Multimodal thin-film transistors, or MMTs, could be pivotal in designing the next-generation of wearables and eco-disposable sensors.
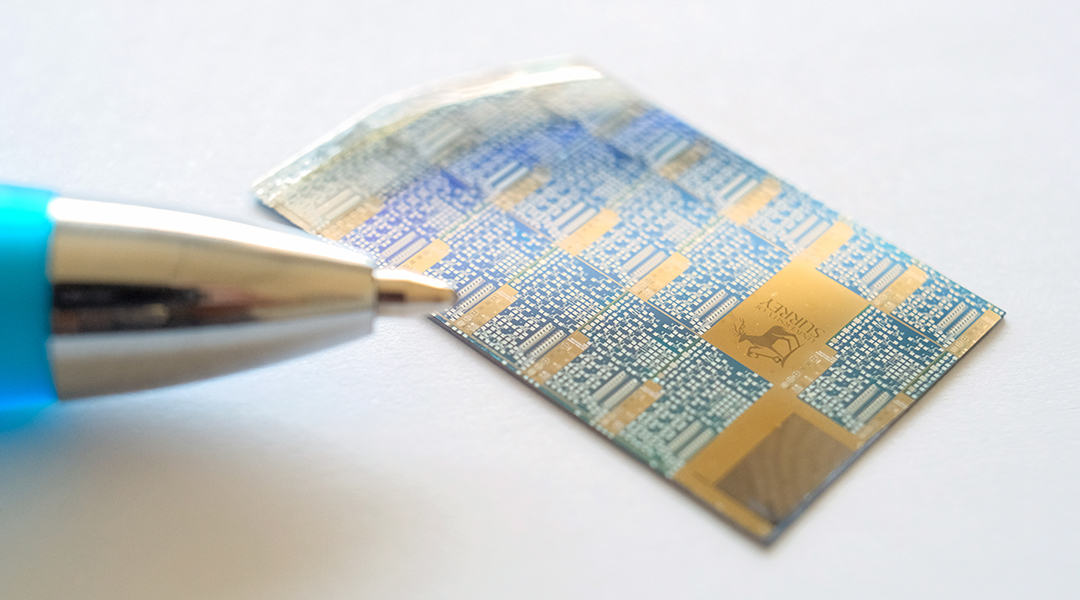

Multimodal thin-film transistors, or MMTs, could be pivotal in designing the next-generation of wearables and eco-disposable sensors.
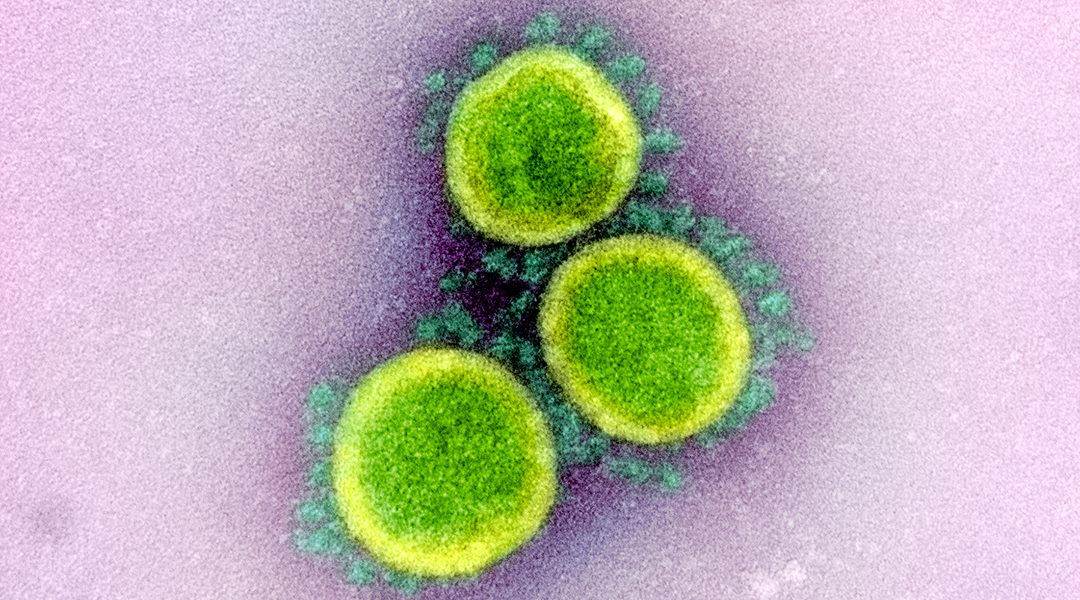
Researchers enhance the immune response against the receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 by presenting it on liposomes, providing a promising strategy for vaccine development targeting this domain.
