A new battery design not only provides energy,not only provides energy, but facilitates automatic surfacing and diving mechanisms in electronic, underwater equipment.
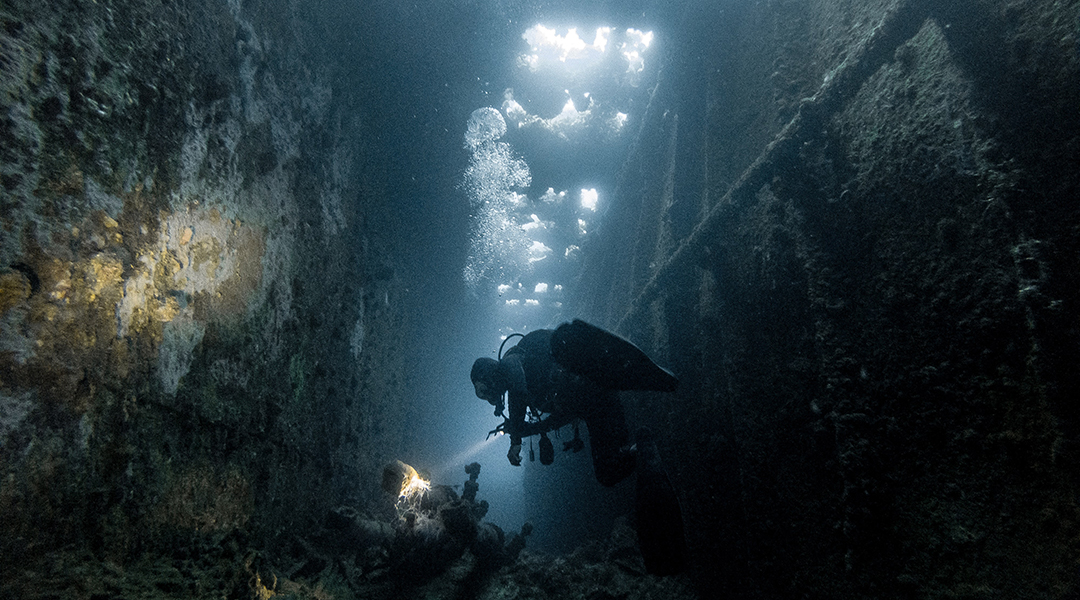


A new battery design not only provides energy,not only provides energy, but facilitates automatic surfacing and diving mechanisms in electronic, underwater equipment.
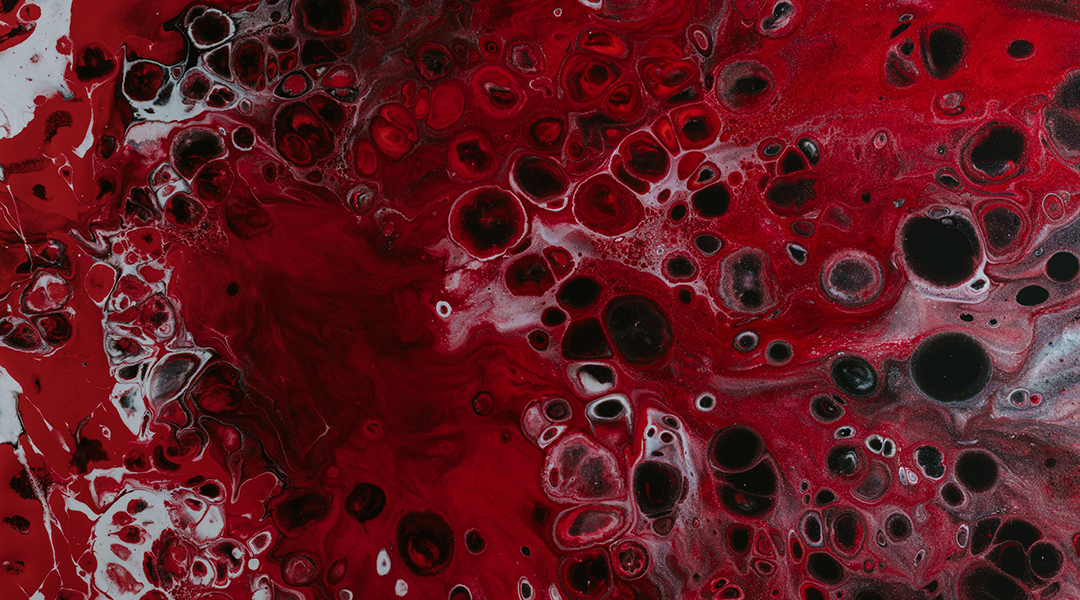

Blood coagulation is a common but delicate physiological behavior and is inspiring new porous materials.
