halide perovskites.
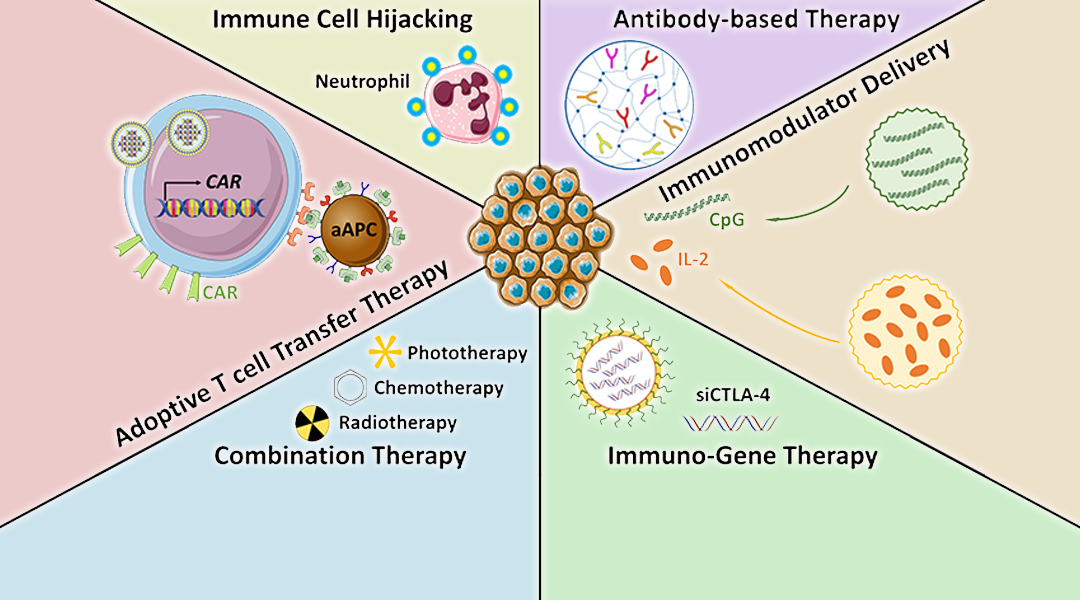
Biomaterials are engineered to improve the safety and efficacy of current cancer immunotherapies.
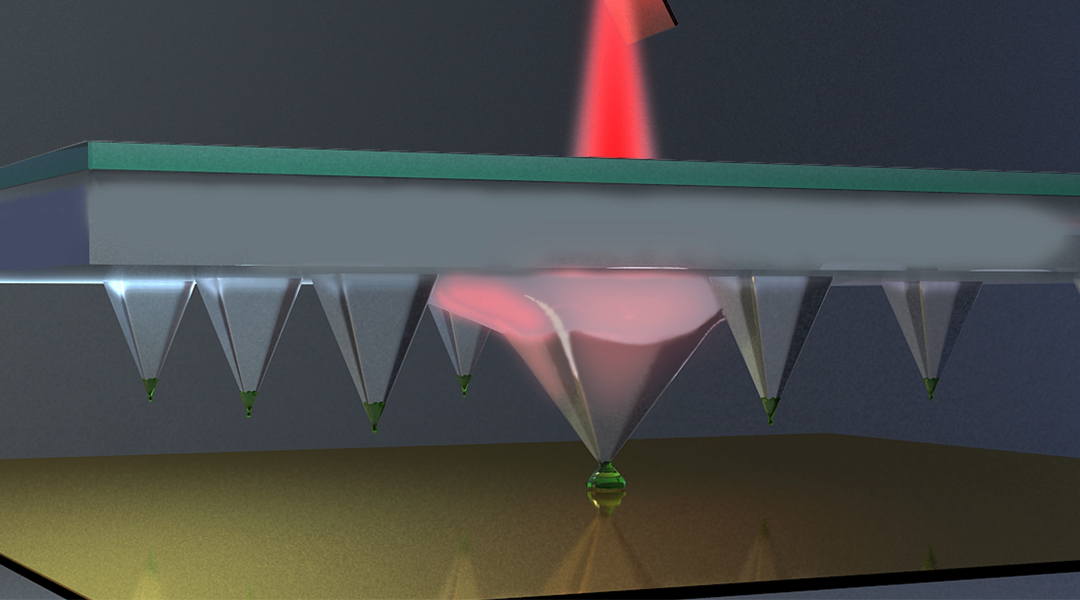
Local control of pens in a large-scale pen array can be achieved by using a nanotube composite that is photo-responsive to fabricate each individual pen.
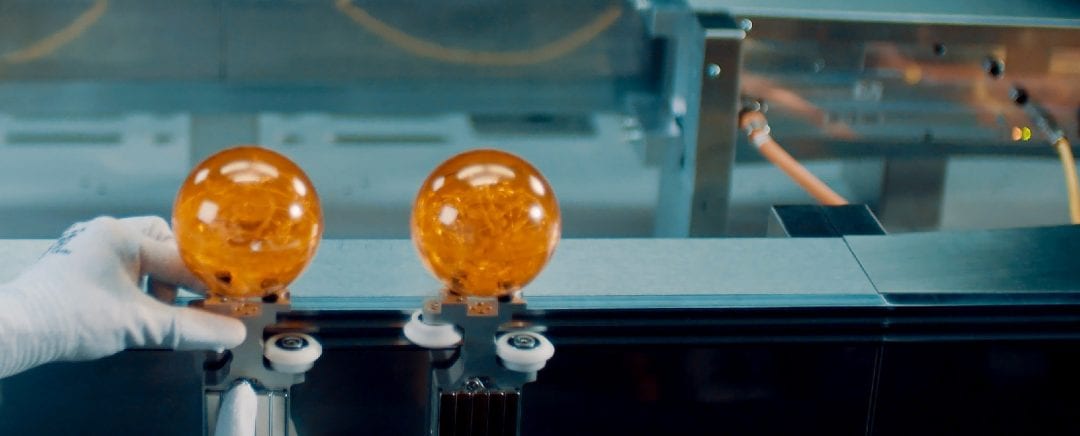
New transport system is pledging to boosts overall equipment effectiveness