The waste chips of paint you strip off the walls might not be so useless afterall.
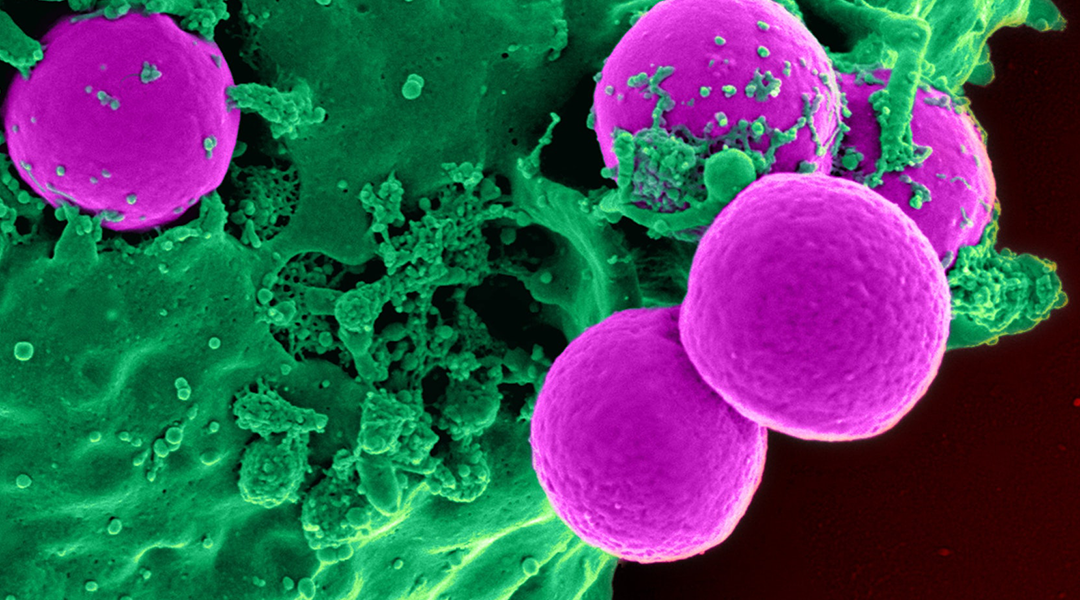
Nanoparticles are not new; bacteria have been making them long before we had a language to name them.
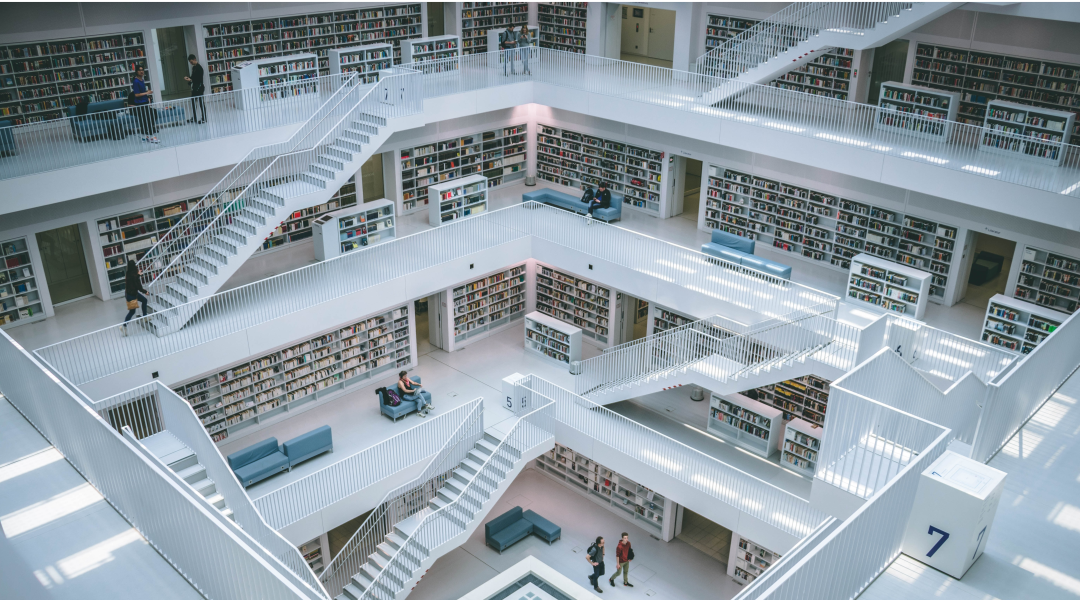

A new computing paradigm could help us to overcome a key performance bottleneck to improve our ability to query large data bases.