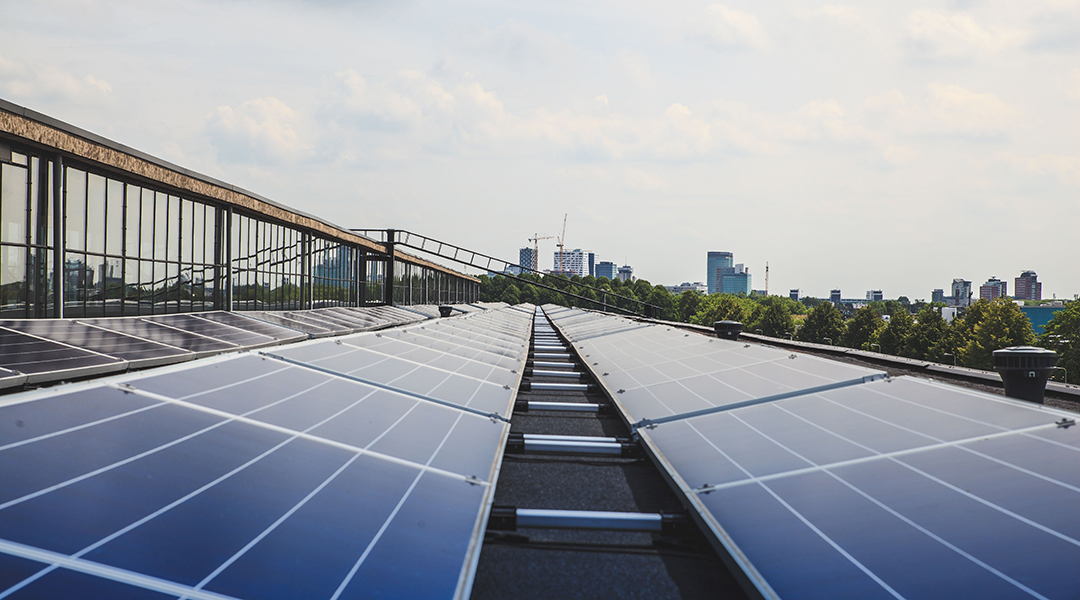

A new manufacturing technique to grow perovskite crystals for high-performance solar cells uses “face masks” to minimize imperfections.
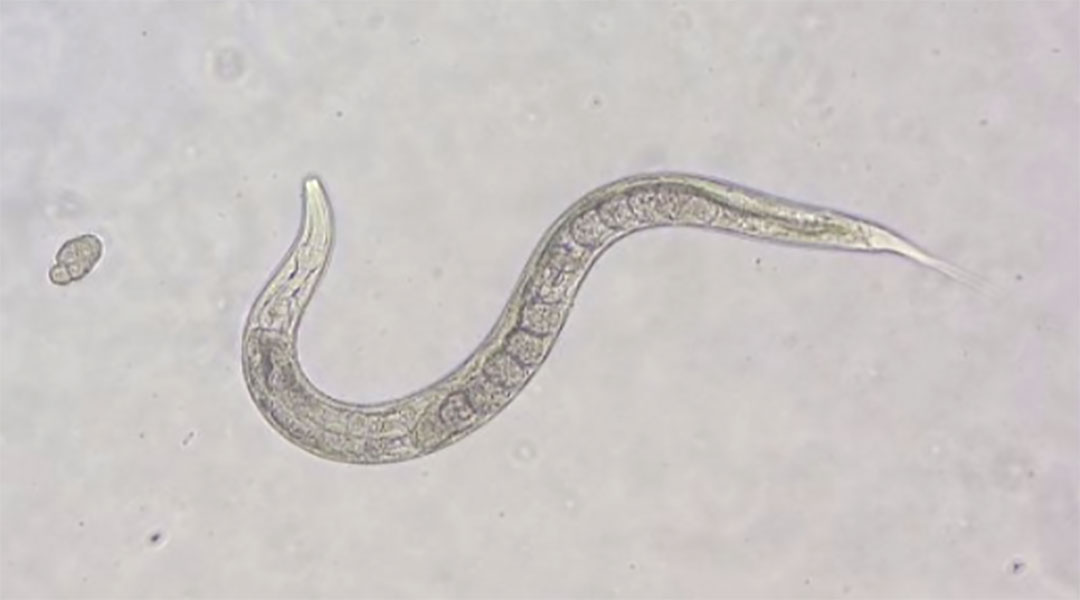
Scientists are turning to C. elegans for biobot designs, guiding their movement through reconfigurable microtopographies.
