A new soft microrobot harnesses electromagnetic and thermal energy at the nanoscale to self-assemble from colloidal nanomachines.
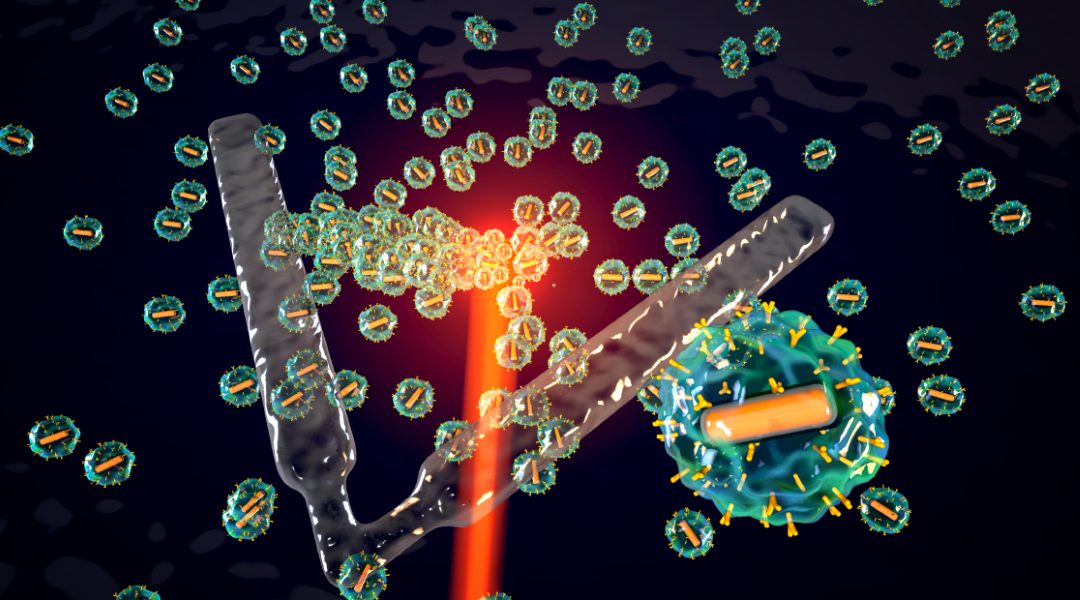

A new soft microrobot harnesses electromagnetic and thermal energy at the nanoscale to self-assemble from colloidal nanomachines.

Scientists create a lightweight wood with incorporated magnetic nanoparticles for electromagnetic interference shielding.

Direct‐write and 3D printing using liquids metals provides an interesting alternative for wiring in circuitry.

A new way of making large sheets of graphene could lead to ultra-lightweight, flexible solar cells, and to new classes of light-emitting devices and other thin-film electronics

If your engine has more than 16 atoms, you’re just wasting space.
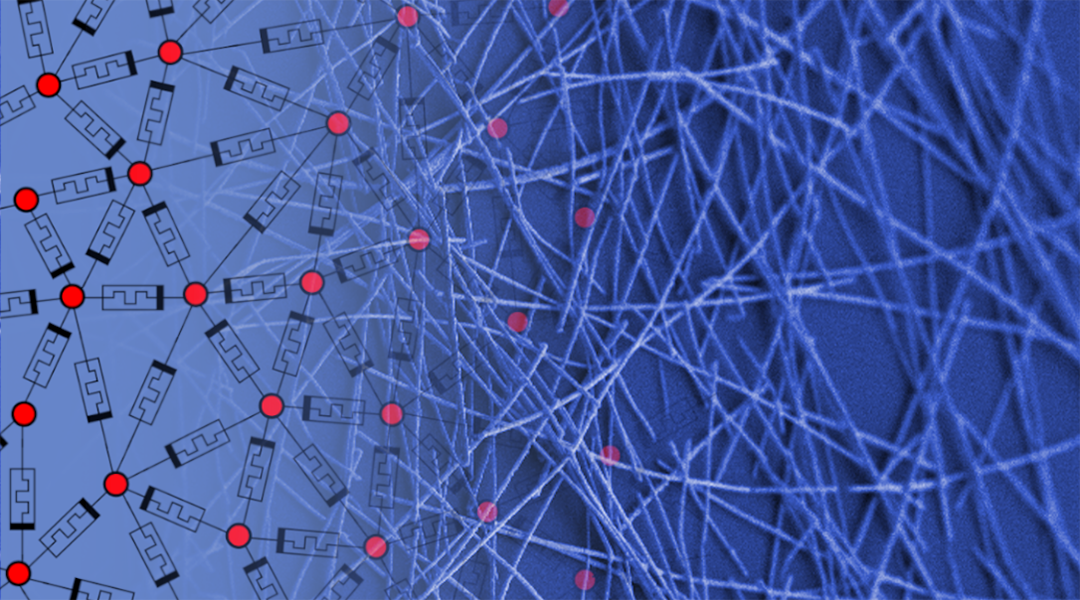

A new bottom-up network built from randomly distributed nanowires can learn, compute, and adapt like a human brain.