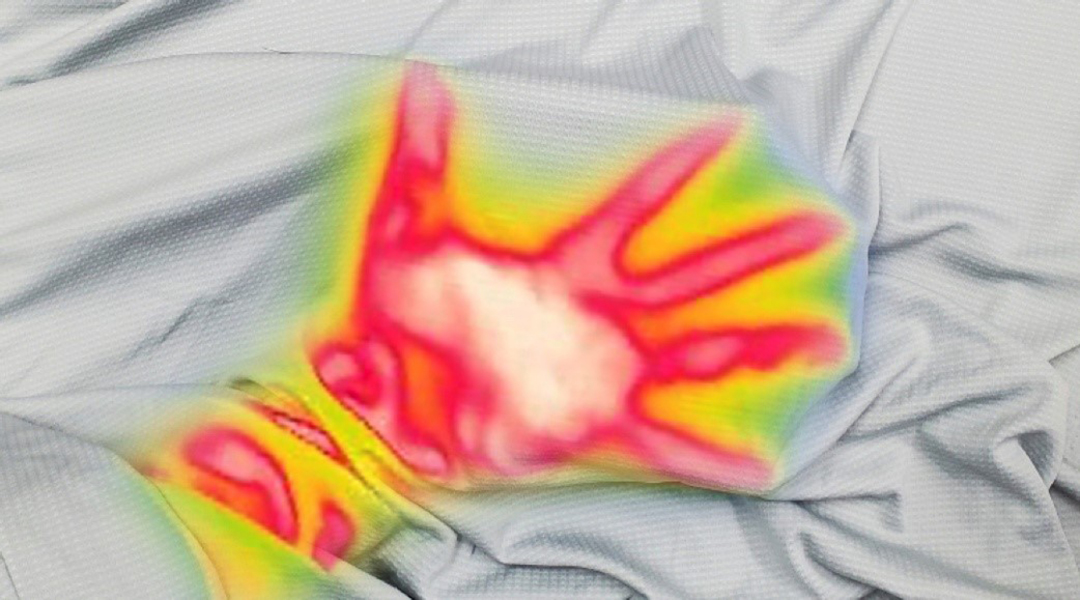
A simple alteration in the functionality of our clothing could surprisingly help lower energy consumption in buildings and homes.