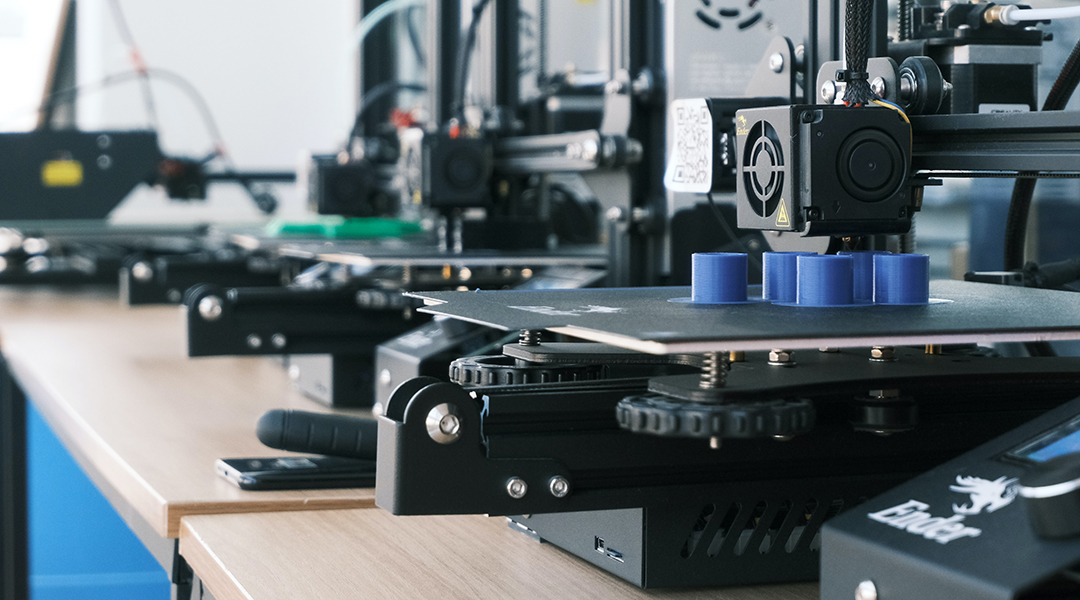

To optimize 3D printing, researchers apply machine learning to minimize waste and optimize structure during the printing process.
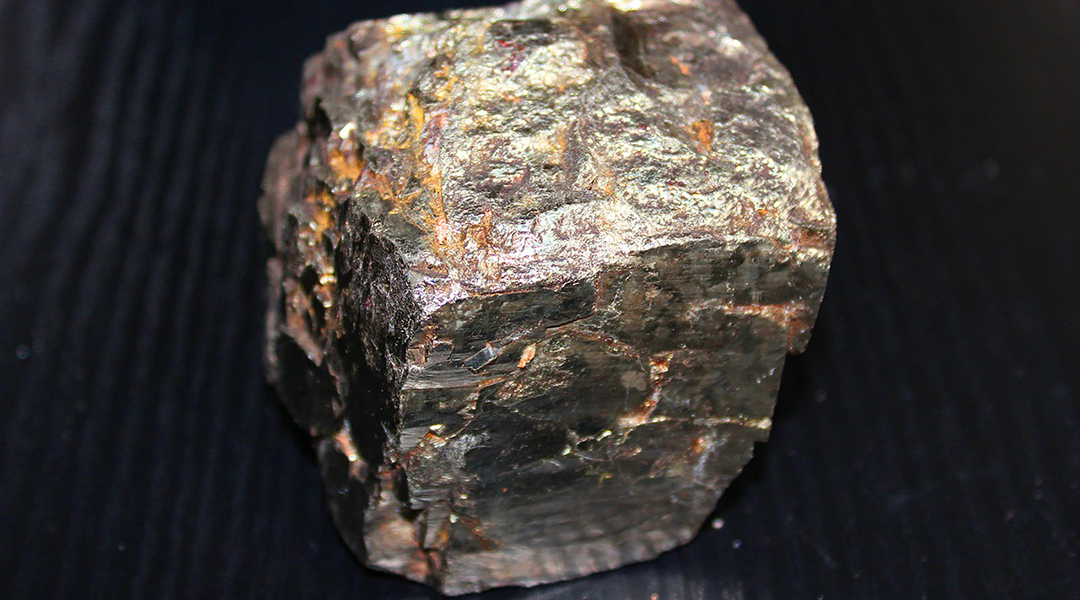

A groundbreaking technique produces tetrataenite, a material used in permanent magnets only found in meteorites.
