Using advanced sensors and a thermally responsive skin, a new robotic chameleon demonstrates mastery over color.
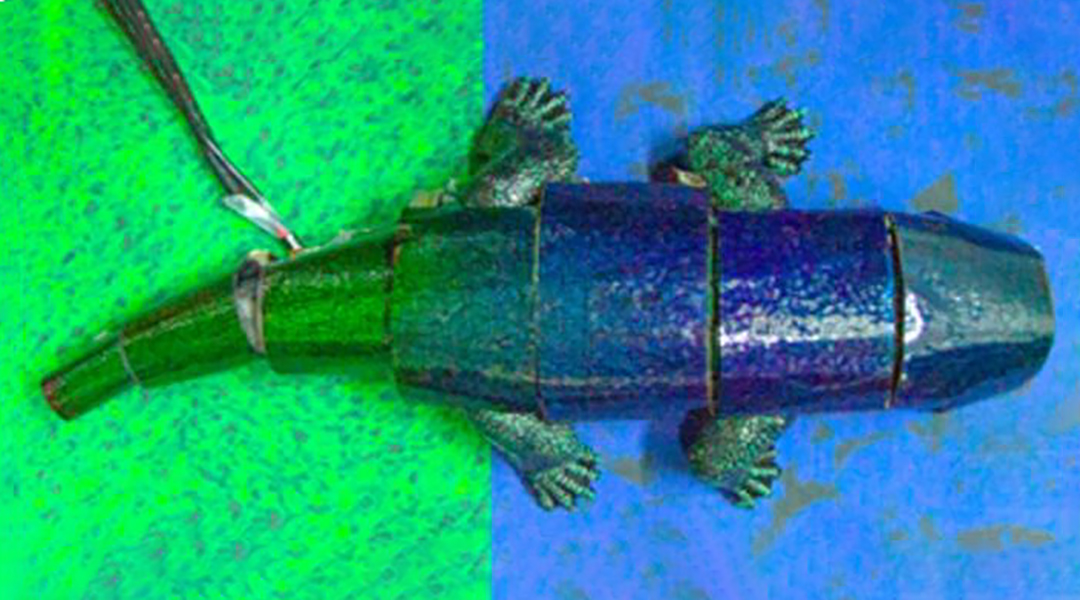