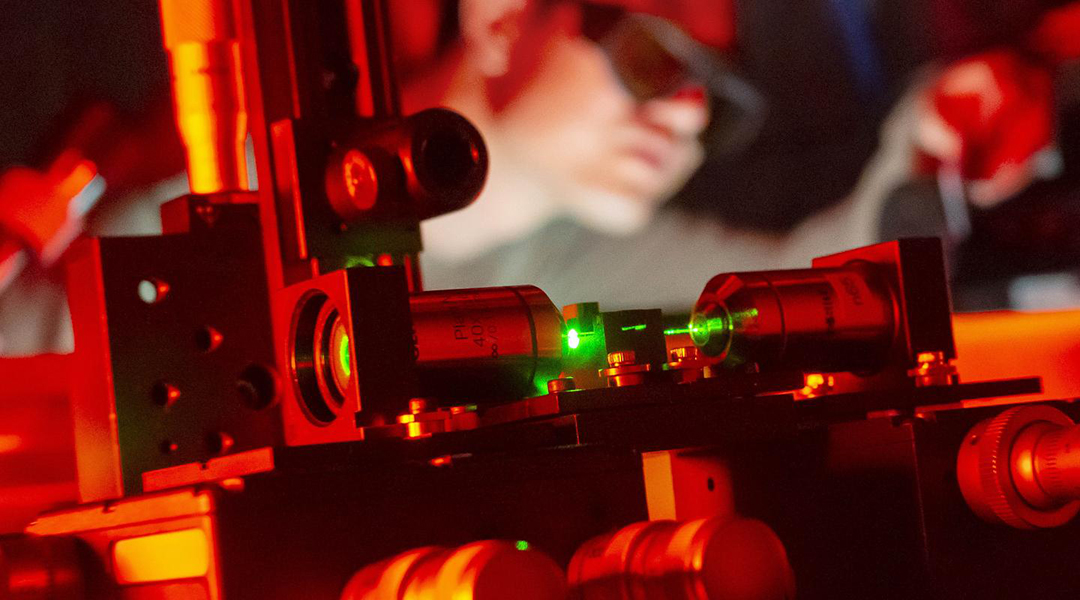

New hybrid optical fibers contain 2D materials that enhance light-matter interactions and open doors for a range of new technological advancements.
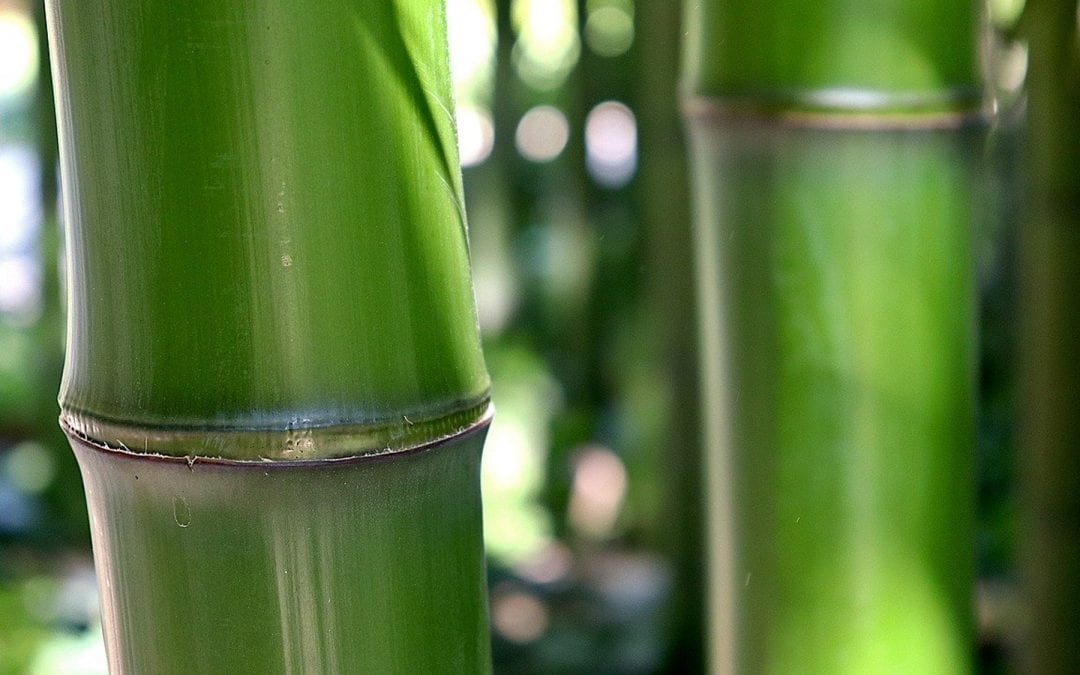

Lightweight but tough, bamboo is the hope for a more sustainable life and future for our planet.