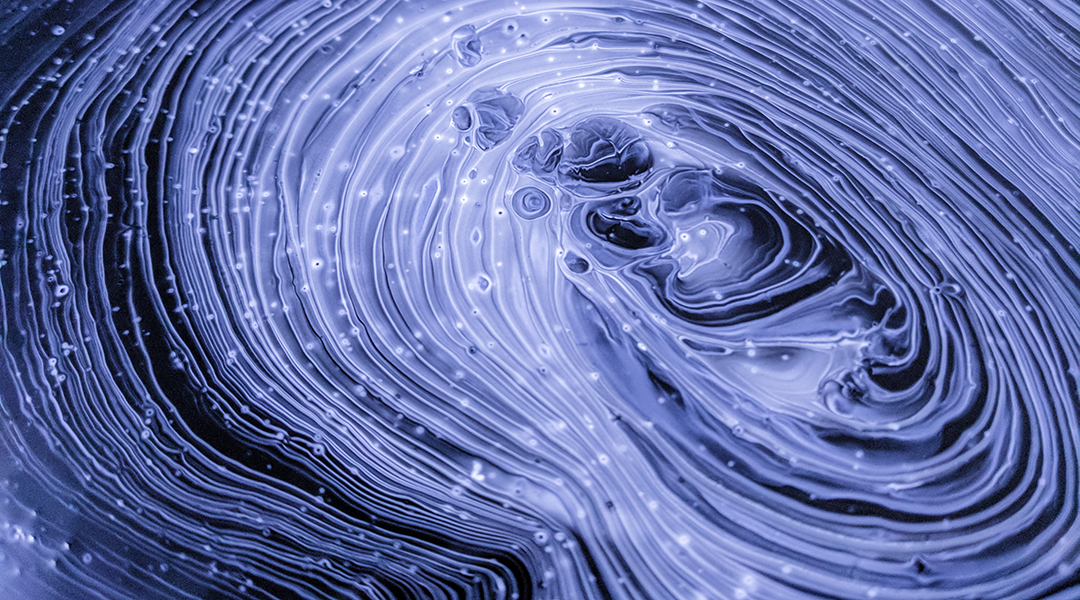

Rigid elements are holding soft robots back from their full potential, and new research suggests swapping in fluid-based systems.
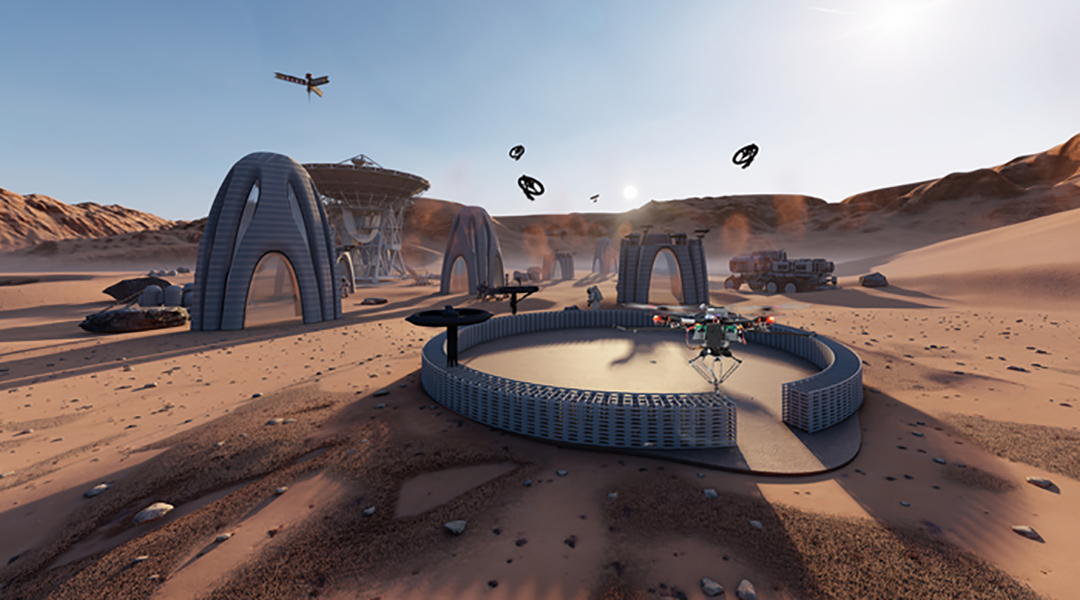

Modeled after nature’s builders, a swarm of 3D printing drones work together to build large structures while in flight.