Using advanced sensors and a thermally responsive skin, a new robotic chameleon demonstrates mastery over color.
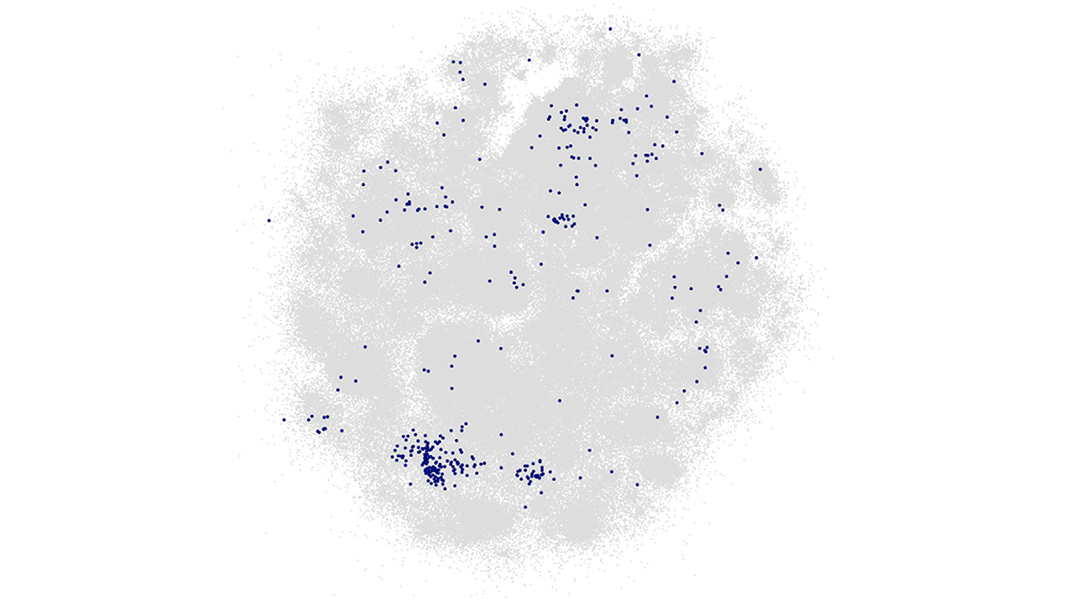
A new machine learning algorithm called “Active Learning” could help identify the best materials for any desired application.
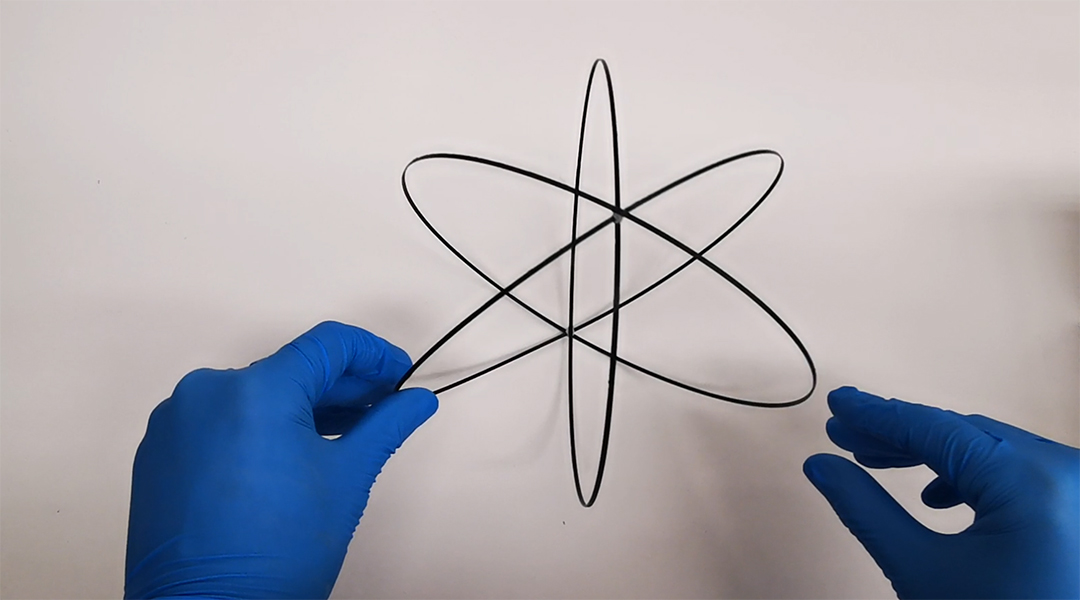
An origami-based design enables self-guided folding and deployment of pop-up structures for various biomedical, robotic, and aerospace applications.
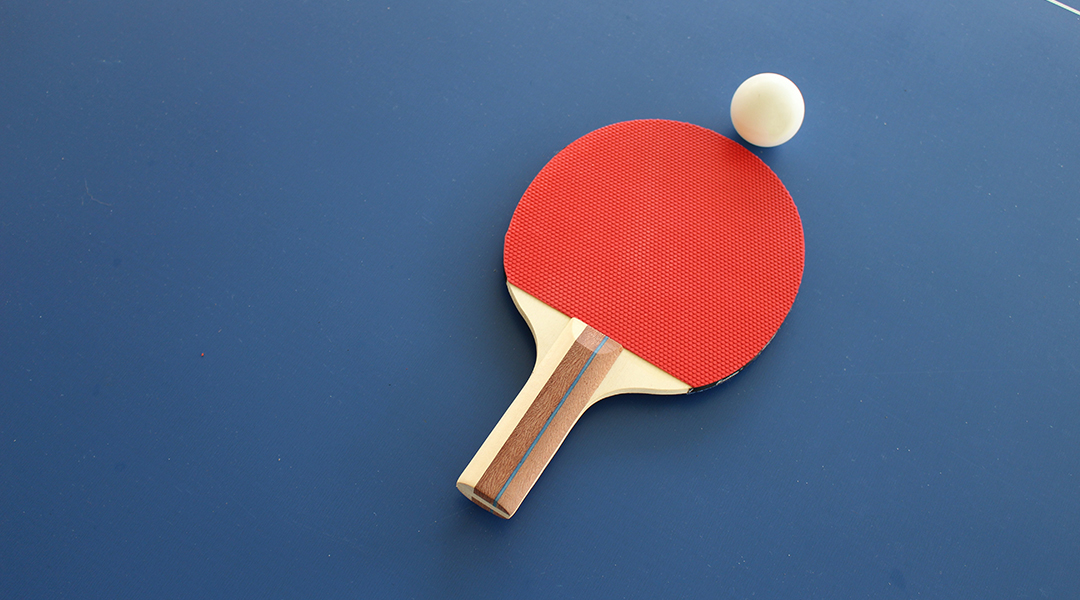