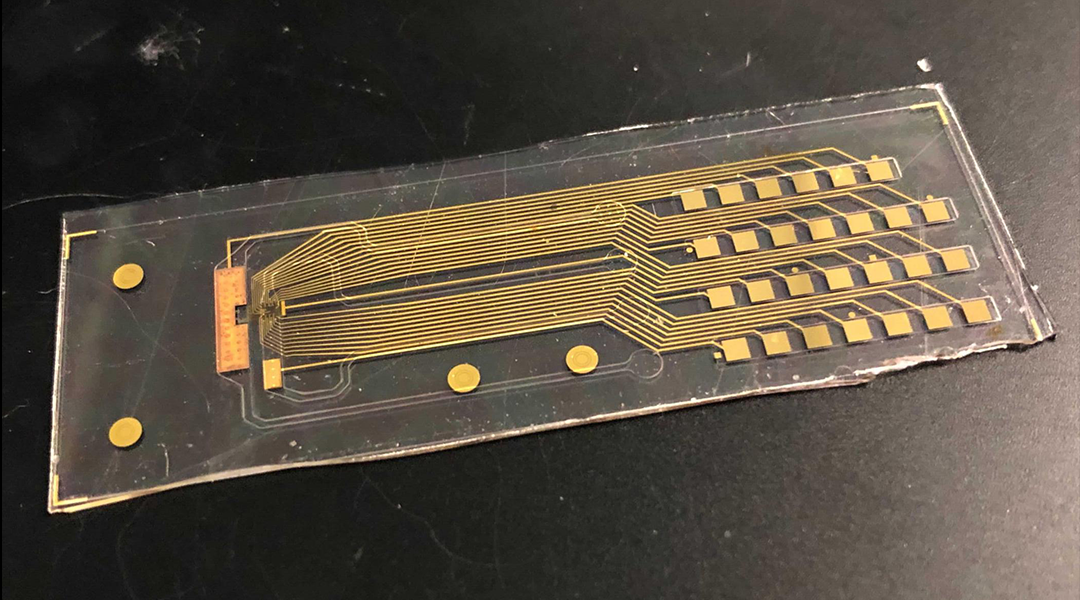
Driven by a machine learning algorithm, the closed-loop biohybrid device maintained a set membrane voltage in human stem cells for 10 hours.
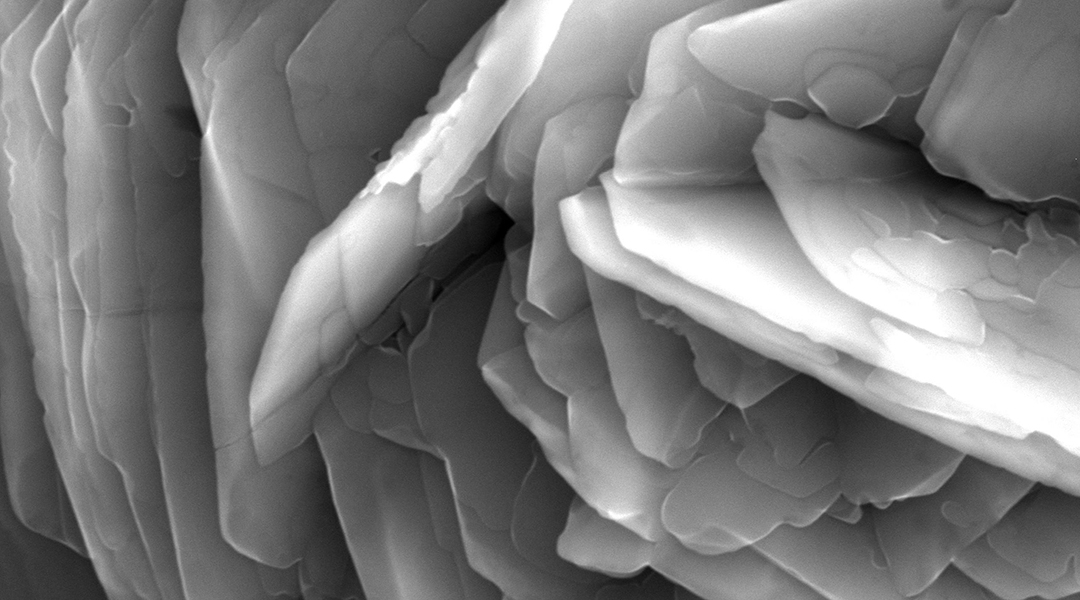

Novel rosette-like formations may open new opportunities in corrosion science, manufacturing of titanium-based implants, and fluid-surface interactions.