Microalgal biorefinery has emerged as one of the sustainable solutions for the production of biofuels and biochemicals. However, there are still some difficulties to be solved.

X‐ray absorption spectroscopy represents a valuable characterization tool for complex materials like multialkali antimonides.
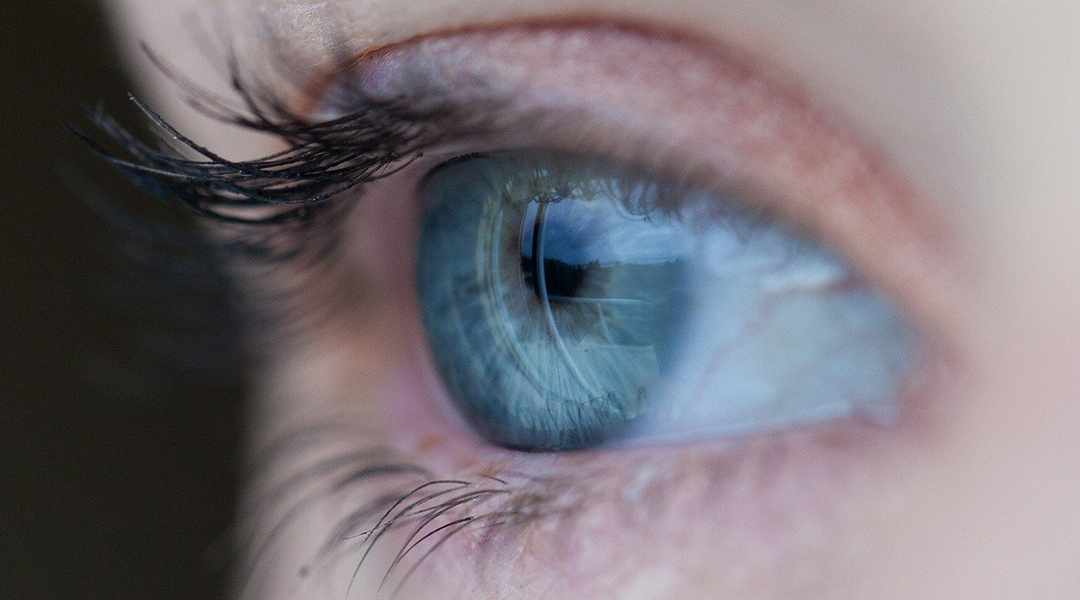

Scientists at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology make artificial eye far better than anything current.
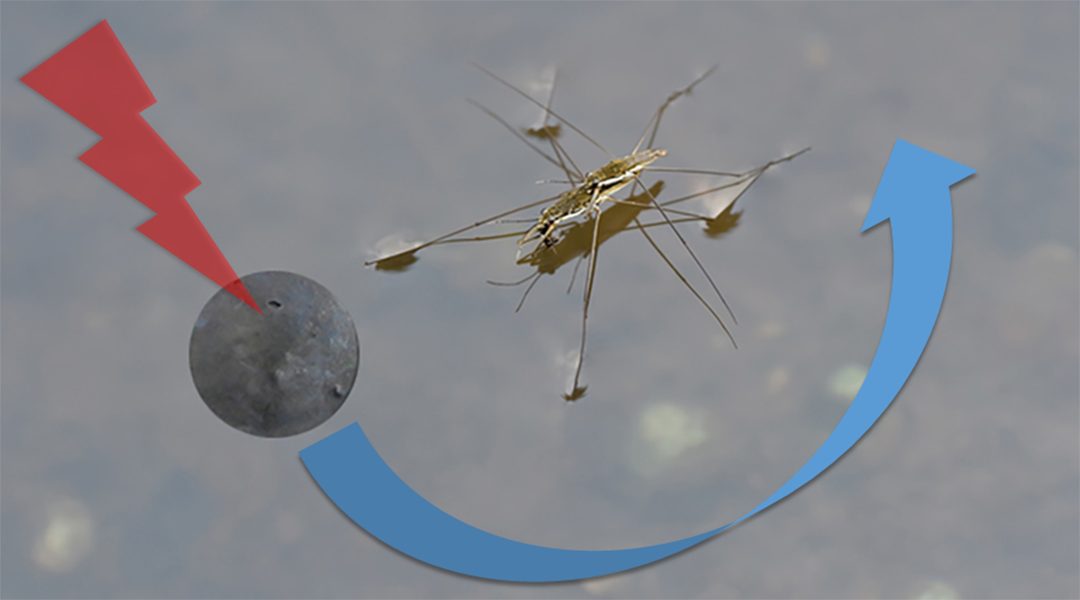
Millimeter-scale robots were shown to mimic the movement and behavior of living insects for advanced materials science, biological, and biomedical applications.