Ping pong is one of the Olympics’ most gripping sports, and researchers in China are trying to make ping pong paddles smart.

Researchers working to understand climate change, find inspiration in the most unlikely of places.

Scientists have developed a polymer-coated glass that can change from transparent to opaque when exposed to sunlight and heat.
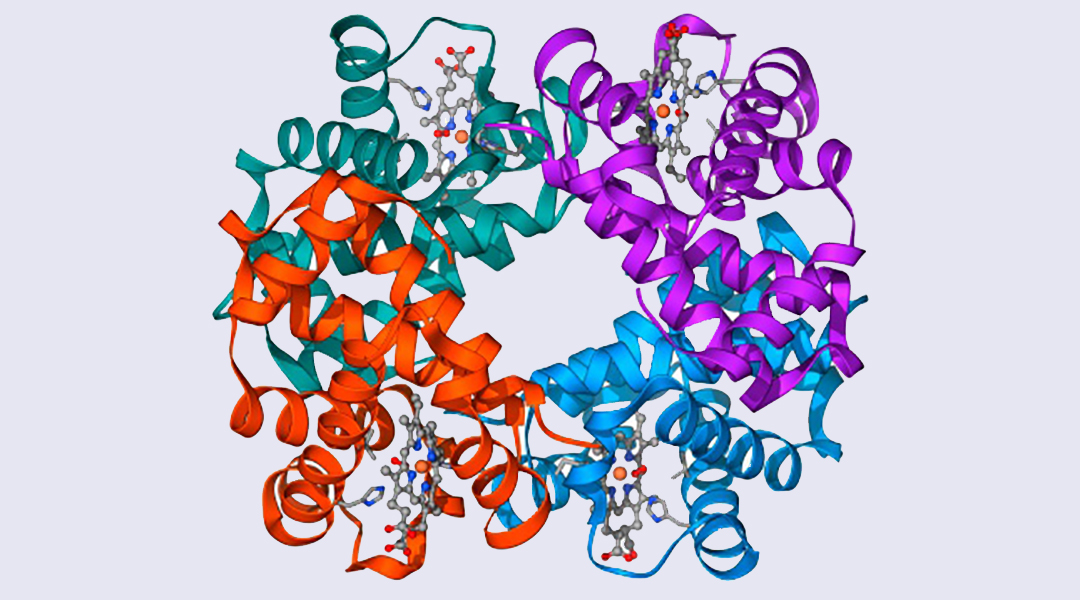
This will be one of the most important datasets since the mapping of the Human Genome, say experts.
Accurately measuring brain signals is critical to determining what actions a user wants to perform.

Genomic editing tools can reverse disease causing mutations to provide cures — once we can conquer the remaining barriers.

New design in lithium-air battery aims to get more electric vehicles on the road.