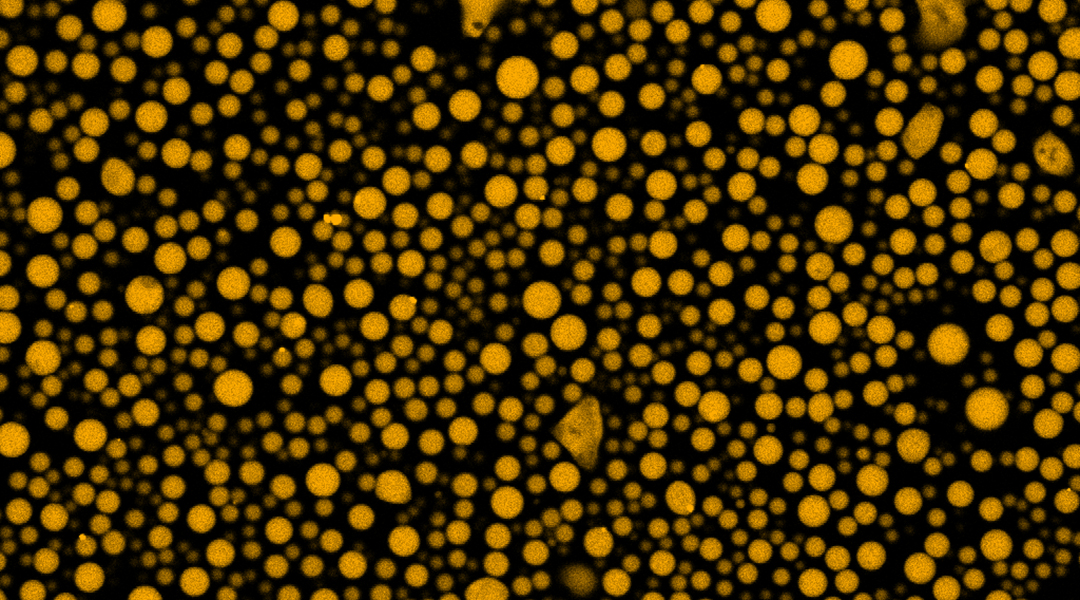
New research inspired by “viral factories” shows the potential of encapsulating target molecules in membrane-free compartments.
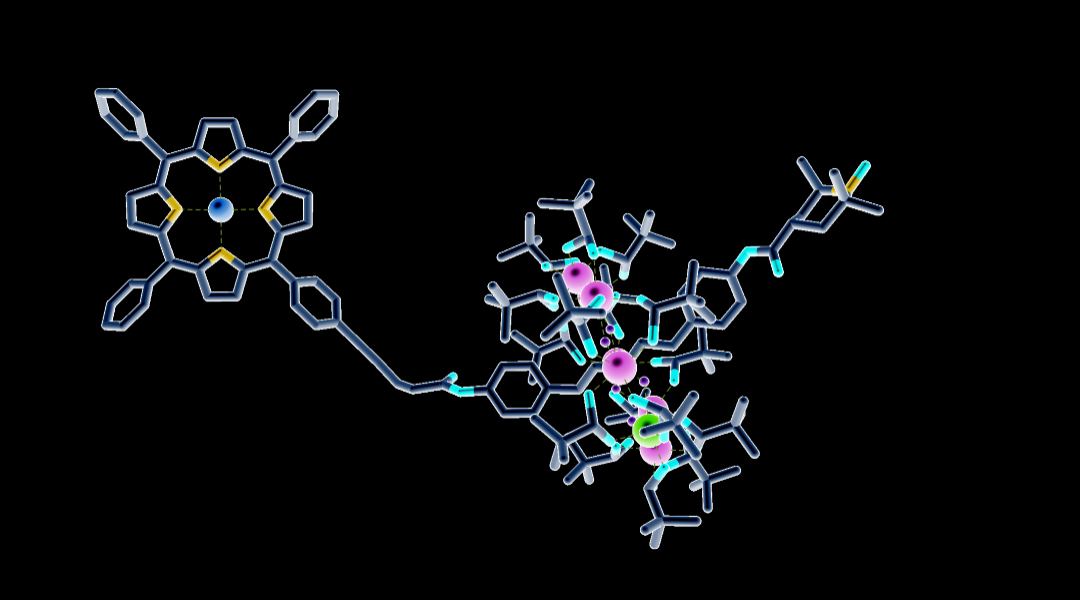
A molecular complex was built to contain three distinct qubits, offering an intriguing architecture for future quantum computers.